Table Of Contents
What Is Trading on Equity?
Trading on equity refers to the corporate action in which a company raises more debt to boost the return on investment for the equity shareholders. This process of financial leverage is considered a success if the company can earn a greater ROI. On the other hand, if the company cannot generate a rate of return higher than the cost of debt, then the equity shareholders end up earning much lower returns.
Key Takeaways
- Trading on equity means the corporate action in which a company raises more debt to enhance the return on investment for the equity shareholders.
- The types of trading on equity are trading on thin equity and thick equity.
- The advantage of equity trading is that a company may earn higher revenue by purchasing assets using borrowed money. Also, it lowers the borrower's tax burden as the interest paid on debt is tax-deductible.
- The disadvantages of a trading name are that their unstable income or volatile profits may adversely affect the shareholder's return. In addition, it sometimes results in the borrowing entity's overcapitalization.
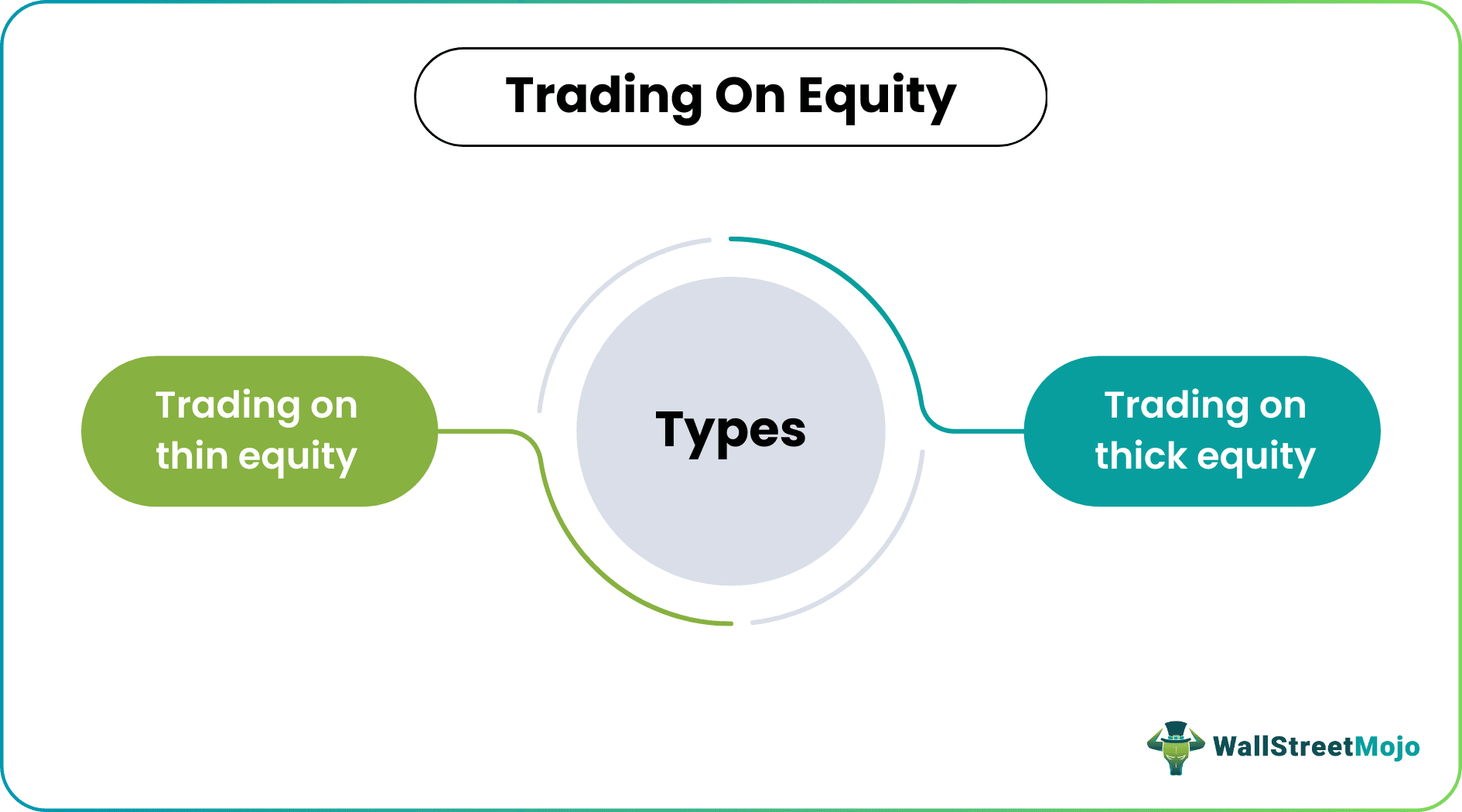
Types Of Trading on Equity
Based on the size of debt funding relative to available equity, it is classified into two types: -
- Trading on Thin Equity: If the equity capital of a company is lesser than the debt capital, it is known as trading on thin equity. In other words, the share of debt (such as bank loans, debentures, bonds, etc.) is higher than equity in the overall capital structure. Trading on thin equity is also known as small or low equity trading.
- Trading on Thick Equity: If the equity capital of a company is more than the debt capital, then it is known as trading on thick equity. In other words, the equity share is higher than that of debt in the overall capital structure. Trading on thick equity is also known as trading on high equity.
Examples
Let us understand with examples.
Example #1
Let us take the example of ABC Inc. to illustrate the impact of trading on thick equity on shareholder return. Let us assume that the company infused $2,000,000 of equity capital and raised $500,000 of bank debt to acquire a new factory. Determine the rate of return for the shareholders assuming the cost of debt to be 5% and that there is no income tax if the factory is expected to generate an annual profit of: -
- $250,000
- $50,000

