Table of Contents
What Is A Stafford Loan?
Stafford loan refers to a student loan offered by the United States Department of Education. These loans are given to students who are admitted to one of the accredited American higher education institutes with strict requirements to qualify and have specific borrowing limits. These loans are provided to students at lower interest rates than other private loans.
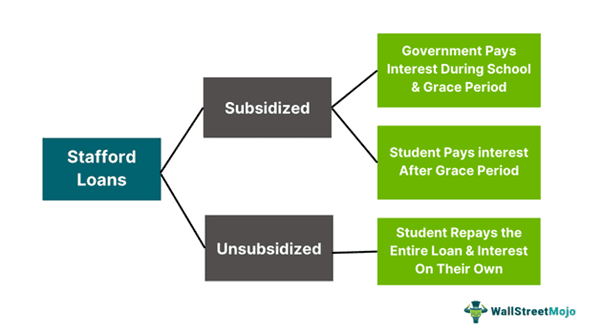
These loans come in two major types – unsubsidized and Subsidized Stafford loans. The former type requires the students to pay all the interest, while the government pays the interest while the student is in school, in the case of the latter type. These loans are issued as a part of the Federal Family Education Loan Program (FFELP) program.
Key Takeaways
- Stafford loans are federal loans disbursed to students to cover their education and related expenses.
- The federal government provides them through the U.S. Department of Education under the FFELP Program.
- The two types are subsidized (the government pays interest before the grace period) and unsubsidized (the Student pays interest and principal).
- The interest rates are generally lower than private loans. Moreover, the repayment schedule is also flexible according to the financial situation of the student after graduation.
- The repayment initially only covers interest, so the payments can be as low as $25.
Stafford Loan Explained
Stafford loans are fixed-rate federal loans offered to students enrolled in accredited higher education institutes in America. Students enrolled in college or university as part of their undergraduate, graduate, or other degrees that require students to attend college at least half-time.
A direct subsidized loan is provided for undergraduate students who express the need for financial help. However, both graduate and undergraduate students can apply for unsubsidized direct loans regardless of their financial needs. To enjoy the benefits of these loans, they must first be admitted into a university or a college and fill out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
The borrowing amount for students varies depending on their financial situation. In some cases, they can borrow a more significant amount. However, the ceiling for subsidized amounts for different stages is as follows:
- Freshmen - $3,500 per year
- Sophomores - $4,500 per year
- Juniors - $5,500 per year
- Seniors - $5,500 per year
Each year, the Stafford loan rates are revised on July 1. As of July 1, 2024, the interest rate for undergraduate students is 6.53%, and graduates and professional students availing the loan get an 8.08% interest rate. These rates are fixed and shall remain the same for the entire tenure of the loan.
However, there are a couple of factors to consider regarding these loans. First, an origination fee of 1.057% is charged for disbursing funds. Second, like all other loans, taking out this loan and repaying it can affect the borrower’s credit score.
Types
The two types of Stafford loans are:
#1 - Subsidized Loans
These loans are the most attractive student loans for multiple reasons. One of the foremost reasons is that the government pays the interest on behalf of the students while they are in school. Moreover, the government does so in the six-month window after school and if the student has any financial issues at a later stage.
Students who want to secure subsidized Stafford loans must express the need for financial help by filling out FAFSA. There are borrowing limits for this type of loan as well. Students can only borrow up to $23,000 in total or a maximum of $5,500 per year. These sums are made available for students within the maximum eligibility period.
#2 - Unsubsidized Loans
Unsubsidized loans are student loans as well. However, the government does not pay any interest. In fact, the interest for such loans keeps accruing during the student’s period at school and within the grace period. Students can choose to pay or not pay the interest while in school or during the grace period.
If students choose not to pay interest during those two periods, the amount will be added to the principal of the loan and added to the tally during repayment. These loans can be secured by all college or university students from accredited institutions without requiring them to have expressed a financial need. The borrowing limits are higher for these loans. Students can borrow a maximum of $31,000 in the lifetime of the loan or $7,500 a year.
