Table of Contents
Neuromarketing Definition
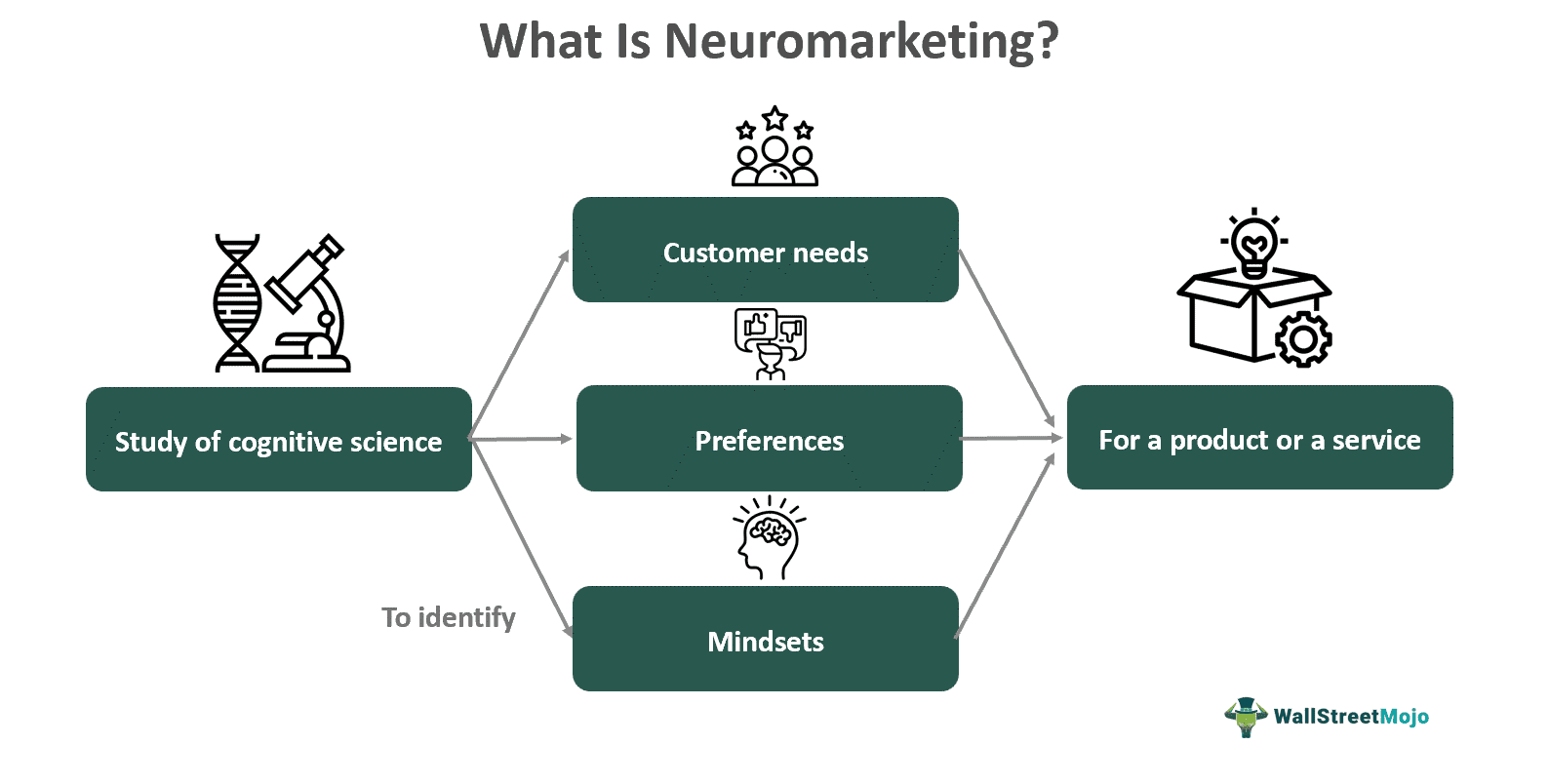
Neuromarketing is a market strategy that involves the study of cognitive science and knowledge of neuroscience to make precise identification of customer needs, preferences, and mindsets around products and services. Customer responses are assessed to create specific advertising campaigns, designs, and packaging.
The technique helps penetrate the non-conscious reactions of people so that brands and companies can create effective marketing campaigns that connect with the target audience by monitoring their brainwave activity, skin response, and eye tracking. It helps organizations understand and predict the consumer's decision-making process and behavior. Brands can use neural and other psychological aspects to gain insight into customer's preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Neuromarketing is the study of the consumer's response that is evoked in their brain by advertising and other brand-related messages like logos, designs, slogans, sounds, music, and all-around experiences.
- The main types of neuromarketing techniques are biometrics, facial coding, eye tracking, pupillometry, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), and electroencephalography.
- It has a broad scope of application across different areas and fields of work, such as politics, entertainment, digital marketing, and advertising analytics, coupled with criticism over data privacy issues and expensive setups.
- The whole concept is criticized for deliberately manipulating customer behavior, but companies conclude by following ethical measures while testing.
How Does Neuromarketing Work?
Neuromarketing is the process of studying consumer behavior, the decision-making process, and all the responses that originate within their brains. It is analyzed using neuromarketing tools, inviting and selecting people as subjects for the study. The collected data is further analyzed to acknowledge the responses and attention given by consumers to an ad campaign, advertising material, product, or service. Multiple types of neuromarketing tools and techniques can be implemented; each one differs from the other and gives explicit outcomes based on how the consumer feels, the emotions evoked, and all types of unconscious responses.
