Table Of Contents
Data Breach Meaning
A data breach occurs when confidential or otherwise protected information is accessed, stolen, or used without authorization. The aim of it can vary depending on the attacker's motive. It occurs when an individual or organization's data is accessed by an unauthorized person or entity, either deliberately or accidentally.
Other breaches happen because of espionage or to gain access to proprietary information or trade secrets for competitive advantage. Some violations result from protests or activism, embarrass the target organization, or damage its reputation.
Key Takeaways
- Data breaches can occur through various means, including cyberattacks, insider threats, physical breaches, or accidental exposure.
- Sensitive information commonly targeted includes personal information such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card numbers, and proprietary information such as trade secrets or intellectual property.
- The consequences of it can be significant, including financial losses, reputational damage, legal matters, identity theft, and loss of intellectual property.
- Preventing it requires a multi-layered approach that includes a range of technical, procedural, and organizational measures.
Data Breach Explained
Data breaches have become a pervasive threat to individuals and organizations in the digital age. Still, their prevalence and impact have increased significantly in recent years due to the growing amount of data generated and stored and the increasing sophistication of cyber attackers.
The origin of such breaches tracks back to the earliest days of computing when computer systems were first connected to networks. Then, as businesses moved online, the potential for cyberattacks and data breaches grew exponentially. Today, such violations can occur through various means, including phishing attacks, malware infections, social engineering, insider threats, etc.
In addition to the financial losses and reputational damage that can result from a breach, there are legal and regulatory consequences. For example, many countries now have data protection laws requiring organizations to protect their customers' personal information and notify them in case of a breach.
Moreover, with the increasing adoption of cloud computing, IoT(Internet Of Things) devices, and other emerging technologies, the risk of data breaches is only set to increase. As a result, organizations must take a proactive approach to cybersecurity and data protection, including implementing strong security measures and conducting regular security audits.
Similarly, individuals must also protect their personal information, including using strong passwords, being cautious about sharing personal information online, and monitoring their financial accounts for signs of fraudulent activity.
Types
Some of the common types of data breaches:
- Malware attacks: Malware is malicious software that infects computer systems and steals sensitive data. Malware attacks can occur through various means, including email attachments, downloads from untrusted websites, and infected USB drives.
- Phishing attacks: Phishing attacks are social engineering attacks that trick individuals into providing sensitive information. Phishing attacks can occur via email, social media, or other communication channels.
- Insider threats: Insider threats occur when an employee or other trusted individual intentionally or accidentally exposes sensitive data. This can occur due to negligence, a lack of training, or malicious intent.
- Password attacks: Password attacks involve an attacker attempting to steal passwords to gain access to sensitive data. This can occur through brute force attacks. Here the attacker tries many possible password combinations or through stealing passwords through social engineering attacks or other means.
- Denial-of-service attacks involve an attacker flooding a system or website with traffic to overwhelm it and cause it to crash. This can result in sensitive data being exposed or stolen during the chaos.
- Physical breaches: Physical breaches occur when sensitive data is stolen or exposed. This is due to physical security vulnerabilities, such as stolen laptops, unsecured file cabinets, or lost USB drives.
Examples
Let us understand it better with the help of examples:
Example #1
Suppose a hacker gains access to a company's database containing sensitive customer information like names, addresses, and credit card numbers. The hacker then sells this information on the dark web to other criminals. They, in turn, use it to commit identity theft and financial fraud. This is an example of a data breach that can have severe consequences for the affected individuals and the company.
Example #2
An example of it is the SolarWinds cyberattack discovered in December 2020. In this attack, a sophisticated group of hackers gained access to the networks of multiple government agencies and private companies. This was done by exploiting vulnerabilities in SolarWinds' software. Consequently, the attackers were able to steal sensitive data and conduct espionage activities, leading to national security and cyber resilience concerns.
