Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Format Function
Format function in VBA one may use to format the given values in the desired format. For example, one can use this function for formatting dates or numbers or any trigonometric values. This function has two mandatory arguments: input taken in the form of a string, and the second argument is the type of format we want to use. For example, if we use Format (.99,” Percent”) this will give us the result as 99%.
In VBA, we need to use the function “FORMAT” to apply the format to cells. Excel formatting is one of the important concepts to master. We all use the common formatting techniques in our daily work: date, time, number, and other important formatting codes. We press the format excel cell option in regular Excel worksheets and perform the formatting duty by applying the appropriate formatting code. However, in VBA, this is not as straightforward as our worksheet technique.

Syntax

- Expression: This is nothing but the value we want to format. In VAB technicality, it is called Expression.
- : What format do you want to apply to the selected expression? We have two kinds of formatting here: user-defined format and built-in format.
- Here, we have VBA date, number, and text formats.
- VBA date formats have a short date, long date, medium date, and general date.
- Number formats have currency, standard, percentage, scientific, yes or no, true or false, and on or off.
- : What is the first day of your week? We can select any day from the list. Below is the list of days and appropriate codes.

- : What is the year's first week? It specifies the week it should use as the year's first week.

How to Use?
Let us apply this function practically to understand the functionality of the FORMAT function. Assume you have the number 8072.56489. You want to apply number formatting to it. Follow the below steps to apply number formatting to it.
Step 1: Start an excel macro and define the variable as a "string" data type.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String End Sub

Step 2: Assign a value to k as our number, 8072.56489.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String K = 8072.56489 End Sub

Step 3: Show the "k" value in the VBA message box.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String K = 8072.56489 MsgBox K End Sub

Step 4: If you run this macro, we will get the below result.
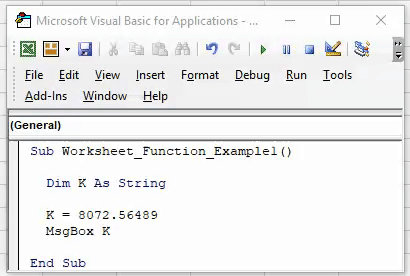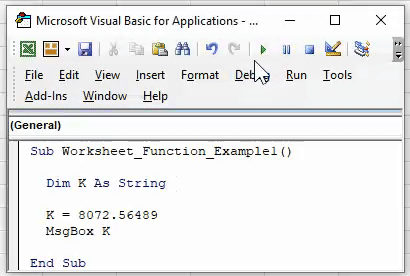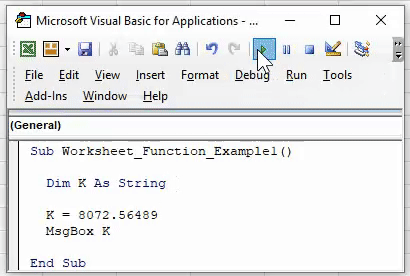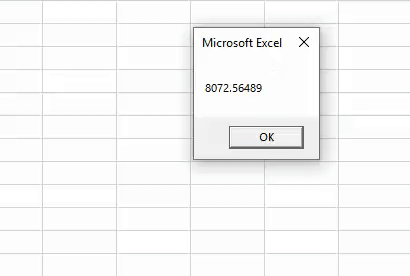
The result is as it is, we assigned the value to variable "k." But we need to apply some formatting to this number to make it beautiful.
Step 5: Instead of directly assigning a value to "k," let us use the FORMAT function.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String K = Format( MsgBox K End Sub

Step 6: Now, for Expression, assign the number 8072.56489.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, MsgBox K End Sub

Step 7: We can use a built-in format or our own formatting code in the formatting option. Now, we will use a built-in formatting style as "Standard."
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example1() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "Standard") MsgBox K End Sub

Step 8: Now, run this code and see the result of the message box.

