Table of Contents
What Is Vendor Management?
Vendor management is the procedure of overseeing relationships and interactions with third-party vendors or suppliers. It includes tasks such as selecting vendors, negotiating contracts, monitoring performance, and ensuring compliance with agreed-upon terms and standards. Effective vendor management aims to optimize vendor relationships, mitigate risks, and maximize value for the organization.
Vendor management tools help with improved efficiency, cost savings through vendor consolidation, and access to specialized expertise. However, it requires significant time and resources for effective implementation and ongoing monitoring. Additionally, reliance on external vendors can introduce risks such as quality issues, delays, and dependency on third-party performance. Effective vendor management balances these factors to optimize vendor relationships.
Key Takeaways
- Vendor management is the procedure of overseeing relationships with external vendors or suppliers. It involves tasks such as vendor selection, contract negotiation, performance monitoring, and risk assessment.
- Effective management in this regard ensures compliance, quality, and value from vendor partnerships. It encourages collaboration, mitigates risks, and optimizes the contribution of vendors to organizational success.
- Vendor management is vital for upholding operational efficiency, cost savings, and quality assurance within the supply chain.
- This process not only ensures communication and collaboration with suppliers but also makes sure that customers are never dissatisfied due to the unavailability of products.
Vendor management Explained
Vendor management is the process followed by companies to manage their suppliers, also known as vendors. It includes various activities aimed at selecting, evaluating, and managing vendors to ensure they meet the organization's needs and objectives. Initially, vendor management involves identifying potential vendors that give products and/or services that are in line with the organization's requirements. Once vendors are selected, the next step is negotiating contracts that define the terms of the relationship, including pricing, deliverables, and performance metrics.
After contracts are finalized, ongoing vendor management systems involve monitoring vendor performance to ensure compliance with agreed-upon terms and standards. This includes assessing vendor reliability, quality of products or services, and adherence to deadlines. Regular evaluation of performances can help find areas for constant improvement and maintain accountability. Additionally, effective vendor management involves boosting open communication between the organization and its vendors, facilitating problem-solving, and addressing issues promptly.
One of the key benefits of the process is improved efficiency and effectiveness in sourcing and procurement processes. By leveraging relationships with suppliers, organizations can access specialized expertise, reduce costs through vendor consolidation, and streamline operations. However, effective vendor management requires careful planning, resource allocation, and continuous oversight. It also involves paving through potential risks associated with vendor reliance, such as quality issues, supply chain disruptions, and data security concerns.