Tools are used to scan people's brains and evaluate physiological and neural signals. Brands and companies use these signals to understand the responses people give for any particular design, advertisement, font, color, and marketing message. Based on this, companies improve their content, strategies, and customer experience, gain competitive advantage, and even develop new strategies to increase sales. With modern technology and innovation, neuromarketing is becoming an integral part of digital marketing and is associated with artificial intelligence and innovation.
The scanning is so granular that it includes every single brain and body activity, from heart rate to facial expressions, gaze, and changes in pupils, emotions, and skin respiration. There are neuromarketing companies that allow and offer the setup and analysis of each technique based on how precise it is, but it can be expensive. Businesses use these tools as per their requirements and affordability.
Techniques
The following are techniques for neuromarketing:
- Eye Tracking - The technique follows the customer's eyeball and gaze to identify where it lands or stops. This way, companies can figure out the color, message, ad, font, and design that successfully draws the most attention from the customer. Eye tracking helps in website design and packaging but does not help in evaluating the customer's emotions.
- Facial Coding - Similar to eye tracking, this technique focuses on the facial expression and the response it makes when a product or brand is placed in front of it. It helps in defining the emotions that people feel, such as happiness, satisfaction, surprise, fear, or anxiety. Through this, companies can improve their ad content.
- Biometrics - This technique involves skin respiration, heart rate, and conductance to identify the engagement level a consumer responds with towards a product, ad campaign, or brand. It expresses people's desires and can be used with eye tracking to make better content and ad campaigns.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging - It is by far the most expensive approach in neuromarketing, and it offers a very detailed analysis that includes recall, customer engagement, and emotional responses. It seeks the blood flow in the brain during high neural activity, which allows businesses to make branding and pricing decisions.
- Pupillometry - When a consumer is invited to monitor their brain activities, they serve as subjects in the study. In pupillometry, the pupils of the subject are taken into focus to conclude. It is a relatively cheap approach and helps in site design, revising ads, and product packaging.
- Electroencephalogram - It allows companies to reveal customer engagement with the assistance of electrical signals coming from the neurons inside the brain. Again, it is an expensive technique, and changes occur in short periods. It may help in improving the ad quality and branding.
Examples
Below are two examples of neuromarketing:
Example #1
Suppose an advertising agency created a new TV ad for a car company. They wanted to test its effectiveness so that they could report that as well as the ad to the automobile company. The agency is called a neuromarketing company, which sets up the whole framework for neuromarketing techniques. The ad agency chooses eye tracking and invites 99 people to become subjects in their marketing study.
Each subject is shown the ad, and the setup records the gaze and monitors the direction of the eyeball. The data, when analyzed, helped the ad agency understand precisely where people looked and paid attention to while watching the advertisement. Based on the insights, the company made improvements in the advertisement's logo design, font, messaging, and slogan and finally sent it to the car company with comparable data.
This way, neuromarketing helped the advertising agency create better content and ad campaigns. It is a simple neuromarketing example. In reality, many other aspects are considered.
Example #2
According to an article from January 2024, YouTube ads are about to become more effective as neuromarketing is going to collaborate with artificial intelligence. Junbi.ai, which is a pretesting and benchmarking platform for YouTube ads, is planning to combine expoze.io's artificial intelligence-powered predictive eye tracking with machine vision to deliver valuable insights to improve the expected performance of YouTube ads.
By hyper-focusing only on one specific platform, the Junbi.ai team developed benchmarks and metrics to assess media and helped marketing teams let go of the scientific data analysis. These metrics are brand attention score, cognitive ease score, and ad breakthrough score. They will be combined with a series of other campaigns and tests of what makes a good ad.
Applications
The applications of neuromarketing are:
- It helps in branding by creating a brand personality and corporate image and evaluating the emotions that are induced by the brand in the consumer's mindset. It includes logos and designs, brand application, and defining assets of the brand.
- The implied application of neuromarketing helps in product packaging; the rational and subconscious aspects of the customers are compared to define packaging, consumption experience, attribute testing, and display visibility with other variables such as pricing, brand recognition, and alternatives availability.
- It plays a significant role in advertising. Companies gauge ad campaigns and graphic campaigns, compare animatics, and assess digital, radio, and publicity material.
- Applied neuromarketing assists in brand building by evaluating pre-and post-tests of the consumer's perception of the brand.
- Apart from the physical and traditional marketing scenarios, it is applied in digital marketing to assess graphic lines, landing pages, usability, user interface, and microsites, along with speed and the average time spent by a visitor or potential customer on a website.
- In other applications, it helps in measuring consumer behavior and experience in a store.
- The content itself is a product; neuromarketing helps the entertainment industry describe the experience while watching a video, reel, TV show, or movie, reading a magazine, or playing video games.
- It is used in politics as well to understand the subconscious mindset of voters and improve speech and information.
Pros And Cons
The pros of neuromarketing are:
- Helps understand the customer in a much better way than traditional marketing.
- Penetrates different layers of a consumer's subconscious mind to determine their needs, reactions, responses, understanding, and desires with a product or service.
- Assists in improving the content, sales, marketing campaigns, services, or goods offered by comprehending psychological reactions.
- The data based on neuromarketing tools and strategies is more concrete and reliable.
The cons of neuromarketing are:
- It comes with ethical concerns, as most people associate it with the notion that it is an indirect attack on their privacy.
- Neuromarketing strategies and insights require specialized skills of interpretation and knowledge to derive preferable outcomes and read patterns and sight trends.
- The whole model of neuromarketing tools and framework is an expensive system and detailed analysis induced more costs and complexity.
- With the increased use of neuromarketing, privacy laws and policies are being introduced to protect data and other legislation.