Consequences
Some of the most common consequences of it are:
- Financial Losses: It can result in financial losses for individuals and organizations. For individuals, this can include identity theft, credit card fraud, and other types of financial fraud. For organizations, this can include the cost of investigating and mitigating the breach, legal fees, and potential fines or penalties for failing to protect sensitive data.
- Reputational Damage: It can damage an organization's reputation by stealing sensitive customer data. Customers may lose trust in the organization and choose to take their business elsewhere, resulting in lost revenue and a damaged brand image.
- Legal Consequences: Depending on the nature and severity of the breach, organizations may face legal consequences such as lawsuits, fines, or regulatory action. Many countries now have data protection laws that require organizations to protect sensitive data and notify customers during a breach.
- Identity Theft: Identity theft is a common consequence of a breach, mainly if the violation involves the theft of sensitive information such as social security numbers or credit card numbers. Identity theft can result in financial losses, damage to credit scores, and other negative consequences.
- Loss of Intellectual Property: In cases where a breach involves the theft of proprietary information or trade secrets, organizations may suffer a loss of intellectual property, which can have severe consequences for their competitiveness and long-term viability.
Prevention
Some of the most effective methods for preventing it are:
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Strong password policies can prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. This can include requiring employees to use complex passwords, enforcing regular password changes, and implementing two-factor authentication.
- Use Encryption: Encryption can help protect sensitive data by making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. This can include encrypting data at rest, in transit, and in use.
- Keep Software and Systems Up-to-Date: Keeping software and systems up-to-date can help prevent vulnerabilities from being exploited. This includes applying security patches and updates promptly.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in an organization's security posture. This can include conducting vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and other types of assessments.
- Train Employees: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices can help prevent data breaches caused by human error. This can include providing training on how to recognize phishing emails, how to use secure passwords, and how to avoid downloading or installing malware.
- Limit Access to Sensitive Data: Limiting access to sensitive data can help prevent data breaches caused by insider threats. This can include implementing role-based access controls, conducting background checks on employees, and monitoring access logs for suspicious activity.
- Plan for Incident Response: A comprehensive response plan can minimize the impact of a data breach if one does occur. This can include defining roles and responsibilities, outlining procedures for detecting and responding to incidents, and providing training on incident response procedures.
Data Breach vs Data Leak
Some key points of comparison between data breaches and data leaks:
- Definition: A data breach is when sensitive information is accessed, stolen, or used without authorization. A data leak is when sensitive information is inadvertently disclosed or exposed, often due to a mistake or oversight.
- Intent: Malicious actors perform data breaches to steal or expose sensitive information. Data leaks are often accidental and may not involve malicious intent.
- Potential Impact: Data breaches can have far-reaching consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal matters. Data leaks may have a minor impact and may not result in the same level of damage as a data breach.
- Cause: Data breaches can occur due to a cyberattack, insider threat, or other means. Data leaks can occur through various means, including misconfigured databases, unsecured cloud storage, or random email attachments.
- Prevention: Both data breaches and data leaks can be prevented through technical, procedural, and organizational measures. Preventive measures can include implementing strong security measures, training employees to handle sensitive data, and having a response plan in case of a security incident.
- Response: In the event of a data breach or data leak, organizations must have a response plan in place to mitigate the impact of the incident. Response measures can include investigating the extent of the breach or leak and notifying affected individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Many nations have data protection laws that require organizations to take steps to protect sensitive data and notify affected individuals in the event of a breach. For example, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act requires healthcare providers and other covered entities to protect patient health information in the United States.
Cybersecurity insurance can help mitigate the financial impact of a breach by covering the costs of investigating and mitigating the violation and any legal fees or penalties that may result. However, cybersecurity insurance is not a substitute for solid cybersecurity measures and should be considered part of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy.
