Table Of Contents
What Are ListObjects In VBA?
VBA ListObjects are Excel tables that we can control using VBA. It can be used to manage rows, columns, and data more easily. In VBA terminology, a table is an object with parts such as range, listrows, listcolumns, etc. To access these parts, we have an inbuilt function known as ListObjects, used with the worksheet function.
VBA ListObject is a way of referring to Excel tables withVBA code. Using VBA LISTOBJECTS, we can create and delete tables and play around with Excel tables in VBA. Since this article is about referencing Excel tables in VBA coding, one should have a good knowledge about these tables.
When the data is converted into to table, we no longer work with a range of cells. Rather, we now work with table ranges. So, this article will show you how to work with Excel Tables to write VBA codes efficiently.
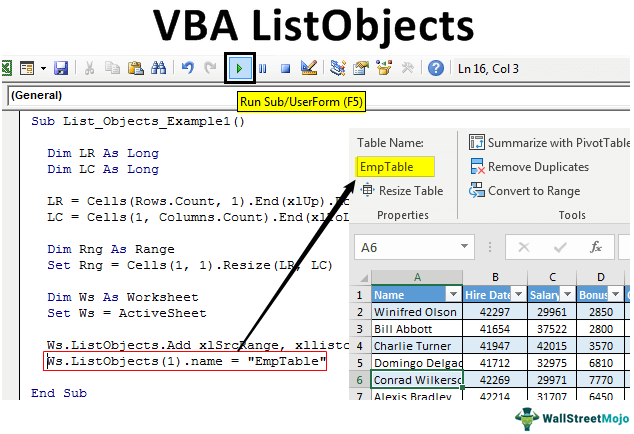
Create Table Format Using ListObjects in Excel VBA
For example, look at the Excel data below.
Using the VBA ListObject code, we will create a table format for this data.
- First, we need to find the last used row and column, so we must define two variables to find this.
Code:
Sub List_Objects_Example1()
Dim LR As Long
Dim LC As Long
End Sub
- To find the last used row and column use the below code.
Code:
LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LC = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
- Now define one more variable to hold the reference of the data.
Code:
Dim Rng As Range
- Now set the reference to this variable by using the below code.
Code:
Set Rng = Cells(1, 1).Resize(LR, LC)
We must use the VBA "ListObject.Add" method to create a table; below is the syntax of the same.
ListObject.Add (Source, XlListObjectHasHeaders, Destination, TableStyleName)
Source: This is where the data comes from. So we can supply two arguments here, i.e., “xlSrcRange” and “xlSrcExternal.”
We use xlSrcRange for a worksheet range, or xlSrcExternal for external sources.
XlListObjectHasHeaders: If the table inserting data has headers or not. If yes, we provide “xlYes.” If not, we provide “xlNo.”
Destination: This is nothing but where the table should be placed
Table Style: We can provide styles to apply any table style.
Now in the active sheet, we are creating the table. The below code would create a table for us.
Code:
Dim Ws As Worksheet
Set Ws = ActiveSheet
Ws.ListObjects.Add xlSrcRange, xllistobjecthasheaders:=xlYes, Destination:=Rng
- After this, we need to give a name to this table.
Code:
Ws.ListObjects(1).name = "EmpTable"
- Below is the full code for your reference.
Code:
Sub List_Objects_Example1()
Dim LR As Long
Dim LC As Long
LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LC = Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Dim Rng As Range
Set Rng = Cells(1, 1).Resize(LR, LC)
Dim Ws As Worksheet
Set Ws = ActiveSheet
Ws.ListObjects.Add xlSrcRange, xllistobjecthasheaders:=xlYes, Destination:=Rng
Ws.ListObjects(1).name = "EmpTable"
End Sub
Let us run the code and see the magic.
It has created the table to the mentioned data and given the table name "EmpTable."
Formatting Excel Tables with VBA ListObjects
Once we create the Excel table, we can work with tables using the VBA ListObject collection.
- First, define the variable as “ListObject.”
Code:
Sub List_Objects_Example2()
Dim MyTable As ListObject
End Sub
- Now, set the reference to this variable by using the table name.
Code:
Sub List_Objects_Example2()
Dim MyTable As ListObject
Set MyTable = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("EmpTable")
End Sub
Now, the variable "MyTable" holds the reference for the table "EmpTable."
- Enter the variable name and put a dot to see the properties and methods of the VBA ListObject.
For example, if we want to select the entire table, then we need to use the “Range,”object, and under this, we need to use the “Select” method.
Code:
MyTable.Range.Select
It would select the entire data table, including the heading.
- If you want to select only the table contents without headers, we need to use “DataBodyRange.”
Code:
MyTable.DataBodyRange.Select
Like this, we can play around with tables.
- Below is the list of activity codes for your reference.
Code:
Sub List_Objects_Example2()
Dim MyTable As ListObject
Set MyTable = ActiveSheet.ListObjects("EmpTable")
MyTable.DataBodyRange.Select
'To Select data range without headers
MyTable.Range.Select
'To Select data range with headers
MyTable.HeaderRowRange.Select
Advertisement
'To Select table header rows
MyTable.ListColumns(2).Range.Select
'To select column 2 including header
MyTable.ListColumns(2).DataBodyRange.Select
'To select column 2 without header
End Sub
Like this, we can use the "ListObject" collection to play around with Excel tables.
Things To Remember
- VBA ListObject is acollection of objects to reference Excel tables.
- To access the ListObject collection, we must specify whichworksheet we are referring to.
- One can access tables on a sheet as follows: Set tbl = Sheet1.ListObjects("Table1")

