The differences between the two are as follows:
Table of Contents
What Is A Trust Protector?
A trust protector is an entity that is given special authorization in relation to a trust. The powers they possess go beyond those of a trustee. They are appointed to carry out specific tasks that are not delegated to the creator, trustee, or beneficiaries.
As the name suggests, they protect the trusts assigned to them. Their powers range from supervision, direction, modification, removal of the trustee, and even termination of the trust. Protectors watch over the trustee and remove them for misconduct or any other such reasons. They essentially ensure the proper operation of the trust as per specifics and the integrity of the operations.
Key Takeaways
- Trust protectors are individuals or entities who are entrusted with the duty of overseeing a trust.
- They protect the trust of the beneficiaries. They primarily work to protect the interest of the settlor or the creator.
- They protect the trust of the beneficiaries. They primarily work to protect the interest of the settlor or the creator.
- They can also make investment decisions if the trustee is incapable of steering the trust in accordance with the agreement.
- They can also make investment decisions if the trustee is incapable of steering the trust in accordance with the agreement.
Trust Protector Explained
Trust protectors are individuals or entities who are third parties entrusted with protecting a trust. They protect the interests of the trust beneficiaries. Protectors play a critical role in administering the trust by following instructions and providing guidance to the trustees. They aim to ensure the trust operates in the specified way and maintains its integrity. They also work to prevent mismanagement and conflicts among trustees.
A trust is a legal arrangement in which a third party is allowed to manage assets for a beneficiary. There are three parties involved in a trust: the settlor or creator of the trust, the trustee who manages the trust assets, and the beneficiaries who receive the benefits of the trust.
Independent protectors are third parties not related to settlers, trustees or beneficiaries. They are appointed to provide unbiased approaches. Those appointed by settlers are often people whom they trust. The ones appointed by beneficiaries are persons who have the best interests of beneficiaries in mind.
The responsibilities of independent protectors include overseeing trust administration and intervening when necessary. They safeguard beneficiary interests through document review, monitoring actions of the trustee, etc. Furthermore, they are entrusted with fiduciary duties sometimes where they are legally liable to act in the interest of the beneficiaries in good faith. Protectors make important decisions such as the appointment of trustees, their removal, amendment of the trust agreement, and distribution approvals. In addition, they regularly review the administration, investments, and documents to determine whether they are compliant with the agreement and the laws.
Role
Below are some of the roles and responsibilities of a protector.
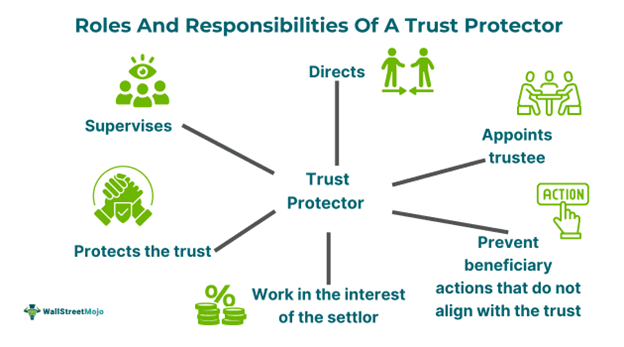
- Supervisor and director: They supervise the trust operations in accordance with the trust agreement. It is a legal document that allows the trust formation, management under a trustee and transfer to a beneficiary. Protectors direct the related actions and ensure that the activities and intentions of the settlers align.
- Authorized personnel to modify trust terms: Protectors can modify and amend the trust agreement or instrument to achieve advantages. These include obtaining favorable tax status, adapting to changes in law, and responding to changing circumstances.
- Appointer: The protector can appoint trustees to protect the trust assets and remove those who fail to perform. One of the trust protector's duties is to ensure competency in the management of the trusts.
- Prevent beneficiary actions: Protectors can prevent beneficiaries from overstepping their boundaries and assume the role of a trustee. This helps in maintaining the integrity of the trust operations.
- Terminator: Protectors may terminate the trust if they believe its operations are not in the best interest of the beneficiaries. Before doing so, they must consider various legal, political, and economic factors.
Examples
Let us look at a few examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Imagine Dan's family, which has a large family trust and various investments. As the family grew and members began moving out, managing the trust became increasingly difficult. To address this, Dan decided to appoint a trust protector to handle the responsibilities. He is aware of the trust protector powers and how they can remove trustees, look into investments, and direct trustees. He is also aware of the substantial trust protector compensation they have to pay. Dan feels that it is best to leave with a protector for easy and stress-free management and proceed with the idea.
Example #2
A study by Philip J. Ruce looks into the trust protector and trustee and whether they shall be given fiduciary powers. The paper discusses the history and development of the concept of a protector. It analyzes various publications, commentaries and trends in law and policy issues, including international cases. It concludes that protectors do not have immunity from legal obligations and that they are fiduciaries. This is because they take care of the trust.
How To Remove?
The removal process may be outlined in the agreement and relevant to the laws. It may involve a vote from the beneficiaries' trustee opinions. There are many reasons why they can be removed. The primary reason is a failure to fulfill duties as in the agreement.
Here are some of the steps involved in the removal of a trust protector
- State the reasons for removal.
- Gather the necessary paperwork to substantiate the reasons.
- Meet with a lawyer.
- Get witnesses who are not beneficiaries.
Advantages
Given below are some of the advantages of appointing a protector to the trust.
- They bring in accountability and ensure proper management of assets by trustees. In addition, they oversee proper function in accordance with the settlor's interests.
- They make the trust arrangement flexible by modifying it according to the rules and requirements.
- Conflict reduction is one of the major advantages. Since they oversee the trust's function, they can reduce disagreements between trustees and beneficiaries.
- They provide a sense of security for the settlor that the management and transfer of trust are in safe hands.
Trust Protector Vs. Trustee
| Aspect | Trust Protector | Trustee |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | A person who has the power to supervise, oversee, appoint, and remove a trustee. | A trustee is an institution or an individual who is entrusted with the role of managing the trust assets. |
| 2. Primary function | They oversee the trust operations. | Trustees are majorly concerned with the management of assets under the trusts and follow trust protector orders in distributing the trust assets to the beneficiaries. They also make investment decisions. |
| 3. Power and liability | They have greater authority and potentially higher liability. | The trustees have lesser power and liability in comparison. |