Therefore, this process plays a vital role in optimizing vendor relationships, mitigating risks, and maximizing value for the organization. By implementing fool-proof systems, organizations can ensure they maintain strong partnerships with vendors, achieve strategic objectives, and drive operational excellence.
Process
This process involves various steps that play multiple vital roles. In the modern day, vendor management software helps companies sort this process and keep a more vigilant eye on its intricacies. The explanation below explores the process in detail.
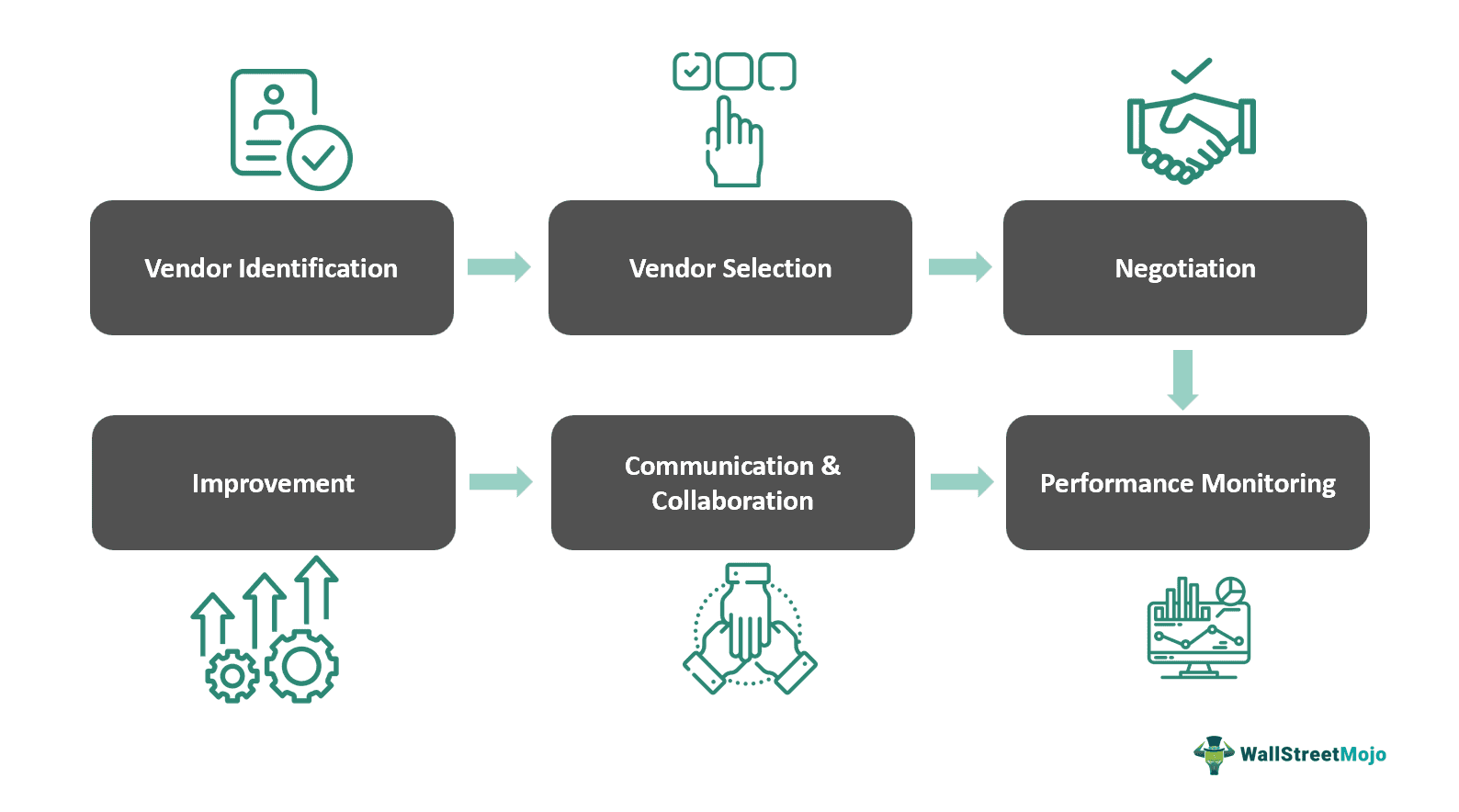
- Vendor Identification: The process begins with identifying potential suppliers who can offer products and/or services that are in accordance with the organization's needs and objectives.
- Vendor Selection: After identifying potential vendors, the organization evaluates their capabilities, reputation, and pricing to select the most suitable vendors.
- Contract Negotiation: Once they are selected, contracts are negotiated to define the terms of the relationship, including pricing, deliverables, and performance metrics.
- Performance Monitoring: Ongoing oversight of the process involves monitoring the performances of suppliers to ensure compliance with agreed-upon terms and standards, including reliability, quality, and adherence to deadlines.
- Communication and Collaboration: Effective management in this regard requires encouraging open communication and collaboration between the organization and its suppliers to facilitate problem-solving and address issues promptly.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular performance evaluations help identify areas for improvement and maintain accountability. It enables organizations to optimize vendor relationships and drive operational excellence.
Types
There are different types of vendor management systems. The most common ones are as mentioned below.
- Strategic Vendor Management: It focuses on establishing long-term partnerships with key vendors in line with the organization's strategic objectives. It involves in-depth collaboration, joint planning, and mutual goal-setting to drive innovation and value creation.
- Tactical Vendor Management: This type of supplier oversight is concerned with day-to-day interactions and operational aspects of vendor relationships. It includes tasks such as procurement, contract negotiation, and performance monitoring to ensure vendors meet operational needs efficiently.
- Relationship-based Vendor Management: A relationship-based process emphasizes building solid and collaborative relationships with vendors based on trust, transparency, and communication. It prioritizes boosting mutual understanding, resolving conflicts, and promoting vendor loyalty.
- Risk-based Vendor Management: Risk-based vendor management centers on identifying, gauging, and alleviating risks associated with supplier relationships. It involves evaluating vendor reliability, financial stability, and compliance with regulatory requirements to minimize potential disruptions and liabilities.
- Performance-based Vendor Management: This type focuses on evaluating vendor performance against predefined metrics and benchmarks. It includes regular performance reviews, feedback mechanisms, and continuous improvement initiatives to enhance vendor performance and optimize value delivery.
Examples
The understanding of a concept is always easier with a tinge of practicality and real-life application angle. The examples below are an account of just that.
