Table of Contents
Occupational Fraud Definition
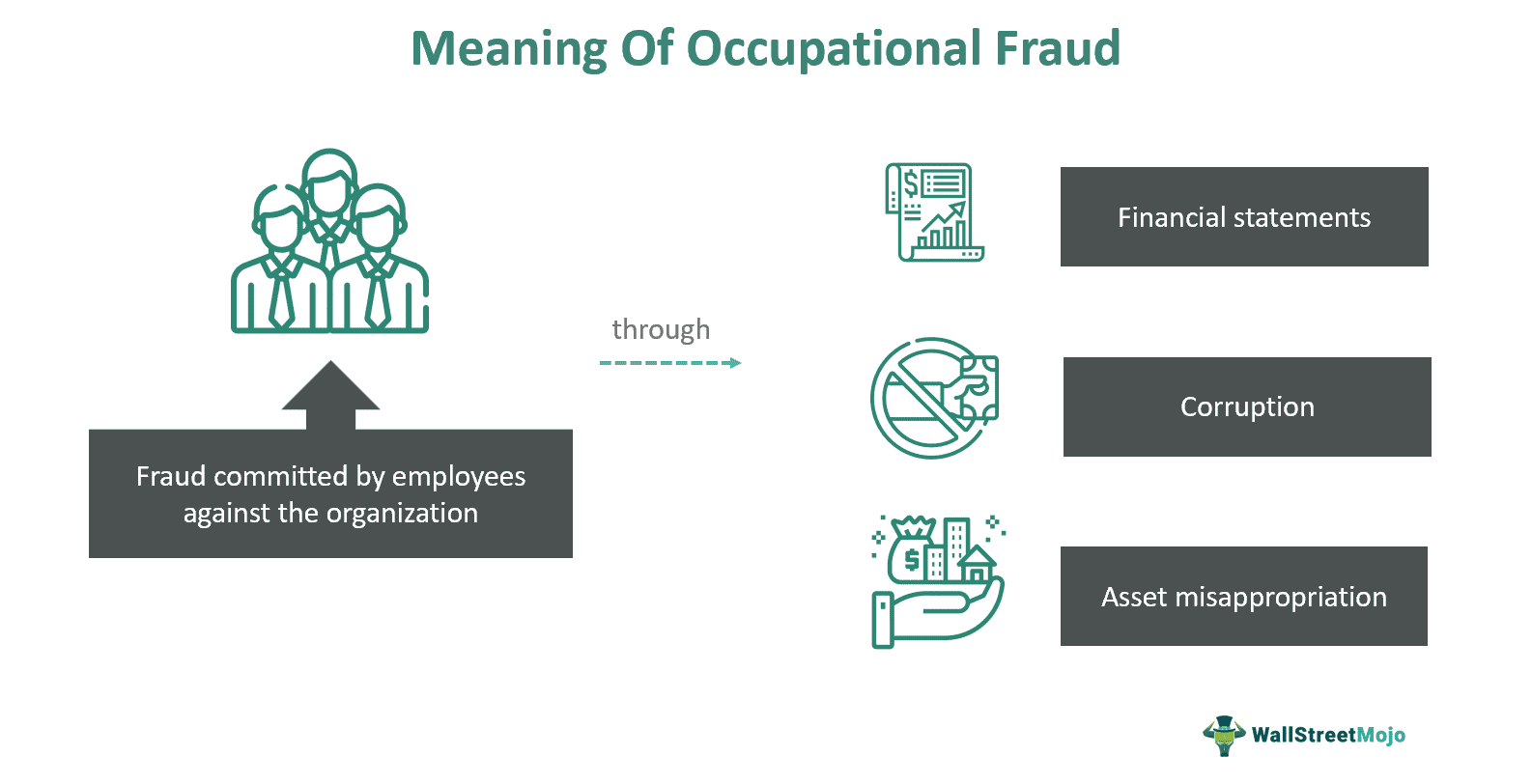
Occupational fraud refers to the frauds or crimes committed by people (or employees) working within the organization. It is also known as employee fraud or internal organizational fraud. Individuals, employees, or management mainly indulge in it due to personal tussles or rivalry against the organization.
The presence of occupational fraud is due to the formation of a fraud triangle in the company. Criminologist Donald R. Cressey further explained this concept in the 1970s. He explained the potential reasons why most occupational fraud cases by employees take place. However, the duration of these frauds can last for a maximum period of 12 months.
Key Takeaways
- Occupational fraud is an intentional act performed by employees to commit fraud against the employer (or organization). Majorly, employees do it for personal benefits.
- The types of this fraud include asset misappropriation, corruption, and financial statements.
- Individuals may manipulate the financial data, offer bribery, or steal the company's resources.
- The least duration of this fraud is between six months to 12 months. However, it can exceed around 60 months (or 5 years).
- Companies can develop a robust internal control system and develop a healthy corporate culture among employees to prevent such fraud.
Occupational Fraud Explained
Occupational fraud is a crime executed by employees against them for some financial or personal benefit. It happens when a certain level of control resides in the hands of employees, and they exploit it for a more extended period. As a result, they are able to fulfill their gains in the long term. However, these frauds do hamper the goodwill of the organization to a greater extent.
