Table of Contents
What Is The Public Goods Game?
Public Goods Game (PGG) is an economic model that emphasizes the contribution of every member of a group to ensure they achieve their common goals. The concept encourages initial ideas for solving a public goods problem and also helps in gaining insights into behavioral economics. In short, this model tends to reflect team dynamics under various scenarios.
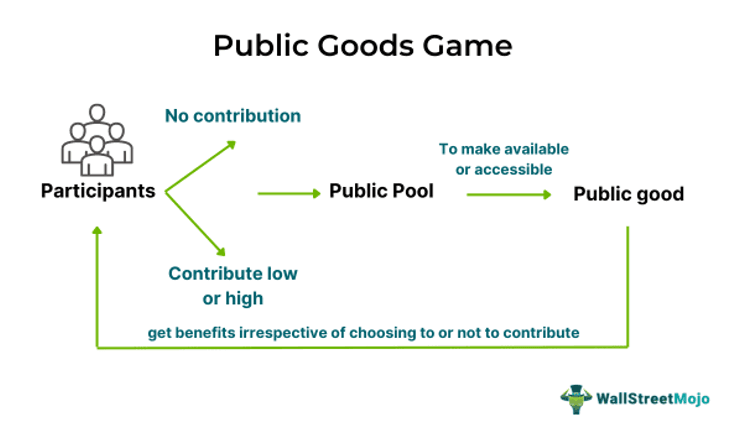
When a group of individuals follows this approach, they agree to share their contribution in a public pool, aiming to fund or boost the process of fulfilling the set social or business objectives. In this experimental approach, however, there are instances where a member or couple of members do not contribute to the public pool, but they still get an opportunity to enjoy the benefits coming from the contributions of other people.
Key Takeaways
- The public goods game in economics refers to an experiment or approach that focuses on the provision of public goods. It aims to understand subject behaviors and how, irrespective of the level of contributions, the public good is still distributed.
- The application of this model spans climate change, political science, behavioral economics, etc.
- This concept could help in understanding the problems associated with contributions and solving problems related to the distribution of public goods, which might be hampered by non-contributions.
- Implementing reward initiatives, punishment imposition, or both might help boost a sense of making contributions among participants.
How Does Public Goods Game Work?
The public goods game in economics brings together people who want to contribute to the availability and accessibility of public goods to society. In short, this approach helps study collective group decisions. Under this game, the participants are given the power to decide on the contribution to be made to a common pool.
Public goods are costly and tend to induce a conflict between self-interest and collective interest. They are also, however, non-excludable, which means all participants, irrespective of their contributions, benefit from the good once it is produced. This often provides an opportunity for some non-contributors to enjoy a free ride on the contribution of others, given the feature of the common pool to divide the benefits in equal proportions, irrespective of the contribution one makes.
The experiment provides insights into situations of social dilemma and the reasons behind individuals' choices. It helps in understanding the factors that push for a decline in public good contributions. Making contributions becomes optionable for the members of the group, as choosing not to contribute equals serving private interest, which justifies the prominence of Nash equilibrium in the public goods game.
Let us explain this using a very simple example. A group of friends plan to celebrate their last day at school in a café. They decide to contribute a certain amount of money to order food and beverages. They all agree to contribute, except for two, who say their parents are out of town, and hence, they cannot arrange for the money. To make sure the plan does not get spoilt, the group still agrees to contribute to the party. Though the two friends did not contribute, they were still part of the group that contributed, and hence, they also enjoyed the treat.
Though participants or members have the liberty to choose whether to contribute or not, ways can be introduced to encourage them to do so for the public good. Some such ways include rewards, punishments, or both to boost and maintain public cooperation. However, rewards have proven to be more efficient than punishments.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Imagine a town in Nevada, US, with a few medium-sized firms. Each of them is involved in producing different types of goods, such as cloth, food, electrical goods, etc., thereby contributing to the town's economy. These firms plan to collaborate and contribute to a shared goal of improving the town economically. Hence, each of them would have to raise funds and contribute toward improving public amenities, like building schools, maintaining roads, better parking spaces, etc., to enhance the standard of living of the people there and have a well-maintained area to boost tourist visits, thereby improving trade and sales.
The group of firms decide equal share of contribution, to which a few disagree. However, the potential contributors still decide to proceed with the plan to initiate the developmental program. Fortunately, the plan works and in five years, there is an increased revenue for each of them along with the progress of the state as a whole. The revenue generation gets a boost for even those firms who choose not to contribute to the initiative. This is how the public goods game works.
Example #2
In November 2023, Forbes published an article discussing how leaders today are more inclined toward meeting their personal demands than fulfilling societal or corporate requirements. The article discussed how having a manager no longer guarantees worker cooperation. Hence, overemphasizing the role of managers requires reevaluation.
The study that provided for this conclusion was based on a PGG-driven meta-analysis of economic experiments. It further advocated how punishments, if judiciously chosen and imposed, could offer the greatest benefits in boosting positive cooperation from corporate managers, making them available for contribution as and when required.
Significance
Given below are some points that reflect the significance of the application of public goods game in different scenarios:
- The approach helps in studying collective action and associated problems.
- It provides public goods, i.e., makes the public goods available and accessible to the common people.
- It helps in understanding the issues of contribution and addressing the shortcomings.
- It helps researchers gain insights into the subject of behavioral economics and psychology.
- The application of the PGG model spans from economic concepts to climate change.