We have comma (,) as thousand separators and decimal rounds up to two digits only.
Like this, we can use many other built-in formatting styles to apply the formatting. Below are some of the codes we have applied.
#1 - Currency Format
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example2() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "Currency") MsgBox K End Sub

Result:

#2 - Fixed Format
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example3() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "Fixed") MsgBox K End Sub

Result:

#3 - Percent Format
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example4() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "Percent") MsgBox K End Sub

Result:

#4 - User-Defined Formats
Now, we will see some of the user-defined formats.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example5() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "#.##") MsgBox K End Sub

Result:

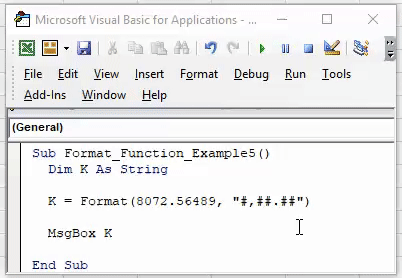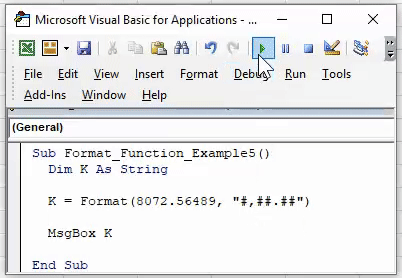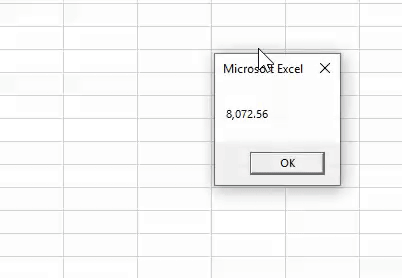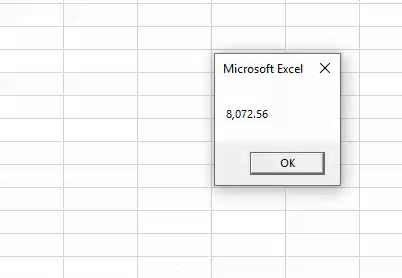
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example5() Dim K As String K = Format(8072.56489, "#,##.##") MsgBox K End Sub

Result:
#5 - Date FORMAT
We have seen some important numbers of formatting techniques. We will have to use the FORMAT function to format the date in VBA.
We have written code to show the result of the date through the variable.
Code:
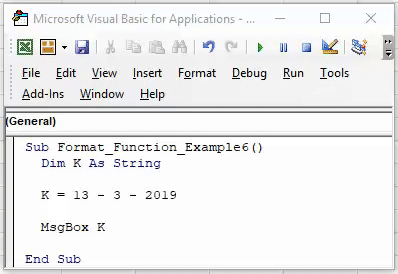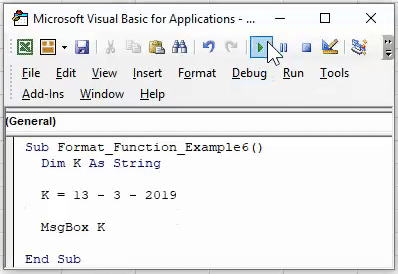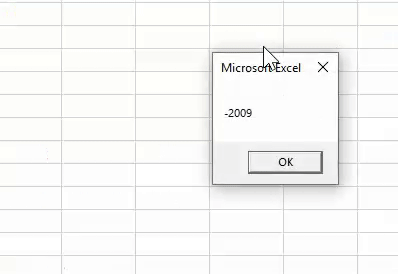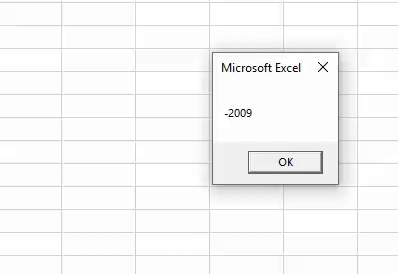
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example6() Dim K As String K = 13 - 3 - 2019 MsgBox K End Sub
When we run this code, we would not get an accurate date. Rather, the result is pathetic.
We need to assign the date format to get accurate dates. So, we first need to supply the date in double quotes and apply the date format.
Code:
Sub Worksheet_Function_Example6() Dim K As String K = Format("10 - 3 - 2019", "Long Date") MsgBox K End Sub
We run this code now. We will get a proper long date.

The "Long Date" is a built-in format. Similarly, you can use the "Short Date" and "Medium Date" options.
Things to Remember
- The value returned by the FORMAT function is the string.
- We can also use our date, time, and number formatting codes, like how we use them in worksheet formatting.
- The FORMAT is a VBA function available only in VBA, not in the worksheet.

