Table of Contents
What Is A Trade Facilitation Agreement?
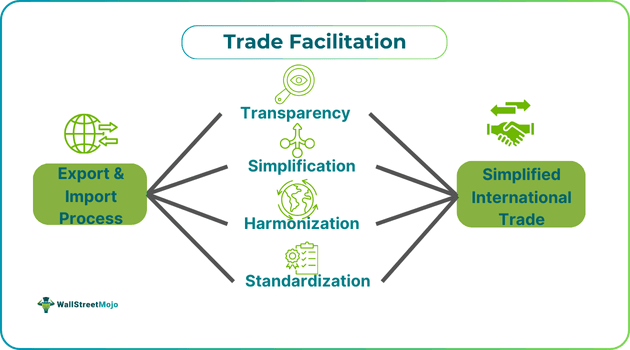
A trade facilitation agreement (TFA) refers to measures that harmonize, streamline, modernize, and simplify legal and technical procedures for importing and exporting goods at international borders. The OECD developed it, enabling economies globally to identify the challenges and strengths of border trade procedures while prioritizing actionable areas.
The TFA is a key element in reducing trade costs and serves as the foundation for the agreement reached by World Trade Organization (WTO) participants on the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement. It helps businesses in developing countries connect more easily with global markets. The TFA applies to WTO members and focuses on enhancing trade volume and economic growth worldwide.
Key Takeaways
- Trade facilitation simplifies import-export processes. Trade facilitation agreements consist of measures that harmonize, streamline, modernize, and simplify legal and technical processes for goods imports and exports at international borders.
- The OECD has worked on TFAs to help global economies identify the strengths and weaknesses of border trade policies and prioritize areas needing immediate attention.
- Its 12 indicators include information availability, trade community involvement, advance rulings, appeal procedures, border charges, formalities, automation, cooperation, consularization, governance, and impartiality.
- Its benefits include reduced costs, enhanced government controls, increased revenue, economic development, foreign investment, integration of least-developed countries, and reduced customs bottlenecks.
Trade Facilitation Explained
The Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) is a multilateral treaty established by the WTO to streamline and simplify customs procedures, enhancing the efficiency of international trade. It includes around 35 technical measures designed to speed up goods' clearance, release, and movement across borders.
TFA mandates member nations to implement measures that reduce bureaucratic delays and promote transparency in customs operations. This includes advance rulings on tariffs, fostering inter-agency collaboration, and publishing trade-related data. The TFA is expected to cut trade costs by almost 15% and improve international trade flows, with particular benefits for developing countries.
Its objectives include creating over 2 million job opportunities and generating more than $1 trillion in additional trade, thereby supporting and fostering economic development and growth. The TFA provides a systematic framework for businesses to enhance predictability in global trade. It also reduces bureaucratic hurdles and improves access to information, empowering medium and small-sized enterprises to participate more effectively in global markets.
In the field of finance, the TFA has had a positive impact by increasing trade volumes and expanding international markets. Additionally, improvements in trade efficiency can open up better investment opportunities, which stimulate economic growth and, in turn, enhance financial stability. Thus, the TFA represents a significant step toward the modernization of global trade practices, reducing trade barriers and boosting trade efficiency, ultimately contributing to stronger economic growth.
Indicators
The WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) outlines the following 12 key indicators:
- Information Availability – Ensuring access to essential trade-related data.
- Involvement of the Trade Community – Engaging trade stakeholders in policy-making processes.
- Advance Rulings – Providing pre-arrival decisions on customs and tariffs.
- Appeal Procedures – Establishing transparent processes for appealing customs decisions.
- Fees – Regulating border charges to reduce trade costs.
- Formalities – Documents – Simplifying trade documentation requirements.
- Formalities – Automation – Promoting digital automation in trade processes to support digital and sustainable trade facilitation.
- Formalities – Procedures – Standardizing customs procedures for consistency.
- Cooperation – Internal – Enhancing collaboration among domestic agencies.
- Cooperation – External – Strengthening cooperation with foreign customs agencies.
- Consularization – Addressing consular requirements related to trade documentation.
- Governance and Impartiality – Ensuring open and fair governance in customs operations.
Examples
Let us understand the topic using a few examples from real life and imaginary ones.
Example #1
In the year 2023, the United States President's Export Council emphasized the importance of establishing a free trade agreement (FTA) with the United Kingdom, particularly as the U.S. approached an election year. This agreement aimed to enhance U.S.-UK trade relations following the U.K.'s exit from the E.U., with a strong focus on trade facilitation, which encompasses measures to streamline and simplify trade processes. By aligning standards and regulations, a US-UK FTA was expected to significantly boost American exports, especially in the digital economy, while fostering innovation in advanced manufacturing and agriculture sectors.
Trade facilitation was important for smoothing negotiations, given the two nations' shared labor and environmental standards. With the U.K. eager to strengthen its economic ties, U.S. negotiators had an opportunity to leverage this enthusiasm to address important issues, including climate goals.
Example #2
In a bustling trading hub called ABC City, Ecologic, a sustainable products manufacturer led by CEO Greener, partners with logistics company Easy Logistics to streamline its global shipments. In September 2024, Ecologic exported organic toothpaste to ABC City's eco-conscious market.
By using advanced trade facilitation techniques like real-time tracking and digital customs clearance, they reduce shipping time from seven days to just five. As a result, Ecologic boosts its market share by 25%, while Easy Logistics enhances its reputation for efficiency. This collaboration highlights how effective trade facilitation can benefit businesses and strengthen global trade partnerships, all while adhering to the Trade Facilitation and Trade Enforcement Act (TFTEA) of 2015, which promotes a competitive and fair trading environment.
Benefits
As per the World Customs Organization (WCO), the following are its benefits:
- Simplifying import and export processes reduces costs and delays, boosting businesses' competitiveness in international and local markets.
- Governments gain enhanced control through modernized trade procedures, improving revenue collection.
- Improved facilitation and controls increase government revenues, particularly in developing nations.
- Additional revenue supports economic and social development by funding national welfare programs.
- Streamlined import and export processes promote foreign investment, enhancing economic growth.
- Trade simplification helps integrate least-developed countries into the international trading system and global economy.
- Simplifying processes removes procedural bottlenecks in customs, reduces transaction costs, and increases trade efficiency.