Therefore, one can calculate the rate of return for shareholders as,
Rate of Return for Shareholders = (Profit – Debt * Cost of Debt) / Equity

- = ($250,000 - $500,000 * 5%) / $2,000,000
- = 11.25%
Therefore, the shareholders earn a rate of return of 11.25%.

Therefore, one can calculate the rate of return for shareholders as,
Rate of Return for Shareholders = (Profit – Debt * Cost of Debt) / Equity

- = ($50,000 - $500,000 * 5%) / $2,000,000
- = 1.25%
Therefore, the shareholders earn a rate of return of 1.25%.
Example #2
Let us take the above example again and illustrate the impact of trading on thin equity on shareholder return. Let us assume that the company raised $2,000,000 of debt and infused only $500,000 of equity to acquire the factory. Determine the rate of return for the shareholders taking the cost of debt to be 5% and that there is no income tax if the factory is expected to generate an annual profit of: -
- $250,000
- $50,000

Therefore, one can calculate the rate of return for shareholders as,
Rate of Return for Shareholders = (Profit – Debt * Cost of debt) / Equity

- = ($250,000 - $2,000,000 * 5%) / $500,000
- = 30.00%
Therefore, the shareholders earn a rate of return of 30.00%.

Therefore, one can calculate the rate of return for shareholders as,
Rate of Return for Shareholders = (Profit – Debt * Cost of Debt) / Equity

- = ($50,000 - $2,000,000 * 5%) / $500,000
- = -10.00%
Therefore, the shareholders incurred a loss of -10.00%.
Effects
The examples illustrated in the previous section show that equity trading is like a lever that magnifies the impact of variations in earnings. As a result, the effect of fluctuation in earnings is stretched on the rate of return earned by the shareholders. Further, the variation in the rate of return is higher in the case of trading on thin equity than in trading on thick equity.
Disadvantages
- Unstable income or volatile profits can impact the shareholders’ return adversely.
- At times, it results in the overcapitalization of the borrowing entity.
For professional-grade stock and crypto charts, we recommend TradingView – one of the most trusted platforms among traders.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.