Table of Contents
What Is Mortgage Insurance?
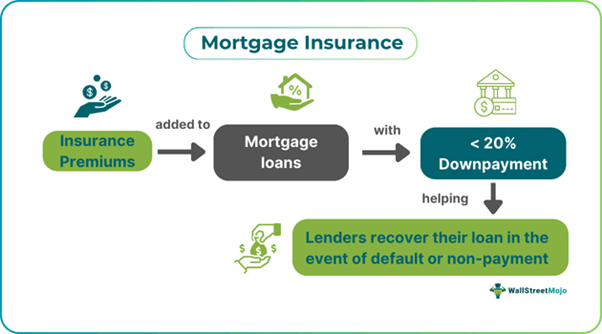
Mortgage Insurance is a type of insurance scheme that safeguards lenders from financial losses in the event of defaults or non-payments. The borrowers paying less than 20% of the price for a property as a down payment require paying for mortgage insurance, which acts as a shield for mortgage lenders if they are unable to recover the loan amount in the future.
It makes obtaining mortgages feasible for even those who were not able to access these options earlier. In the process, borrowers have to pay premiums mostly as part of the monthly payments toward the mortgage. The Federal Housing Administration (FHA) makes paying for this insurance mandatory to make homeownership affordable to and achievable by all.
Key Takeaways
- Mortgage insurance represents a policy product offered by insurers that protects lenders from financial loss in case of loan defaults by the borrower.
- Its types include Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI), Qualified Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP), Mortgage Title Insurance, and Mortgage Protection Life Insurance.
- It provides benefits to both lenders and borrowers, like- affordable rates, required protection, and opportunity for financial inclusion.
- It safeguards lenders when defaults occur on the mortgage, which is different from life insurance, which offers a financial payout to beneficiaries after the policyholder's demise.
- On the contrary, homeowners insurance provides coverage for damages that occur in a residential space.
How Does Mortgage Insurance Work?
Mortgage insurance represents a financial product that safeguards lenders against any losses in case of loan defaults, whether government-sponsored insurance, such as FHA or Private Mortgage Insurance (PMI). The borrowers pay the premium for the insurance coverage for the benefit of the lender. One can use various online mortgage insurance tax calculators to calculate the premium paid toward the insurance schemes.
Lender mortgage insurance comes into existence when a borrower applies for a mortgage with a down payment lower than 20%. They supplement it with insurance premiums to mitigate mortgage default risks. Moreover, the borrowers either have to pay the insurance upfront, monthly or both as per the type of the loan. FHA loans need an upfront premium and monthly payments to ensure more protection against defaults.
As and when borrowers default on their payments, the insurance helps the lenders recover their due loan balance, removing the financial risk involved. Hence, this insurance coverage enables borrowers to qualify for mortgage loans that they would not ordinarily receive otherwise, as the downpayments fixed are usually high.
The mortgage insurance cost is based on credit score, loan amount and down payment. Though it increases monthly housing costs and impacts affordability, it is still considered highly useful for borrowers with limited money and first-time purchasers, thereby increasing opportunities for home ownership for homeless people.
As it decreases lender risk, it has led to a stable and healthy lending environment while supporting the growth of the real estate sector. Furthermore, it has encouraged banks to provide loans to a diverse segment of borrowers and help contribute to financial and economic inclusion.
Exploring insurance options can help you find coverage that fits your unique needs. For those interested in comparing a range of insurance products, resources like SuperMoney make it easier to review and select policies from top providers.
Types
Mortgage insurance exists in different forms in the market. Let us learn about their different types below:
#1 - Private Mortgage Insurance
This is the most common type of insurance to shield a mortgage loan deal. This is the best option where a home seeker cannot pay the downpayment of 20% of the property price. This insurance type allows borrowers to buy insurance to back their mortgage loan, thereby giving lenders, the private insurance companies in this case, an assurance for repayment even in the event of default or non-payment due to any reason.
