Table of Contents
What Is Financial Globalization?
Financial globalization refers to the integration process whereby the local financial systems, including domestic markets, financial institutions, and services of different countries across the globe, interact and connect with international financial institutions, markets, and services. The key drivers of such globalization are policy decisions and technological growth.
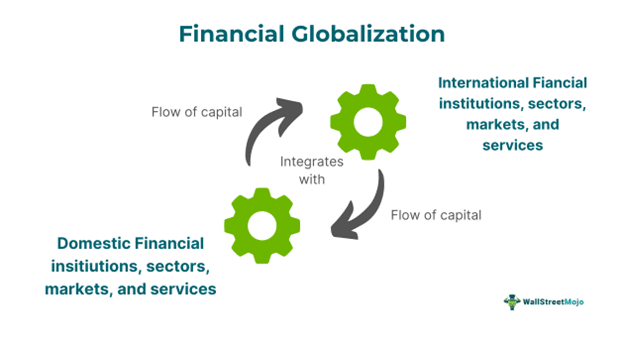
Such cross-border integration is essential for the growth of domestic financial sectors, services, procedures, practices, and the overall economy. Moreover, it helps developing countries strengthen their financial systems while ensuring effective corporate governance and proper information flow. It also facilitates accelerated foreign investment, affordable foreign transactions, risk mitigation, and increased cross-border capital flow.
Key Takeaways
- Financial globalization refers to an international integration process that connects domestic financial systems with global financial markets, institutions, sectors, and services.
- It aims to ensure the global flow of capital and resources between world economies. It promotes the economic growth of developing countries and opens up capital investment avenues for developed economies.
- Technological advancement, policy decisions, global market forces, and international capital flow are the key drivers of international financial integration.
- It has various macroeconomic impacts, such as economic interdependence, strengthening of financial systems, and global financial imbalance. Additionally, it fosters global financial cooperation, social progression, and overall economic development.
Financial Globalization Explained
Financial globalization is an approach to integrating and connecting the local financial sectors, markets, institutions, and services with the international financial system to ensure substantial economic growth. Global integration of the financial systems helps the nations explore more diversified investment opportunities in the world economies. However, it presents various challenges in the macroeconomic scenario.
This phenomenon is widely influenced by returns on investments, market dynamics, and risk profiles. However, the two prominent economic forces, i.e., supply and demand, are the key players in shaping this process:
- Demand: Since developing economies need substantial investments for their economic growth, infrastructure, and trade development, this process helps. Developed nations can invest their excess funds in these growing markets.
- Supply: Further, developed nations find potential investment avenues for building wealth by contributing capital to these emerging economies.
Also, according to the Markowitz Portfolio Theory, managing risk against returns is essential. Global investing allows world economies to diversify their investment portfolios, thereby reducing risk. This diversification enhances returns through global portfolio management.
History
The current growth of financial globalization can be marked from the mid-1980s when various nations worldwide observed liberalization in capital control and policy decisions. The emerging economies rapidly adopted this phenomenon to ensure speedy economic growth and more consumption stability by exporting their goods and services to the international markets.
Although the process brought positive outcomes for these nations, the onset of the economic crisis in the late 1980s made this decision questionable when the primary sufferers were these developing countries. Also, a few Asian nations and Mexico faced the same situation in the financial crisis during the 1990s. These nations were criticized for easing capital control, which led to the heightening of bankruptcies and market failures during the crisis.
Causes
Financial globalization phenomena have gained immense significance in recent years due to their contribution to global economic development. Given below are some causes:
- Global Market Forces: The various factors of the international market, like emerging markets maturity, diversification of the financial instruments, and economic interdependence, have resulted in global financial integration.
- Cross-Border Investment Flows: Other key drivers of such international interactions include the need for cross-border capital flow, such as foreign direct investment, bank loans, and international financial market investments. These drivers arise from factors like currency stability, investment uncertainties, and the need for economic growth.
- Policy Decisions: The government's efforts, such as liberalizing investment and trade policies, have led to global financial integration of world economies.
- Technological Development: As technology has advanced, the emergence of fintech innovations, digitalization, cybersecurity, and telecommunications have all contributed to this phenomenon.
Examples
Global financial integration has increased the opportunities and challenges for the world economies, as evidenced by the following examples:
Example #1
Suppose ABC nation is a developing country. The government eased its international trade and investment policies to secure capital from the global markets and other nations. The agenda is to ensure capital inflow for the development of sectors such as education, infrastructure, healthcare, and technology within the nation. This aim is to reduce unemployment, enhance the standard of living, and curb poverty. The foreign direct investment resulted in more job prospects for local citizens. However, domestic businesses suffered due to the extensive price and quality competition from these international brands in the local markets.
Example #2 - Financial Globalization Examples in the Philippines
Inrecent years, international financial integration has contributed to the economic growth of the Philippines by significantly reducing unemployment levels. However, financial globalization has not eliminated poverty and inequality in the country. While the rising levels of trade, financial openness, and labor migration were some key highlighted benefits, they have also presented challenges pertaining to targeted policies for inclusive and sustainable development of the country.
From the 1990s to the 2000s, the Philippines experienced a higher trade openness, with a rising GDP from 88.1% to 101.0% due to its free trade policies, such as reduced transportation costs and advancements in information and communication technology (ICT), particularly in electronics and electrical components. The development of the ICT-BPO sector also played a significant role in boosting trade, with the overall trade alleviating GDP to 101.4% in 2010.
In addition, elevated financial openness with higher capital flows raised GDP from 3.1% in the 1990s to 3.4% in the 2000s despite financial crises. Further, in 2010, the capital flow surged growth to 4.6% of GDP, supported by foreign exchange liberalization reforms and the entry liberalization of foreign banks, which marked a victory.
Effects
Given below are the various debatable impacts of this phenomenon so far:
- Betterment of Overall Financial System: When local financial markets, services, and institutions engage with and operate with the international financial system, the overall financial sector improves globally.
- Expedites Economic Growth: While efficient capital allocation in different economies can ensure the growth of infrastructure, human resources, and technology worldwide, potential risks, including capital flow volatility, external shocks, and economic interdependence, are rising simultaneously.
- Economic Interdependence: As the financial systems of different nations synchronize their financial stability and economic progress, they are exposed to global market vulnerabilities and risks due to greater economic interdependence.
- Global Financial Integration: It promotes global financial connectivity to increase nations' economic resilience and growth. However, this also elevates the possibilities of financial volatility and economic shocks.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The world has witnessed many challenges and adverse outcomes of such integration, as discussed below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| This phenomenon has various macroeconomic advantages, including optimal international resource allocation and accelerated economic growth worldwide, especially in developing nations. | According to critics, financial globalization and financial crisis go hand in hand. |
| Also, such an integration limits macroeconomic fluctuation risk while allowing developing economies to share their risk. Businesses can cater to the international market, thus being less impacted by domestic market volatility. | It may lead to a currency crisis when a nation's significant indebtedness results in more exports and an imbalance between domestic supply and demand. |
| It also helps investors mitigate investment risk by diversifying their money across different asset classes in various geographical locations. | It may decrease the effectiveness of domestic government policies over cross-border financial integration, thus emphasizing the need for the development of global financial policies. |
