Table of Contents
What Is Electronic Payments Network (EPN)?
The Electronic Payments Network (EPN) refers to an automated clearing house platform facilitating financial transactions electronically between individuals, businesses, and banks for commercial and individual use in the private sector. It serves the purpose of bulk debit or credit transfers originating and settling in the private sector by using secure and efficient fund transfers.
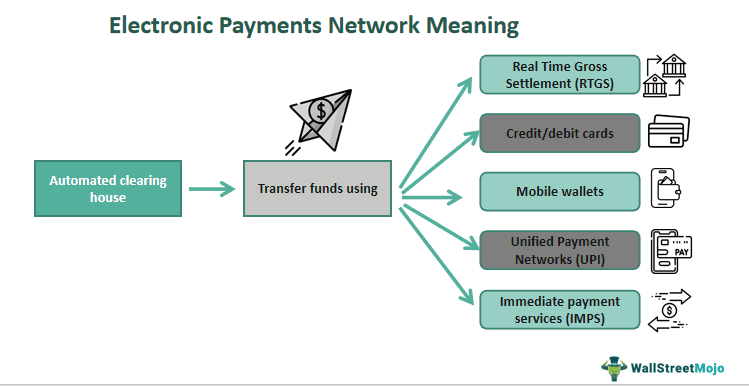
It is mainly used to quickly transfer funds between accounts within the same bank or different banks. It gets utilized for one-time debit transfers and recurring payments like internet and telephone payments. It provides hassle-free, quick, and secure transactions for Social Security benefits, insurance premiums, loan payments, and payroll deposits.
Key Takeaways
- The Electronic Payments Network (EPN) is an automated clearinghouse system that enables electronic financial transactions between individuals, businesses, and banks in the private sector.
- It facilitates bulk debit and credit transfers, providing a secure and efficient means of transferring funds to support commercial and individual use, allowing for seamless transactions within the private sector.
- It is a clearinghouse for electronic fund transfers, while the Federal Reserve is a central banking system operated by the US government.
- Employer initiates ODFI to deposit funds into employee's bank account, EPN sends funds to employee's bank, RDFI deposits salary, and ODFI and RDFI settle the account.
How Does Electronic Payments Network Work?
The Electronic Payments Network is defined as an automated clearing house formed by private sector banks, depository institutions, and credit unions to allow fast, secure, and reliable fund transfers between customers, merchants, and banks. Central private banks formed and owned The Clearing House Payments Company LLC (PayCo) to manage it. Automatic clearing house (ACH), or the clearing house electronic payments network, whose history dates back to the New York Clearing House Association (1850), is its backbone.
EPNs comprise many parts, including payment networks, payment service providers, payment gateways, and payment processing networks. Payment gateways enable authorization and processing of the payments initiated by consumers or firms. Moreover, payment service providers manage the actual payments in real time. Payment processing networks also offer the facility to transfer money from banks to merchants. In addition, payment networks provide an avenue for the exchange of funds between merchants and customers.
To initiate EPN, a user, like an employer, initiates an originating depository financial institution (ODFI) through its bank in order to deposit funds into its staff's bank account. The company managing the payroll deposits then submits the funds to the receiving depository financial institution (RDFI) of the employee, which is their bank. The ODFI deposits all the funds in batches to employees' direct deposit files and sends them to the relevant EPN acting as the ACH handler. After this, the EPN-ACH sends all the funds to the employee's bank or RDFI through electronic funds transfer. After that, RDFI deposits the salary to the employee's savings or checking account. Finally, ODFI and RDFI settled the account with each other.
Merchants have become adept at accepting payments from all payment methods, like debit & credit cards, online payments, digital wallets, and regular bank transfers. Banks use it to obtain loan repayment through the ACH mandate and enable mass payroll deposits to staff by employers. EPN and FedACH – both form the most extensive electronic payments network that manages all the private and government sector transactions made online in the US.
Examples
Let's use a couple of examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Mr. Smith, an entrepreneur with a small company, engages Bank X for all his financial requirements. They have the resources to execute the payroll for their workers who have Bank Z accounts. Thus, Mr. Smith may conduct electronic salary deposits from Bank X towards Bank Z through the EPN, guaranteeing that the employees get their wages immediately into their accounts and providing a simplified and effective payment solution.
Example #2
An article published on 12 March 2024 discussed the astonishing growth of real-time-based payments aided by EPN. Being a private segment ACH network, EPN, which is run by the clearing house, conducted a whopping $52.4 trillion worth of transactions, representing an 8% surge in transaction volume on EPN in 2023. Moreover, its growth momentum has exceeded the overall US ACH network, showcasing the paradigm shift of payments towards electronic payments for consumers and businesses.
All payment segments of transactions like person-to-person transfers, B2B transactions, and direct deposits. Further, the collaboration between the clearing house and MasterCard has advanced real-time payment technologies, enabling its innovation. Hence, it has also led to broader adoption of EPN throughout business sectors and customers.
Electronic Payments Network vs Federal Reserve
Let us compare the two using the table given:
| Electronic Payments Network | Federal Reserve |
|---|---|
| It is a clearing house for financial transactions to transfer funds electronically. | The Federal Reserve System of the US government operates it. |
| The private and public sector uses it for funds transfer. | Handles monetary policy, promotes financial stability, and regulates banks. |
| It handles bulk transactions for the private sector. | It offers the broadest range of financial services and transactions using Federal Reserve Banks' Automated Clearing House (FedACH). |
| A consortium of private banks manages it to facilitate the bulk of private sector transactions. | Federal Reserve manages FedACH to handle bulk transactions in the public sector. |
| It mainly oversees the funds transfer of private individuals or entities from one bank account to another. | It aids in transactions between bank-to-bank and banks to other financial institutions and acts as a bridge between EPN & FedACH. |
| Swift transfer of funds happens here. | Any fund transfer can happen based on the transaction and service type. |
| It provides a more secure and efficient form of electronic money transactions to the private sector. | It regulates monetary policy, controls the money supply in the market, and manages the rate of interest and the economy of the US. |
| It has to comply with the regulations, guidelines, and security protocols regarding data protection issued by the Federal Reserve. | It acts as a nodal body for approving and implementing security protocols and measures in the financial sector. |
| Its functions are defined and controlled by the Federal Reserve. | It controls and oversees ethics and compliance. |