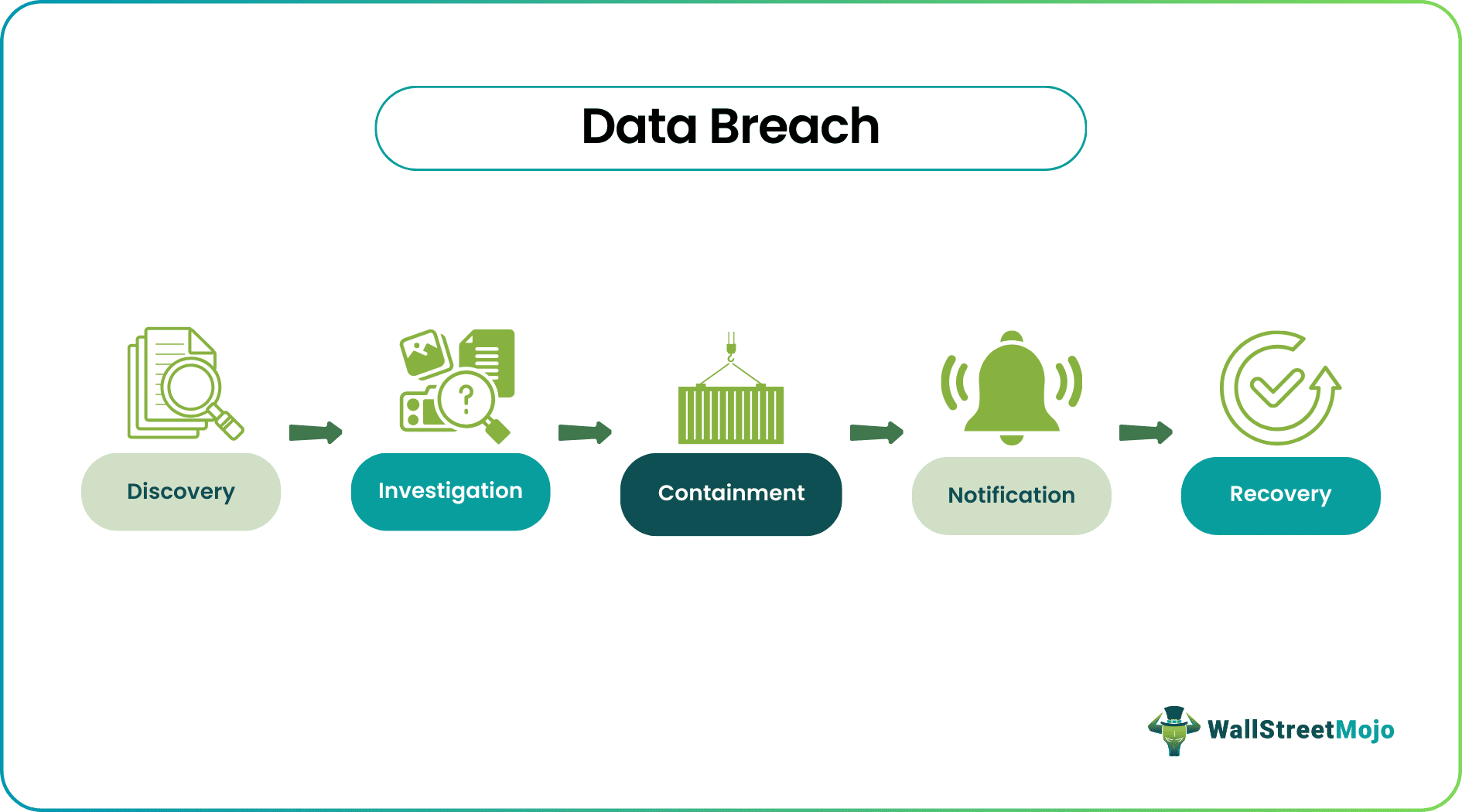
Organizations should have a response plan that includes notifying affected individuals, conducting an investigation to determine the extent of the breach, and taking steps to prevent a similar incident from occurring.
