Table of Contents
What Is Keynesian Put?
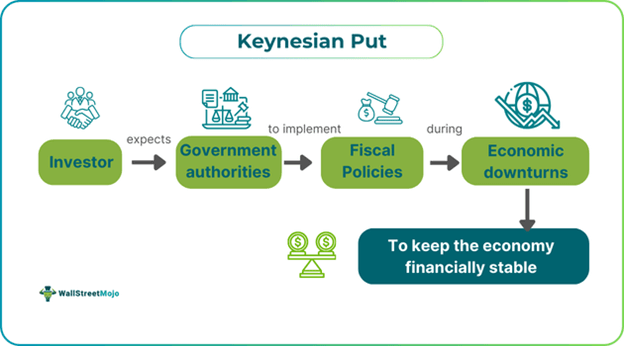
Keynesian Put refers to investors' expectations that the fiscal authorities will increase spending to maintain growth and inflation at par with the global economy. The concept also focuses on how the government controls the economy and its growth through monetary and fiscal policy measures during a depression or recession.
Keynesian put and Keynesian theory are similar in specific ways. Both emphasize the importance of government involvement in stabilizing the economy. The concept is concerned with the relationship between total economic spending and total economic output, as well as the current impact of inflation and employment levels on the economy.
Key Takeaways
- Keynesian Put is the expectation that the fiscal authorities will increase spending to maintain growth and inflation at par with the global economy. The support is given in times of downturn.
- The term was first coined by Bank of America's analyst Merrill Lynch in 2016. The policies routinely cut interest rates in response to turmoil in the financial markets.
- Through monetary policies, central banks can help restore trust and keep the flow of credit flowing to families and businesses, making it act as a safety net to support financial markets in times of crisis.
Keynesian Put Explained
Keynesian put is based on the idea that the government or the concerned monetary authority would spend money to promote economic growth and keep inflation rates low. This support is given in times of downturn. Analyst Merrill Lynch, Bank of America, coined the term for the first time in 2016 with reference to the Greenspan Put, introduced by then-Federal Reserve Chair Alan Greenspan. The Greenspan Put states monetary policies to overcome recession. The policies routinely cut interest rates in response to turmoil in the financial markets.
Keynesian put acts as a safety net to forestall a financial crisis from getting out of hand and causing havoc on the economy. Investors may start to pull their money out of the market during times of downturn or financial crisis as they lose faith in the financial system. This might lead to a fall in asset prices and credit markets to contract.
In such scenarios, the central banks introduce initiatives in the financial markets, help rebuild confidence, and stop a liquidity crisis from turning into a solvency crisis. Through such implementations, the flow of money and credit to businesses and families, which is crucial for job creation and economic growth, can be maintained. Economists anticipate the government will raise expenditures and offer unemployment and insurance benefits. They expect the government to provide financial assistance to individuals and small enterprises with respect to the level of decline in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Examples
Let us check the instances below to understand the concept of Keynesian put better:
Example #1
Suppose Country Xyle, like other countries, witnessed the adverse impact of COVID-19 on its economic growth. The investors, seeing the worsening situation, expected the government authorities to intervene. As a result, in response to the pandemic, the Xyle government passed an act in March 2020, which contained several financial provisions to aid individuals, companies, and state and local governments. It included provisions for forgiving small business debts, expanding unemployment benefits, and making direct payments to individuals.
In addition to these steps, the central bank of Xyle also carried out several monetary policy actions to support financial markets and guarantee the smooth operation of the credit markets. Cuts in interest rates, the acquisition of assets, and the creation of loan facilities were some actions taken to give financial institutions liquidity.
Overall, the Keynesian approach worked in favor of the Xyle economy as the government responded to the COVID-19 outbreak. Despite enormous obstacles and unpredictability, the authorities contributed through these measures to making the economy resilient.
Example #2
The European Central Bank's (ECB) response to the European sovereign debt crisis illustrates how Keynesian put works. In 2010, several Eurozone nations experienced substantial difficulties relating to their sovereign debt, raising questions about the Eurozone's stability and the larger European economy.
The ECB cut interest rates to historically low levels to promote economic growth and increase lending to consumers and businesses. By doing so, the ECB signaled to the financial markets that it had decided to keep interest rates low to boost the economy. It also provided forward guidance (voluntary exchange of bonds), supporting the economy and keeping interest rates low.
Importance
The Keynesian approach is crucial because it helps prevent financial crises from getting out of hand and wreaking havoc on the economy. It can also help prevent the escalation of financial crises into complete economic depressions. Through monetary policies, central banks can help restore trust and keep the flow of credit flowing to families and businesses by acting as a safety net to support financial markets in times of crisis.
Central banks may stop this downward spiral by stabilizing financial markets and establishing a solid framework for economic expansion and job creation. The Keynesian approach can assist the whole economy through fiscal and monetary policy in addition to supporting financial markets.
For example, central banks can help stabilize asset prices by lowering interest rates and buying assets to provide liquidity to financial institutions. Implementing fiscal policy measures like increased government expenditures and tax reductions can also avoid a recession.