#2 - Qualified Mortgage Insurance Premium
Those who are not eligible for conventional mortgage loans opt for mortgage loans with insurance offered by FHA. Hence, the default risk is even more when it comes to this type of insurance in the mortgage. The federal authorities accept applications and approve them even from borrowers with low credit scores, which could be as low as 500, and comparatively lesser downpayment percentage of up to 3.5%.
#3 - Mortgage Title Insurance
This type of insurance in a mortgage protects borrowers in case of title issues post-purchase of a real estate property. This is required when a person takes up a mortgage loan for a property, and after the sale and purchase are complete, the property is found to belong to someone other than the one who sold it.
#4 - Mortgage Life Insurance
As the name implies, it is a combination of the features and provisions of mortgage insurance as well as life insurance. While the former protects lenders from suffering in the event of defaults, the latter is meant to protect borrowers' heirs if they die carrying loans.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
A November 2024 publication stated that the possibility of the mortgage insurance industry to grow up to 10%. The Radian group made this projection for 2025, given the attractive interest rates dominating the market, thereby enhancing investment returns and maintaining the robust persistency rate. Moreover, in the 3rd quarter of 2024, Radian witnessed $13.5 billion worth of fresh insurance, which is a bit lower than Quarter 2, with $13.9 billion. The report indicated an upgrade in the persistent rate from 83.6% to 84.4% in 2023.
The report advocated Radian’s insurance policies being made available at lower rates, thereby minimizing the chances of cancellations given the refinancing opted for in the current high-rate environment dominating the market.
Example #2
Let us assume that a first-time home purchaser, Lily of Old York City, applies for a mortgage loan of $500,000 with Moonrise Bank. She gave $20,000 as a down payment, which was only 5% of the price of the home, lower than the usual standard payment of 20%. Hence, to balance the risk, Moonrise Bank asks for an insurance mortgage from Safety Insured Limited, for which Lily pays $200 monthly as the insurance premium, protecting the bank in case she defaults.
After one year, Lily goes through financial challenges and skips repayments. Safety Insured Limited pays the bank $60,000 as the outstanding loan balance. The amount helped stabilize her finances and minimize losses for the bank. This shows how mortgage insurance is critical for feasibly owning a new dream house.
Benefits
It offers benefits to both lenders and borrowers in the following manner:
- Borrowers can opt for mortgages at below 20% downpayment.
- Mortgage insurance offers protection and security of funds to the lender.
- It enables lenders to offer borrowers affordable interest rates and loan terms.
- It induces confidence and stability in the lending market.
- It serves as a roof for borrowers, protecting them even when they fail to pay the loan due to accidents, layoffs or natural calamities.
- It plays a significant role in the financial inclusion of people who are unable to get the benefits from banks.
- It injects liquidity into the market, spurring economic and employment activities and adding to the nation's economic growth.
Mortgage Insurance vs Life Insurance vs Homeowners Insurance
Let us use the table below to understand the distinction between the three:
| Mortgage Insurance | Life Insurance | Homeowners Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| It safeguards lenders when defaults occur on mortgages. | Offer financial payout to beneficiaries after the demise of the policyholder. | Provides coverage against home damages |
| Provides coverage to the due loan amount for lenders. | Offers amount for mortgage repayment and serves various financial needs. | Consists of coverage for home structure, liability protection, and personal belongings. |
| Offers safety to lenders by giving them a way of recovering loan amount in the event of default. | Offers safety to dependents or families of policyholders. | Gives protection to homeowners. |
| Becomes important to pay for when the downpayment threshold to below 20%. | Remains optional as per financial goals. | Homeowners with a mortgage must opt for it. |
| The borrower has to pay the premium. | Premium paid by policyholder. | Premiums paid by homeowners. |
| Amount is decided with respect to the downpayment and loan size. | Differs with respect to health condition, policy term, and size. | Differs by risk factors, home value and location. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

