Table of Contents
What Is Regulation Y?
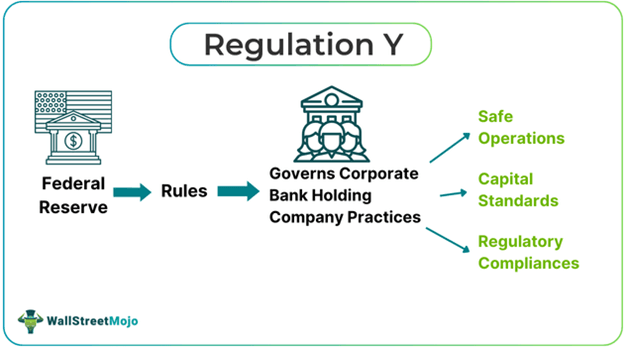
Regulation Y is a banking regulation that governs the operations and practices of corporate bank holding companies and certain state-member banks. Issued by the U.S. Federal Reserve in accordance with the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, it has been continually updated with new rules and regulations.
It applies to both domestic and foreign bank holding companies in the United States that do not offer banking services directly but hold controlling interests in one or more banks. Regulation Y primarily establishes rules and approval processes for mergers and acquisitions and defines the minimum capital ratios bank holding companies must maintain for healthy operations.
Key Takeaways
- Regulation Y is the set of governing rules controlling corporate bank holding companies. It defines the types of transactions by bank holding companies that require approval from the Federal Reserve Board.
- It was Introduced on September 1, 1956, under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, it has been regularly updated with new regulations.
- Regulation Y establishes three main compliance requirements: capital, liquidity, and risk management, ensuring that institutions are well-prepared and operate smoothly.
- It defines capital ratios, activities requiring Federal Reserve approval, and mergers and acquisitions (M&A) while serving as a framework for monitoring and overseeing non-banking firms.
Regulation Y Explained
Regulation Y provides the framework for bank holding companies and corporate practices of state-member banks. Under its provisions, certain transactions require Federal Reserve approval. Regulation Y was established on September 1, 1956, under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, the International Banking Act of 1978, and the Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery, and Enforcement Act of 1989, to regulate bank holding companies.
The key functions of Regulation Y include:
- Defining minimum capital reserves and ratios for various categories of capital.
- Regulating mergers and acquisitions between bank holding companies.
- Assisting non-banking firms in seeking Federal Reserve approval for specific transactions and activities.
- Stating permissible non-banking activities for bank holding companies, state-member banks, and foreign banks operating in the U.S.
- Managing the appointment of new senior officers in bank holding companies or state-member banks during turbulent times.
Regulation Y has helped the U.S. Federal Reserve streamline the framework for non-banking corporations and state-member banks. According to Regulation Y, well-managed banks must have satisfactory regulatory ratings and meet capital standards relative to their size and services. It also mandates a 30-day public comment period for transactions seeking Federal Reserve approval. Some application requirements have been removed to ease the process for well-managed and financially healthy banks, though critics argue that this may increase associated risks.
Certain basic transactions, such as securities acquisitions made in good faith, are exempt from Regulation Y. This is due to ongoing updates and efforts to reduce regulatory burdens on healthy banks. Since 2000, the Federal Reserve has updated Regulation Y more than 30 times.
Requirements
There are three main requirements under Regulation Y:
- Capital Requirements: Banks, certain member banks, and bank holding companies must maintain sufficient capital based on the minimum ratio guidelines outlined in Regulation Y. This supports banking operations, transactions, activities, and acquisitions. The capital requirement depends on the institution's current capital levels, size, and service complexity. Large institutions may need to raise additional capital.
- Liquidity Requirements: Banks and holding companies must ensure sufficient liquidity to meet obligations to creditors and depositors. This includes maintaining access to multiple funding sources to cover short-term financial needs.
- Risk Management Requirements: Bank holding companies must oversee risk management systems to identify, measure, manage, and respond to risks such as operational, market, or credit risks. This applies to financial transactions, mergers, acquisitions, and other activities.
Importance
The importance of Regulation Y includes:
- It establishes rules for the activities of bank holding companies and specifies transactions requiring Federal Reserve approval.
- It sets standard criteria for ensuring the healthy functioning of banks.
- It facilitates mergers and acquisitions of bank holding companies.
- It provides guidelines for domestic and foreign bank holding companies operating in the U.S.
- It serves as a framework for monitoring transactions and reducing risks, helping prevent financial fraud.
- Without Regulation Y, there would be no standardized guidelines or oversight for the operations and activities of bank holding companies.
Regulation Y vs Regulations YY
The key differences between Regulation Y and Regulation YY are:
- Regulation Y governs both domestic and foreign bank holding companies, while Regulation YY applies only to certain companies supervised by the Federal Reserve Board, including specific foreign organizations.
- Regulation Y outlines transactions that require Federal Reserve approval for bank holding companies. In contrast, Regulation YY mandates that large banking institutions maintain liquid asset buffers to ensure market resilience and their ability to meet financial obligations.
- Regulation Y has a broader scope, covering requirements for bank holding companies and member banks. Regulation YY, however, has more limited guidelines, primarily focused on liquidity and risk management for large institutions.
