Table of Contents
What Is A High Risk Customer?
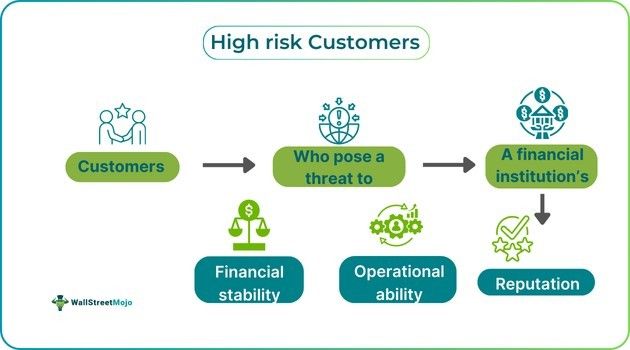
High-risk customers are businesses or individuals who possess the potential to cause financial, operational, reputational or legal harm to a company. They are seen as a threat and categorized based on their financial status, poor security, regulatory status, industry or business practices.
Identifying customers who are in the high-risk category helps prevent financial crimes. It also helps organizations comply with rules, manage risks, protect their reputations, and maintain operational integrity. These customers are more likely to be linked to money laundering and financial crimes, and prevention of association is considered a wise choice.
Key Takeaways
- High-risk customers are those categorized as high-risk due to the nature of financial transactions. They may be triggers to financial instability and operational difficulties.
- This is because they could be potential catalysts for financial crimes, including money laundering and terrorism financing.
- Potentially exposed persons, credit card theft, money laundering individuals, multiple account customers, high risk country customers, complex ownership customers, and risky profiles are some of the high risk categorized customers.
- Enhanced due diligence for high risk customers by following KYC procedures, inconsistent information, and not being transparent with the details provided.
High Risk Customer Explained
High-risk customers refer to financial institution customers who have the potential to commit fraud and deceit. They can commit large crimes such as money laundering, terrorism financing and other financial crimes. They are identified based on varied factors such as geographical location, personal and business accusations, occupation and financial activities.
These customers are to be monitored regularly. It ensures that the institutions comply with the national and global rules and regulations of money laundering. It helps institutions prevent financial blunders and lead to their financial instability. Monitoring these customers prevents operational standbys and rectification time. This also avoids reputational damage. Genuine customers may see this as a deterrence to their trust and discourage others from investing their funds in it. Additionally they may also withdraw existing funds from such institutions.
Identification and management of customers posing high risk is critical for establishing a secure and profitable business. These customers can pose various challenges, such as financial instability, resource exhaustion, compliance issues, legal challenges, reputational damage etc. They impact a company's operation, finances and reputation that may sometimes be irreversible. They are especially risky in a setting where there are transactions that are often large and complex such as a B2B setting.
Types
Given below are some of the types of customers categorized as high-risk
- Politically exposed persons: They are individuals who are or were in a public position and exploit their power to gain financial favors. These individuals may be political party leaders, senior government officials, people in high judicial ranks, military officers of high ranking, etc. They may involve themselves in corruption and money laundering as they have access to funds with their influence and status.
- Credit card theft: Individuals use fraudulent credit card information or steal it from legitimate consumers. Companies that do not have capable fraud protections may suffer financial loss from such transactions. The associated chargeback fee and transaction costs also add to the company's financial burden. It can also result in a loss of trust among legitimate customers.
- Money laundering individuals: These individuals (sometimes entities) are engaged in financial transactions to hide the source of funds. These funds are often accumulated from illegal activities. These people conduct transactions that typically don't align with their business profile and display unusual patterns. It can include overpayments, frequent large transactions to high-risk countries.
- Multiple account customers: These are individuals and entities involved in using multiple accounts to commit fraud. They are often observed in cases where discounts, incentives and special circumstances are given to new customers. They exploit these incentives and cause financial loss. They use multiple emails, phone numbers, etc., to create multiple accounts and avail themselves of them multiple times.
- High risk country customers: They are entities or individuals from countries that are ranked as high-risk. These countries have a history of fraud, money laundering and other financial crimes. They are risky in cases where there is limited financial transparency, a lack of regulatory oversight and complex business structures. Engagement in high-risk industries can also be a red flag.
- Complex ownership structure customers: These are entities or individuals who use complex ownership arrangements to conceal the true owners or beneficiaries of assets. They fulfill these arrangements through trusts, offshore entities and holding companies. They lack transparency, use multiple entities and prefer offshore jurisdictions.
- Risky profiles: There may be customers who do not have a clean background and have a doubtful reputation. They are entities and individuals who have been involved in controversies(financial), legal issues and involvement in criminal activities.
How To Identify?
Given below are some of the pointers that help in the identification of risky customers
- Politically exposed persons can be identified by using specialized databases, conducting due diligence, and regularly updating customer information. Monitoring transaction patterns and consulting public information and media records can also help.
- Fraudulent credit card transactions can be identified by inconsistent shipping and billing information and successive high-value transactions. They can also be revealed by transactions of large purchases by first-time customers, their unusual communication patterns, and the implementation of fraud detection tools.
- The false information provided by money laundering customers can help identify them. Their market value will be inconsistent, and intermediaries who are often not needed will be used. Funds will also be rapidly moving, and careful monitoring of such activities can help identify them.
- Cross-checking information provided by customers can identify multi-accounting customers. Analyzing IP addresses and fingerprints, observing abnormal promotions use, and pattern recognition also help.
- Customers from high risk countries can be identified through geographic risk assessments, use of such data, checking the sanction lists etc. Similarly, periodic risk assessments and placing a risk-based approach with due diligence are always recommended.
- Beneficial ownership verification can be used to identify individuals with complex ownership status. Scrutiny of offshore entities, review of legal documentation, use of specialized tools and continuous monitoring will also help.
- Background checks can help understand the risky profiles of individuals and entities. Reference to media articles and industry-specific information can also be used to identify them.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1 - A Hypothetical Example
Dan is a businessman who has dealings overseas, and some of them are in high risk countries. Dan had approached a local bank to open a new business account, and the bank's onboarding team categorized him as a high risk customer in the bank. Dan had to furnish all his and office addresses and the other bank accounts he owns to comply with the bank's KYC requirements. They also wanted details of the business activities he carries in all the locations and the source of his funds.
They scrutinized several transactions as he was a high-risk customer in the bank. Luckily for Dan, he could provide legitimate sources. If not, he would have been reported to the Anti-money laundering authorities.
Example #2 - Real-Life Example
The European anti-money laundering (AML) reforms were adopted in May 2024. This marks a milestone in the EU's attempt to detect and prevent financial crimes. Several reforms were introduced.
Due diligence measures for customers who want a golden passport were introduced. They are also extended to net-worth individual customers who provide wealth management services (EUR5 million or more). Similarly, the regulation requires identity records to be updated every five years, at least for high-risk customers.
It recommends that firms conduct risk assessments and identify money laundering and financing risks. These assessments should include assessments of activities, products, delivery channels, transactions, geography and customers. Revision of risk assessment methodologies is also recommended.
Importance Of Identifying High Risk Customers
Below are some of the points that highlight the importance of identifying high risk customers:
- Identifying high-risk customers is a regulatory requirement, and financial institutions must comply. Banks must especially note high-risk customers.
- It helps prevent and detect fraud, money laundering and terrorist financing.
- It is effective in preventing reputational damage.
- Enhanced due diligence for high risk customers can be enabled through periodic monitoring.
- It strengthens internal controls and aids in proactive risk management.
- It helps in avoiding regulatory penalties.
