Table Of Contents
What Is Competency Mapping?
Competency mapping identifies an employee’s key competencies, skills, and traits. Employees' performance is measured using set parameters. The analysis compares individual strengths, weaknesses, leadership qualities, innovation, emotional intelligence, decision-making skills, and interpersonal communication.
These analyses are expensive; it is a lengthy and tedious process. Mapping increases a firm’s productive efficiency and reduces turnaround time. Also, these analyses are further classified into four subtypes—motivational, social, emotional, and intellectual competencies. This analysis is also used for developing a structured recruitment process.
Key Takeaways
- Competency mapping ascertains employee strengths, weaknesses, skills, morals, attitude, aptitude, and morale based on set parameters.
- Primarily, the parameters are categorized into KSA—knowledge, skills, and attitude.
- Many firms build a competency analysis framework to regulate recruitment. In such firms, the HR department relies on automated analysis—to gauge talent and skill gaps.
- Change is often challenging for employees. Thus, communication and smooth transitions are key.
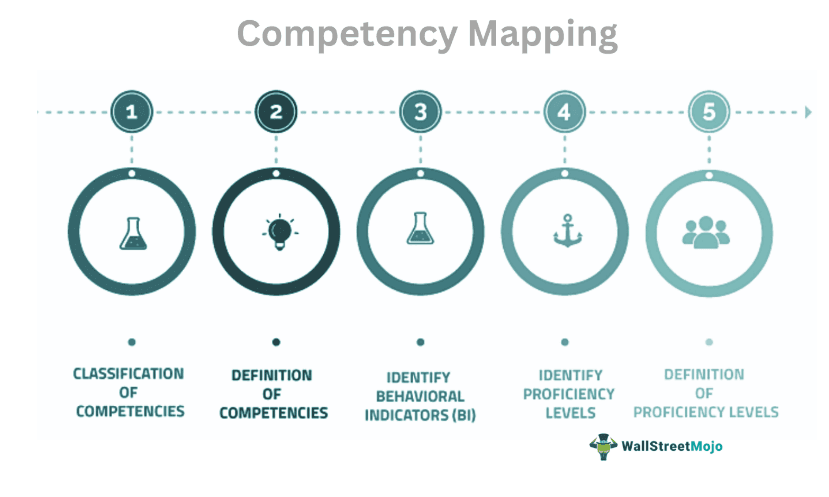
Competency Mapping Process
Competency mapping refers to a set of skills and traits possessed by an employee. It is a complex strategy that outlines how the employee can perform a particular skill in a minimum amount of time. When individual employee efficiency rises, it also reduces the firm’s turnaround time.
Further, based on competency analyses, firms transfer, promote and delegate new roles to improve the employee’s performance and efficiency. The competency of a particular employee is determined based on the individual’s strengths, weaknesses, skills, values, attitude, aptitude, and morale. This approach is also seen in recruitment. The human resources department also maps the competency of candidates. HR managers judge employees and potential candidates in the recruitment process.
Steps
Competency mapping steps and processes are as follows:
- A job analysis is conducted; every employee receives a questionnaire. The questionnaire collects data about individual skills, responsibilities, mindset, and attitude.
- Similarly, interviews are conducted to gauge employees’ responses.
- The human resources department uses collected data, t to create competency-based job descriptions.
- If there is a change in roles, the employee and the firm sign a new agreement—upon mutual consent.
- Some companies share the results of competency analysis with the employees. Feedback helps employees understand where they stand among their peers.
- A detailed competency analysis report is prepared. The report also highlights areas where an employee can improve. The report also suggests strategies and training for the growth of the employee.
- Finally, the top-level management decides which strategy to implement ad how.
Types
Let us look at competency mapping types.
#1 - Intellectual Competency
Some employees possess analytical skills and critical thinking naturally. This helps in problem-solving, but the role must have scope for the employee to act on those skills.
Others might possess communication skills or language abilities. Some excel at organizing, planning, and leadership. Employee abilities vary between different industries and sectors.
#2 - Motivational Competency
Some individuals respond better to external reinforcement or motivation. Some people are, naturally, more ambitious. But it is important to note that ambitious employees get frustrated if they feel their career is stagnant. On the other hand, the same ambitious section of the workforce is willing to put in the extra effort.
Analysts determine motivation based on the completion of deadlines, goal-oriented progress, and time management.
#3 - Social Competency
In most firms, employees are required to interact with each other. Thus, communication is very important. Analyst gauge social competency based on teamwork, team building, professional relationships, and networking abilities.
#4 - Emotional Competency
This component ascertains the emotional quotient of an employee. A high emotional quotient enables an individual to manage stress, work for long hours, focus, and maintain optimism.
The emotional quotient is emotional control. Such employees are more professional. They exhibit a healthy work-life balance. They are better at separating work and personal lives.
Examples
Now, let us look at competency mapping examples.
Example #1
Jeremy owns a data solution company. Jeremy realizes that his company’s performance is mediocre. On a positive note, management is smooth.
To initiate improvement, Jeremy runs a competency analysis. He wants to understand if and how he can increase individual productivity and collective efficiency. Jeremy conducts a critical incident analysis.
Every employee undergoes a psychological evaluation. In addition, Jeremy distributed a relevant questionnaire. Jeremy conducts detailed analysis based on the collected data—questionnaires and psych eval interviews. He identifies the areas of improvement and implements them.
There is a massive reshuffle within the workforce. Some employees were promoted, and some were transferred. Entire teams were restructured. Jeremy also identified a lack of external motivation.
Change can be challenging for employees. But Jeremey’s proactive maneuver paid off. Within four weeks, there was a visible increase in firm productivity.
Example #2
Many firms are building a competency analysis framework to regulate recruitment. HR departments rely on automated analysis to gauge talent and skill gaps.
Automation has become an edge over competitors. But this approach continues well beyond recruitment. The use of technology and innovation increases productivity and reduces turnaround time. It also brings down costs (due to efficiency).
Advantages And Disadvantages
Competency mapping advantages are as follows:
- Competency analysis provides crucial feedback to employees. After analysis, they are better informed of firm objectives and organizational goals.
- It helps in developing a structured recruitment process.
- Competency analysis provides crucial data. Top-level management uses this data for decisions, transfers, restructuring, and training.
The disadvantages are:
- Data and feedback are useful only if the employees want to improve. Sometimes employees lack motivation.
- Analyses do not increase performance unless there is a fundamental change within the organization. Implementation is tricky.
- Competency analysis is expensive, time-consuming, and tedious. At times, the impact does not justify the expenditure.
- Often, change is challenging for employees. The employees may not share the enthusiasm shown by top-level managementggressive maneuvers can backfire; communication and smooth transitions are key.
Difference Between Skill Matrix And Competency Mapping
Now let us discuss the difference between skill matrix and competency mapping.
- The skill matrix assesses an operator's capabilities and machine utilization. In contrast, competency mapping is based on KSA (knowledge, skills, and attitude).
- Skill matrix is commonly used for reviewing the performance of labor or blue-collar workers. Competency analysis focuses more on the intellectual abilities of employees.
- The skill matrix narrows down a particular task and ascertains employee performance fon contrast; competency analysis gauges employee motivation, mindset, vision, aptitude, and ambition.
