Table of Contents
What Is Token Swap?
Token Swap refers to the process of exchanging one cryptocurrency for another with the same value through platforms like centralized exchanges (CEXs) & decentralized exchanges (DEXs). It enhances liquidity and facilitates seamless trading within the cryptocurrency market.
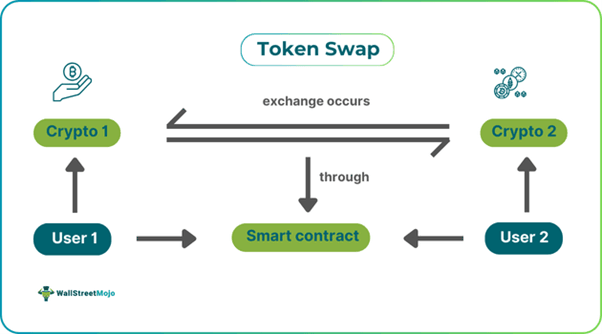
The token exchange that happens might include more than one blockchain, be it public or private, operating simultaneously for the execution. A Hashed Timelock Contract (HTLC) deployed in the blockchain manages the entire process. The exchanges are atomic transactions carried out through a token swap smart contract and at a rate agreed upon by the involved parties.
Key Takeaways
- A token swap reflects the exchange of one cryptocurrency with another without converting it to fiat currency, enhancing liquidity and facilitating seamless trading within the cryptocurrency market.
- Its types include regular, atomic, and cross-chain transactions.
- It involves selecting a reputable exchange platform, registering, verifying trading limits, submitting tokens, selecting pairs, reviewing transaction details, confirming swaps, waiting for completion, and checking the cryptocurrency wallet.
- Token swaps involve no third party to facilitate the trade but rather execute the deal based on a smart contract, making the transactional process more secure, faster, and less expensive.
- However, the lack of privacy and vulnerability makes traders consider whether to opt for it.
How Does Token Swap Work?
A token swap marks the exchange of a token of one cryptocurrency with that of another cryptocurrency having a similar price and quantity. It can occur through direct exchange between users or migration to another blockchain from the existing one. The exchange is carried out by trading cryptocurrencies seamlessly through DEX collects tokens to respective liquidity pools, allowing direct trading between users through respective token swap distribution without them having to pay for fiat conversions.
Token swap in crypto transactions and processes remain embedded in the blockchain. It allows users to capitalize on arbitrage and enhances the market's liquidity, providing users an opportunity for greater diversity in their portfolio. Such a working system is vital in decentralized finance (DeFi) where users handle their assets effectively with more independence.
These swaps entail execution through smart contracts guaranteeing security and transparency. As a result, it has been successful in giving users the power to trade in Binance exchange and even other exchanges without mediators.
Such swap transactions are revolutionizing traditional finances, enabling more efficient and faster trading mechanisms through token swap exchanges.
Types
There are three major types of token swaps, which have been discussed below:
- Regular Swaps: Such swaps occur through centralized or decentralized exchanges. No external wallet transfer happens here. The process is straightforward, as no fiat currency conversion is required.
- Cross-Chain Swaps: These swaps represent the exchange of tokens between different blockchains using a bridge connecting the two networks. HTLC facilitates this transaction and both parties must complete the process within the given time frame for successful completion of the same. These are also called atomic swaps.
- Token migration: This is the type of swapping where tokens are upgraded to a new and more advanced blockchain network. This typically occurs when a project successfully raises required funds on one blockchain and is ready to operate on another network.
Process
It consists of six steps, as shown below:
- Step 1 - Select the most reputable exchange platform supporting the desired token swaps, having adequate liquidity options and required security features.
- Step 2 - On the chosen platform, one must register or log in to one's account, completing all mandatory verifications for higher trading limits.
- Step 3 - Check if the tokens desired for swap are compatible with the platform. If yes, submit the required tokens within a wallet, ensuring the minimum balance is met.
- Step 4 - Choose the pair of tokens for the swapping while ensuring the pair has adequate liquidity.
- Step 5 - Review details of transactions like fees and confirm the swap to initiate the exchange process.
- Step 6- Once the concerned platform receives the confirmation, it releases the tokens in the users’ wallets.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic:
Example #1
An online article published on 16 September 2024 discusses the partnership of OKX wallet with 1inch to enhance the token swap experience on a DEX aggregator. OKX has begun supporting 1inch's APIs and fusion swaps in its multi-chain wallet, collecting liquidity from almost 500 DEXs.
As a result, it has given many benefits to users like enhanced efficiency by accessing optimal routes and rates throughout DeFi ecosystems, improved security by having built-in MEV safety against sandwich and front-running attacks, greater flexibility by giving access to CEX and DEX liquidity, leading to seamless trading, reduced slippages, better pricing, larger trades using a single interface and deeper liquidity.
Example #2
Let us assume a crypto trader, Aliza, of Old York City, uses a platform for swapping EasySwap, her 100 token X for token A. EasySwap holds 1,000,000 token X and 500,000 token A as it operates through a liquidity pool financed by users. Aliza starts the swap, and the platform determines the exchange rate per its liquidity pool.
The high liquidity of EasySwap allows minimal slippage experience for Aliza to receive 499,990 token A instead of the expected 50,000 with only a slight difference in value. It shows how the higher liquidity of the platform allowed her to get almost similar valued tokens smoothly, benefiting her significantly.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Let's use the table below to understand the pros and cons of token swapping for a common trader:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Gives users access to multiple cryptocurrencies in a streamlined manner, giving them opportunities to diversify portfolio. | Token swaps must be executed within specified time frame. If not used within the period, the tokens get locked. |
| They bypass intermediary steps to make swaps faster. | Additional costs might be applicable with respect to the fluctuating exchange rates. |
| No third-party risks are involved as users retain full control of their assets during swapping. | Low liquidity and high market volatility may lead to slippage issues for users. |
| The deal is executed through a token swap smart contract; hence no third-party services are involved, which one has to pay for. | If the underlying code falters, it makes the swapping of tokens vulnerable. |
| Token swaps facilitate interoperability, given the involvement of two different blockchain networks. | Lack of privacy as transactions remain publicly visible. |
| One can use their existing tokens to buy new ones, which enhances the liquidity of the crypto market. |