Qualification Requirements
The requirements to qualify and find out the Stafford loan interest rates are:
- The student must be an American citizen, eligible non-citizen, or national
- Must have a high school diploma or an equivalent of the same (For Example: GED)
- The student must be admitted at least half-time in a certificate-granting program or degree from an eligible institution
- For subsidized loans, there must be an expressed financial need, and students shall be required to fill out FAFSA and will be required to sign an MPN (Master Promissory Note
- Applicants must not have any pending or arrears in previous federal student loans
How To Repay?
Repayment of these loans, along with Stafford loan rates, begins only six months after college graduation. This six-month window is commonly referred to as the grace period. After the grace period, students must start repaying the loan.
The typical repayment term is ten years. However, students have the option to choose different plans, such as income-driven repayment, graduated repayment, or extended repayment.
Repayment options such as income-driven repayment calculate the monthly repayment based on family size, income, and other such factors and determine the amount students must pay each month. Typically, after 20-25 years of repaying these loans, the remaining amount is waived off or forgiven.
Borrowers can also combine their federal student loans through Federal Direct Consolidation Loan. These loans consider the weighted average of all the loans that are part of the consolidated loan and round off the rates to the closest 1/8th of a percentage point.
Limits
Unsubsidized and subsidized Stafford loans have two types of limits: an aggregate limit and an annual limit. The value of these loans depends on the borrower's stage of education. The limit for subsidized loans is considerably lower than that for standard Federal Stafford loans.
Another factor that should be taken into consideration is whether the students are dependent or independent. However, for students with subsidized loans, the limits are the same for both dependent and independent students.
The subsidized loan annual limits for students of different grades are:
| Grade | Annual Limit |
|---|---|
| Freshman | $3,500 |
| Sophomore | $4,500 |
| Junior | $5,500 |
| Senior | $5,500 |
| Graduate | NA |
The annual limits for unsubsidized loans for dependent and independent students, depending on their grades, are:
| Grade | Dependent Students | Independent Students |
|---|---|---|
| Freshman | $5,500 | $9,500 |
| Sophomore | $6,500 | $10,500 |
| Junior | $7,500 | $12,500 |
| Senior | $7,500 | $12,500 |
| Graduate | NA | $20,500 |
Benefits
The benefits of Stafford loan interest rates are:
- The foremost benefit is that these loans have significantly lower interest rates than private loans.
- Most of these loans do not require interest payments until the grace period (six months) is completed. This period gives students time to secure a regular income and repay the loan.
- For subsidized loans, the government pays interest while the students attend school, reducing the overall payment.
- Once the repayment schedule starts, the amounts are reasonably low. These payments usually only cover the interest, so they can be as low as $25 initially.
- The ability to negotiate repayment plans with the federal government allows students to choose a repayment plan that fits their financial situation.
- After making repayments for these loans (typically 20-25 years), the remaining amount is forgiven.
Stafford Loan Vs Perkins Loan Vs Direct Loan
The differences between Stafford, Perkins, and direct loans are:
Stafford Loans
- Stafford loans are student loans provided directly to students instead of their parents by the federal government.
- The two major types of loans are subsidized Stafford loans and unsubsidized loans. In the former category, the government pays the interest on behalf of the student while they attend school. In the latter, the students have to repay the entire loan on their own.
- The interest rates are reasonably low in comparison to other forms of student loans.
- The students can also choose a repayment schedule based on their financial situation.
Perkins Loans
- Perkins loans are low-interest funds offered by the university or college’s financial aid department to graduate and undergraduate students who have expressed their need for financial assistance.
- Since the institution provides the loan, students repay the amount to their college or university directly.
- The repayment of these loans commences nine months after the student graduates from their university/college.
- If students drop out of college before the course is completed, they shall be given a half-time student status. Therefore, they shall have to start repaying the loan immediately.
Direct Loans
- Federal direct loans are provided directly by the United States Department of Education.
- Just like Stafford loans, they have subsidized and unsubsidized types with similar features.
- The department also offers direct PLUS loans to the parents of students (graduates, undergraduates, and professionals).
- It also has the option to combine some or all federal loans into one consolidated loan with a singular service provider.
