Table of Contents
Batch Payment Meaning
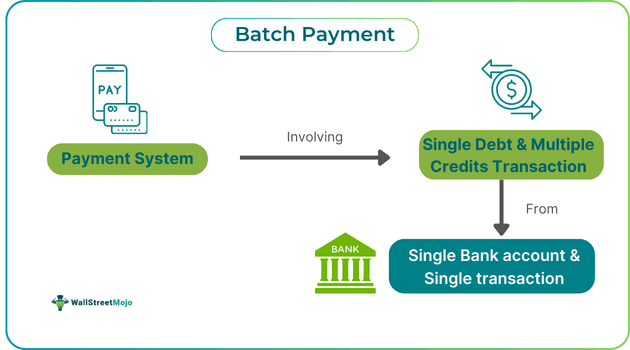
A batch payment refers to the disbursal of payments to multiple recipients at one time using a single bank account in a single transaction. It reflects itself as a single debit and multiple credits on bank statements, making the transaction efficient and time-consuming and avoiding numerous distinct payments.
It optimizes the daily financial transactions related to businesses for e-commerce companies. It has been used to pay salaries, service providers, suppliers, and vendors. The entire process consists of creating batches, sending them to related banks, and validating the correct receipt of payment by vendor or bank.
Key Takeaways
- A batch payment permits multiple recipients to be paid at one go from a single account in the form of one debit and multiple credits, increasing efficiency and saving time.
- It reduces human errors, but it lacks immediate payment processing, hindering businesses that need immediate funds access.
- Its automation provides sound protection of transactions from fraud and unauthorized payments using two-factor authentication.
- Manually, it could lead to payment delays, negatively impacting vendor relationships and cash flow.
- It is more suitable for a high volume of transactions, whereas real-time processing ensures the immediate availability of funds to all.
How Does Batch Payment Processing Work?
A batch payment definition can be stated as a payment system in which single debit & multiple credit transactions are gathered and processed collectively at scheduled intervals or predefined periods. It does not do these transactions in real-time, individually, and immediately. However, it benefits for settling supplier invoices, payroll, and recurring payments.
It works in three steps:
#1 - Batch Creation
It starts with forming a batch, where all eligible and authorized payment requests are collected during a certain time frame or day. Nevertheless, relevant authorities review and authorize invoices before they are collected into a single batch.
#2 - Sending To Banks
After the batch is created, it is transferred to the payment processor and the bank as a single transaction. This decreases the number of individual transactions requiring processing to streamline the flow.
#3 - Validation of Receipt
- Post-batch submission, the bank or payment processor validates the batch payment. Then, they ascertain that all transactions are correctly processed and confirm the complete transfer of funds to designated vendors or accounts. Such validation aids in error mitigation and security enhancement and is used in batch payment in Xero.
- It has implications like a significant improvement in cash flow management by guaranteeing on-time payments while decreasing transaction costs. It also reduces manual errors, enhancing overall operational efficacy. As such, it has become an integral part of various fields like corporate and retail finance by its virtue of handling a high volume of transactions efficiently. Since it can be automated, it allows seamless integration of financial workflows with itself.
- It has led to significant impacts concerning the financial aspect of businesses. It has improved the relationship of vendors, employees, and suppliers with respective companies due to timely payment processing using various services, such as batch payment Odoo. It has also reduced companies' operational costs and contributed to their better cash flow management. Therefore, companies have preserved their cash flow estimates and budgeting accuracy and increased their revenues.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Let us assume ABC Technology Limited, located in New York City, is doing the monthly payments of 50 freelancers in batch mode. Its finance manager, Almain, utilizes the company's banking portal to start the payments. Every freelancer has been listed in the software along with their bank details and payment amounts that range from $600 to $2000. Almain creates the payment data on the 1st of every month by selecting all the freelancer's accounts in batch mode.
Furthermore, she also allocates $55000 in each batch. After the commands are confirmed and executed, the software disburses the salaries automatically in batches. As the transaction proceeds, the system generates transaction reports for record keeping. Such payments in batches save valuable time and ensure on-time payments to every freelancer immediately.
Example #2
An online article published on 06th September 2023 discusses the ONDC joining by the Dunzo seller app, which has goals of onboarding 20000 merchants within 45 days. Its headquarters are in Bengaluru, and it is a fast commerce business startup that joined the ONDC chain last year. The article discusses the delay in the salary of staff by Dunzo due to fundraising troubles. In the beginning, it said the salary disbursal would take place by 04th September, but now it has been delayed by one or two days and would be done in batches of payment.
Moreover, it has assured paying of 12% yearly interest on salaries delayed since June 2023. Besides, the company is in negotiations with investors like Lightrock and Lightbox to raise $80-100 million. However, it has been struggling financially because of $1309050.60 claims made by its vendors. In the past year, Dunzo, owned by Google (19% shares) and Reliance (25.8% shares), have fired more than 500 employees while raising $500 million.
Advantages And Disadvantages
It has several benefits and losses for its users, as pointed out in the table below;
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Time-saving because of simultaneous handling of multiple transactions, increasing operational efficiency. | Slowing settlement times leads to delayed cash flow as it happens at the end of the fixed batch processing period. |
| A business pays transaction cost per transaction instead of per transaction, reducing costs. | Increases the risk of cyber fraud as whole transactions in a batch could be exposed to them. |
| Reduces human errors like duplicate payments through transaction consolidating. | It needs immediate payment processing, hindering businesses that need immediate access to funds. |
| It helps simplify reconciliation using consolidated transactions. | This puts challenges before businesses in handling errors or disputes, as issue resolution can be quite complex for any single transaction. |
Automated Vs. Manual Batch Payment Processing
Both are related to payment of batch processing of payments but have certain differences:
| Automated Batch Payment Processing | Manual Batch Payment Processing |
|---|---|
| It saves much time in large volume transactions, simultaneously enhancing efficiency for accounts payable teams. | It takes a lot of time in execution, slowing down operations as it needs hands-on handling of every transaction. |
| Minimizes the risk of human error using benchmarked payment workflow and reduces manual input. | It may consist of manual errors like miscalculations and duplicate payments. |
| It enables reporting and real-time tracking, offering good visibility concerning financial transactions. | Manual payment tracking becomes cumbersome, leading to slowing down in finding discrepancies or issues. |
| Provides sound protection of transactions from fraud and unauthorized payments using two-factor authentication | It lacks robust security metrics making it vulnerable to fraud or unauthorized payments during payment processing. |
Batch Payments Vs. Real-Time Processing
Between the two types of payment processing, there are many differences, as the table below shows:
| Batch Payments | Real-Time Processing |
|---|---|
| Processes multiple transactions in batches at fixed schedules suited to voluminous and time taking transactions. | Facilitates immediate transaction approval and settlement, offering an instant opening to funds and amplifying cash flow management. |
| Minimizes manual time consumption and errors. | Removes uncertainty in individuals' and businesses' transaction confirmation. |
| It is more suitable for a high volume of transactions, helping to reduce transaction costs. | Every transaction is processed individually on a real-time basis, increasing per-transaction costs. |
| It helps businesses schedule flexibility for companies in payment processing as per their operational needs. | It asks for continuous resource designation and becomes complex because of its requirement for low latency. |
