Table of Contents
Payment Reconciliation Definition
Payment reconciliation refers to an accounting procedure of verifying the correctness and updation of financial records present in the balance sheet with the bank statements. It serves the purpose of verifying account balances, identifying discrepancies, updating financial records accurately and preventing fraud in a company's financial department.
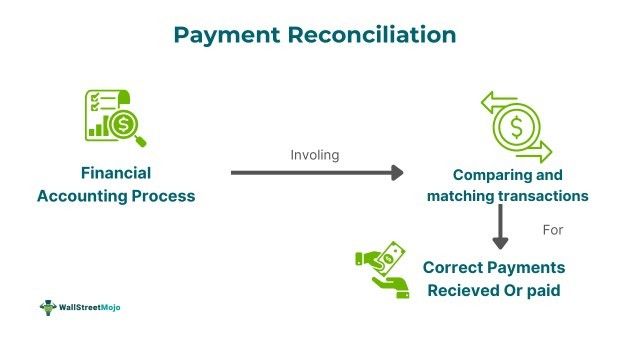
It can be carried out daily, weekly, or monthly basis in a firm. It facilitates one to chase late or unpaid invoices. It helps businesses manage their financial records effectively and avoid major discrepancies leading to losses or lawsuits. It has played an important role in cash flow management optimization.
Key Takeaways
- Payment reconciliation represents an accounting procedure making sure that the bank statement and balance sheet's financial records are accurate and updated.
- Its types are bank reconciliation, credit card, merchant, accounts receivables, accounts payable, cash, and digital wallet reconciliation.
- Its benefits include- ensuring accurate records, detecting discrepancies, fraud, and unauthorized payments, settling late invoices, preventing bounced checks and overdraft fees, and providing a financial health assessment.
- Its risks comprise - delayed financial report preparation, data loss, over/under payments, sophisticated & time-consuming processes, human error, delayed payments, and hindrance in budget planning and financial challenges.
How Does Payment Reconciliation Work?
Payment reconciliation represents a financial process involving comparing and matching transaction records, ensuring accurate payments are made or received as per transactions recorded in financial statements or accounting books of a business. Its working involves many key steps to make financial records accurate. First, all the necessary documents, like internal records covering invoices and external records covering bank statements. Then, one has to match all the transactions recorded in internal data with the entries in the bank or external records.
In this way, one can find any peculiar, different, or missing transactions recorded. After that, one must examine these discrepancies in depth to discover the real causes, like potential fraud to simple mistakes in data entry. Next comes correcting or addressing all such discrepancies to ensure the records become accurate and error-free. Then, all the processes carried out must be doubly checked to make adjustments that align with each other perfectly.
After that, the process has to be approved by the manager or supervisor. Lastly, the complete reconciliation process must be documented, all discrepancies moted, causes listed, and resolutions written down. After that, one has to regularly review the documentation to conserve accuracy and enhance internal controls.
Types
As per the complexity and size of the business, one can use different types of reconciliation of payment as below:
- Bank reconciliation depicts the most often used type for matching bank statements with internal records.
- Credit card payment reconciliation deals with matching of transaction of credit card with that of bank statements.
- Merchant reconciliation involves matching reports of internal records against the ones provided by different processors used.
- Accounts receivables reconciliation comprises the matching with the outstanding invoices concerning the outstanding due of the customer.
- Accounts payable reconciliation centers on authenticating one's records of payments due and bills to align with similar records with suppliers and vendors.
- Cash reconciliation matches collected cash with sales receipts to detect fraud.
- Digital wallets like Amazon payment reconciliation, although scarce, help in reconciling all transactions made using digital wallets with internal records.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
An online article published on 27 June 2024 discusses the manner in which Ripple (XRP) has leveraged blockchain technology to break the barrier of reconciliation of payments. As a result of the usage of blockchain technology, ripple enhanced its efficiency and accuracy of international transactions. Ripple has based its core solution on blockchain technology, providing immutability, security, and transparency to ensure complete and accurate data reconciliation.
Its solution of payment reconciliation process has features comprising tracking of transactions in real-time by the automated reconciliation engine, international support team, evolutionary user interface and customized payment reconciliation reporting. Moreover, it has planned future developments related to improvements in data quality, advanced filters, payment analytics widgets, and scheduled reporting. In a way, the innovative approach developed by Ripple aims to create a secure and frictionless global payments system to deal with the expectations and needs of users.
Example #2
Let us assume that a software company called XYZ Corporation in Old York City uses Finreco automated reconciliation software for payment reconciling. Its finance manager, David, uses the software and automatically collects data from - internal accounting statements, invoices and bank account statements of XYZ Corporation. During one such report generation, David found a discrepancy regarding an invoice of $6000 paid to vendor ABC Corporation from California that was not reflected in bank records.
Hence, David decided to match payment data through other systems. Therefore, the Finreco software scourges deeply and finds the payment got delayed because of bank holidays. After that, the software updates the records and addresses the issue. Further, such an efficient process of reconciliation saves time and imparts financial accuracy to XYZ corporation.
Best Practices
To make the process of reconciliation smoother, one has to follow the best practices below:
- Set up a documented and clear process explaining tools, steps and responsibilities utilized for reconciliation.
- Automation of most of the reconciliation process to streamline error flagging, matching, and data entry.
- Deploy standardization of data formats like numbering systems, currencies, dates, and transaction categories to uncomplicate matching.
- Separate staff duties by dividing the world between staff members to increase control and minimize errors.
- All records must be accurate, well-organized and clear concerning transactions, reconciliation reports, and receipts.
- Spend more on staff training to make them understand the minutes of the reconciliation process, spot errors and know their responsibilities.
- Undertake routine reviews of transactions weekly or daily to find and resolve discrepancies.
Benefits
There have been significant benefits of reconciliation of payments as listed below:
- It ensures records remain accurate.
- Helps discover any latent discrepancy, fraud or unauthorized payments.
- Settle late or unpaid invoices.
- Acts as a preventing tool against additional fees of bounced checks or overdraft fees.
- Shows any existing pattern in cash flow and spending of the company.
- Getting a good grasp and sense of the firm's financial health.
Risks
With benefits also come risks to the system of reconciliation, as listed here;
- In the case of physical reconciliation involving high-volume transactions, it becomes time-taking and sophisticated process.
- For the same reason, some human error may creep into the data allowing loss of accuracy.
- Likewise, manual reconciliation may delay mass payments to publishers, suppliers and freelancers.
- Manual reconciliation may lead to over or underpayment to employees, vendors, and freelancers.
- Similarly, manual reconciliation may lead to delayed preparation of financial reports.
- It may also lead to hindrance in timely planning of budgets, and responding to financial challenges.