Example #1
Hallmart is a supermarket chain that operates in over 15 cities across U.S. and Mexico. To ensure that their stores are always filled with all types of inventory and customers are satisfied on the front, they introduced a central vendor management software.
Once the management finalizes suppliers for different products, the software tracks their performance on the basis of on-time deliveries, quality of the product, and competitive pricing.
Throughout the process, Hallmart ensures constant communication with suppliers regarding upcoming requirements, feedback on packaging, and payment schedules. The software not only helps them understand their suppliers and their products but also keeps their customers happy.
Example #2
PayShepherd, a vendor relationship management platform tailored for heavy industry firms, has secured $7 million in seed funding. The platform streamlines contractor management, replacing the standard of labor-intensive paper processes in the industry.
Through automation, PayShepherd centralizes, digitizes, and verifies all submissions related to labor, equipment, and materials. It offers comprehensive features such as contract compliance, real-time visibility into costs, predictive budget monitoring, and tools for enhancing vendor relationships. With this system, industrial operators gain complete control over spending and ensure compliance while boosting improved collaboration with vendors.
Best Practices
In a business world where things are constantly changing and growing, a few practices set the best apart from the rest. A few such practices are explained below.
- Thoroughly evaluate supplier capabilities, reputation, and pricing to select suppliers that align with organizational needs and objectives.
- Negotiate detailed contracts that clearly define roles, responsibilities, deliverables, timelines, and performance metrics to mitigate misunderstandings and disputes.
- Maintain open and transparent communication with vendors to encourage collaboration, address issues promptly, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Regularly monitor vendor performance against agreed-upon metrics to identify areas for improvement and maintain accountability.
- Cultivate solid and trust-based relationships with suppliers through regular interactions, feedback mechanisms, and conflict resolution strategies.
- Identify, gauge, and eliminate risks associated with supplier relationships to minimize potential disruptions and liabilities.
- Implement feedback loops and continuous improvement initiatives to optimize supplier performance, drive innovation, and maximize value for the organization.
Benefits
The benefits of vendor management tools are as mentioned below.
- Effective oversight can lead to cost savings through vendor consolidation, negotiation of favorable pricing terms, and efficient procurement processes.
- By monitoring supplier performance and ensuring adherence to agreed-upon standards, vendor management helps maintain product or service quality and consistency.
- The management in this regard allows organizations to find and negate risks associated with supplier relationships, such as supply chain disruptions, quality issues, and compliance breaches.
- Establishing strong partnerships with suppliers can provide access to specialized expertise, innovative solutions, and market insights, enhancing the organization's competitiveness and ability to meet evolving business needs.
- Streamlining supplier management processes and boosting collaboration with vendors can improve operational efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and enable better resource allocation within the organization.
Risks
- While we have discussed the advantages of vendor management systems, there is another side of the coin, too. The risks of the concept are discussed below.
- Over-reliance on external suppliers can create dependency, making organizations vulnerable to disruptions if they fail to deliver as expected or face financial instability.
- Lack of adequate oversight and monitoring can lead to quality control issues. It refers to issues such as substandard products or services, which can damage the organization's reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Outsourcing certain functions to vendors may pose data security risks, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations, particularly if vendors have access to sensitive information.
- Failure to ensure compliance from suppliers with laws and regulations standards in the industry can result in legal liabilities, fines, and reputational damage to the organization.
- Factors external to the company, such as natural disasters, geopolitical events, or economic downturns, downturns can disrupt operations on the supplier's side, affecting the organization's supply chain and business continuity.
Vendor Management vs Procurement
Both vendor management systems and procurement are functions of the same broader process. However, there are distinctions in their fundamentals and intricacies. The comparison below shows us their differences in detail.
Vendor Management
- It focuses on maintaining and optimizing relationships with existing vendors or suppliers.
- The process involves tasks such as evaluating vendor performance, negotiating contracts, and monitoring vendor compliance.
- It aims to encourage collaboration, ensure quality, and maximize value from vendor relationships.
- The impetus is placed on long-term partnership building and continuous improvement of supplier performance.
Procurement
- Procurement is the exercise of sourcing, buying, and acquiring goods or services needed by an organization.
- It includes activities such as identifying procurement needs, soliciting bids or proposals from vendors, and selecting suppliers.
- It focuses on obtaining the best value for money, typically through cost-effective purchasing practices.
- This process is primarily concerned with transactional activities related to acquiring goods or services rather than ongoing relationship management.