The occurrence of occupational fraud cases is visible in different areas, like assets and financial statements. Employees take advantage of the discrepancies in the system and management and commit fraud in return. And such frauds can vary with their duration. In short, they can be as short as two or three months to a maximum of 12 months. However, in some cases, such fraud can last for more than 60 months (around five years). As a result, these organizations face losses in this situation. For instance, for frauds detected within six months, the median loss is around $47,000—however, the cost increases unless the fraud gets detected. Similarly, for frauds undetected for more than five years, the loss is around $800,000.
The frequency of the detection of occupational fraud cases by employees takes place in a shorter span (less than six months). As it moves towards further, the chances also reduce from 33% to around 4–6%. However, it again depends on the type of activity performed under the veil of this fraud.
Types
Different types of occupational fraud red flags are noticeable in organizations. Some of them include asset misappropriation, corruption, and financial statement fraud. Let us further understand them in detail:
#1 - Asset Misappropriation
The standard prototype of employee fraud is visible within assets. In this fraud, employees or management try to misuse or steal the resources of the company, most commonly. A few significant assets include cash, inventory, and equipment. Furthermore, it also includes fraudulent schemes in billing, payroll, and expense disbursement. However, checks and payments can be tampered with by the employee.
Moreover, the report to the nations on occupational fraud and abuse has reported almost 86%, compared to others. However, the loss incurred is minimal in this case.
#2 - Corruption
This category includes fraud in terms of bribery, extortion, kickbacks, and conflicts of interest against the employer. Employees use it to gain personal benefits, with a frequency rate of around 50%. However, the loss in this case is slightly higher by $50,000 than asset misappropriation.
#3 - Financial Statements
In this fraud, employees intend to deceive the employer by manipulating the company's financial statements. Either the financials are underrated or overrated to hide certain items on the sheet. Here, the fraud is primarily against investors, stakeholders, or regulators. However, the median loss in this case is as high as $593,000.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to comprehend the concept for better understanding:
Example #1
Suppose Kevin is an accounting associate working in Jusbt Ltd. It has been around seven years since he started working for this company. However, Kevin noticed that the company needed subordinates on this team. As a result, he started taking advantage of this situation. He started showing a dummy transaction to an anonymous party and transferred the respective amount to his account. This fraud went undetected for around three years, and Kevin continued to own a wealth of $2 million.
At this stage, the company's auditors witnessed an unusual transfer of cash to a third party. During the investigation, they found a pattern of transactions between the anonymous party and Kevin. Later, Kevin confessed that he had noticed a loophole in the company, and he wanted to fill his pockets. Therefore, an amount of around $5 million was stolen from the company's cash balance.
Example #2
According to a recent 2024 report to the nations on occupational fraud and abuse, they reported a loss of $1.5 million per fraud case. In total, the fraud loss was around $3.1 billion. Likewise, organizations had to sacrifice around 5% of their revenue to these frauds. Most of them occurred due to at least one pandemic factor, a lack of controls, or an override (dominance) of existing controls. However, in these cases, the minimum duration was around 12 months (one year).
Detection
There are specific ways through which employers can detect occupational fraud red flags in the organization. Let us look at some methods in brief:
- Irregularities In Financial Records - The most popular red flag noticed in organizations is in financial statements. There can be unexplained differences in the financial items (like income, expenses, and asset value) that raise questions about the record-keeping system. If such irregularities occur, there is a chance of occupational fraud.
- Unexpected Changes In The Employee's Behavior Or Lifestyle - Another way to detect such fraud is to observe the behavior of the employees in the organization. There can be sudden or unexpected change in their behavior or their way of living. For instance, some employees may start having a luxurious lifestyle which is otherwise not suitable as per their budget.
- Poor Internal Controls - At times, there can be no supervision of the internal control system. There may be no senior executives or managers handling a department. In such cases, the employees may commit fraud and fill as much as wealth under the table.
- High Levels Of Employee Dissatisfaction - Apart from the factors discussed, the level of employee satisfaction may also indirectly lead to this fraud. An employee may not be satisfied with the treatment or remuneration provided to them. Hence, indulging in these frauds is more prevalent.
Prevention
Employee fraud can lead to massive losses to the organization on a macro level. However, with proper measures, it is possible to prevent it to a certain extent. Let us look at some methods:
- Firms and organizations can deploy a robust corporate culture of unity, diversity, and integrity among employees. It creates a sense of belonging among them.
- They can enhance and develop a robust internal control system in the company. It ensures that each department supervises activities and financial transactions.
- Implementing a robust reporting mechanism also reduces the occurrence of such frauds. Firms can establish confidential procedures so that whistleblowers can actively participate in such wrongdoings.
- During the hiring process, organizations can check the background of an employee in detail. It ensures the candidates have no fraudulent history or intentions to do so against the employer.
- Lastly, companies can install advanced software solutions and technology that do not allow permits to only concerned persons and not anyone else. It further prevents unwanted access by unauthorized persons and protects the company's sensitive data.
