Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Val Function
The Val function in VBA is a built-in string function used to extract numeric values from a string. It reads the string from left to right and returns the number it finds until it encounters a non-numeric character. This is helpful when working with mixed data that includes both letters and numbers, and you need to isolate the numeric part.
For example, if a variable contains the value "A10", the Val function will return 0 because it starts with a letter. But if the string is "10A", it will return 10. Here’s a simple example:
Dim result As Double
result = Val("10A")
MsgBox result ' It will show 10
VAL stands for VALUE in VBA terminology. This function converts the string containing numbers to an actual number.
For example, if you supply the text string "1234 Global," it will return only the numerical part, i.e., 1234.
When we download or get the data from web numbers, usually, they are stored as text values in a spreadsheet. However, conversion of text to numbers is the hardest task if you are unaware of the correct function in Excel.
As a regular worksheet function, we have a function called VALUE, which will convert all the strings representing numbers to exact numbers with a simple function in the worksheet. This article will show how VBA can achieve this using the VAL function.
Key Takeaways
- The VBA VAL function extracts numeric values from the beginning of a string and stops reading at the first non-numeric character. This includes spaces or letters.
- It is useful for converting strings with mixed types into numbers for calculations.
- It ignores any text after the numeric portion and does not generate errors if the string contains non-numeric characters.
- If the string starts with a non-numeric character, the VBA Val returns 0.
- The result is always returned as a numeric value.
Syntax
The VBA Val function has only one argument: String.

- String: It is simply a string value. We are trying to get the numerical part out of it.
So, the VAL function converts the supplied string to a numerical value.
Note: The VAL function always ignores the space characters and continues to read the numbers after the space character or characters.
For example, if the supplied string is "145 45 666 3," it will ignore the space characters and return the result as "145456663."
Examples Of VAL Function In Excel VBA
Example #1
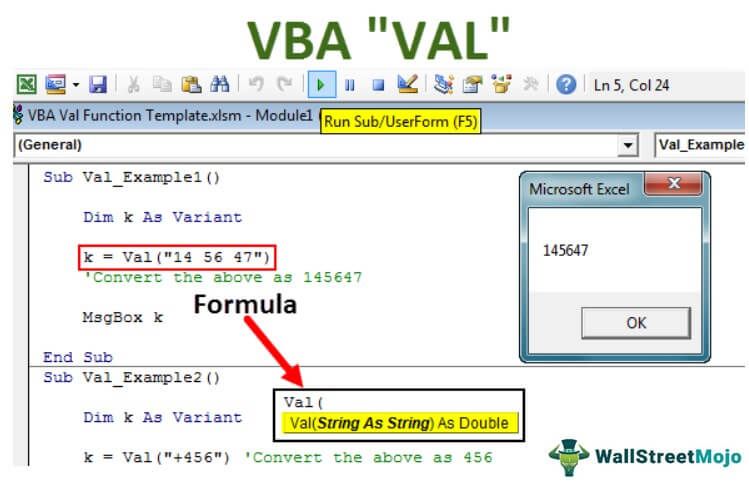
Let us try the first example with a simple number, "14 56 47."
The below code is for you.
Code:
Sub Val_Example1()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("14 56 47")
'Convert the above as 145647
MsgBox k
End Sub
In the above code, we declare a variable k of type VariantThis type can hold any type of data such as numbers, strings, etc.
The code uses the Val function to try converting the string "14 56 47" into a number.

When you run VBA code using the F5 key or manually, it will return the result as "145647" ignoring all the space characters, as shown below.

Example #2
In this example, we will see that the result of the string is "+456."
Code:
Sub Val_Example2()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("+456")
'Convert the above as 456
MsgBox k
End Sub
- We declare a variable k with the data type Variant, which allows it to store different types of data.
- k = Val("+456")
- The Val function can recognize the plus sign at the beginning and will convert the entire string to the number 456.
- We then display the value stored in variable k in a message box. In this case, it will show 456.

You can run this code manually or through the F5 key to return the value as 456 by ignoring +456.

Example #3
Now, let's try the same number with a negative sign.
Code:
Sub Val_Example3()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("-456")
'Convert the above as -456
MsgBox k
End Sub
We declare a variable k as a Variant, allowing it to hold any type of value, including numeric or text.
We use the Val function to convert the string "-456" into a numeric value. The function reads the minus sign and the digits correctly, returning the number -456.
This displays the value stored in k in a message box. The user will see -456.

This code will only return the value as -456 because it should show the number with the operator sign.

Example #4
Now, let's try this string "100 Kg."
Code:
Sub Val_Example4()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("100 KG")
'Ignores KG and returns only 100
MsgBox k
End Sub

The macro demonstrates how the Val function extracts only the numeric part from a string.
In this case, Val("100 KG") returns 100 because it reads digits from the start and stops when it reaches the space before "KG", which is non-numeric.
The result, 100, is then displayed in a message box.

If you run this code manually or using the F5 key, the above code ignores "KG" and returns only "100" in the VBA message box
Example #5
Now, try the date string, "14-05-2018."
Code:
Sub Val_Example5()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("14-05-2019")
'Returns 14 as the result.
MsgBox k
End Sub

The Val_Example5 macro uses the Val function to extract a number from the string "14-05-2019". The function reads from left to right and stops at the first non-numeric character. As a result, only 14 is returned and displayed in the message box.

Example #6
Now, try the string "7459Good456."
Code:
Sub Val_Example6()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("7459 Good 456")
'Returns 7459 as the result.
MsgBox k
End Sub

The Val_Example6 macro demonstrates how the Val function processes a string that begins with numbers followed by text. In the line Val("7459 Good 456"), the function reads the numeric part 7459 and stops when it reaches the space before the word "Good", which is non-numeric.

Example #7
Now, try the string value "H 12456."
Code:
Sub Val_Example7()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("H 12456")
'Returns 0 as the result.
MsgBox k
End Sub

Run the above code using shortcut key F5 or manually, then it returns the result as zero. Because the first character of the string we supplied is non-numerical, the result is zero.

Example #8
Now try this string “24545 . 2”.
Code:
Sub Val_Example8()
Dim k As Variant
k = Val("24545 . 2")
'Returns 24545.2 as the result.
MsgBox k
End Sub

The code returns the result as 24545.2 because the VBA VAL function considers the character dot (.) as the decimal character and returns the result accordingly.

TO learn VBA quickly and become an expert, we recommend you check out the Excel VBA Crash Course for Absolute Beginners.

