Table Of Contents
Double Taxation Meaning
Double taxation is a situation where taxes are levied at two different levels on the same source of income. This means that individuals and entities must pay taxes twice on the same income or profit earned. It holds significance in two scenarios – international trade and corporations.
The corporation owners are taxed against the entity's profit first and then as its shareholder. On the contrary, in international trade, the income is taxed at an international level first and then at the national level.
Key Takeaways
- Double taxation refers to the income tax imposed twice on the same earned income, asset, or finance transaction by the same or multiple jurisdictions.
- The principle of taxation affects C corporations, where business profits are taxed at corporate and personal levels.
- International businesses pay dual taxes as their income gets taxed in the country where it is earned, and then this income is again taxed when it is sent back to the business' home country.
- Drafting an agreement and signing it can help countries give mutual consent to the eradication of double taxation while dealing with each other.
Double Taxation Explained
Double taxation, as the name suggests, makes the same income or earnings taxable twice at different levels. This taxation principle may be applied both at corporate and personal levels. In addition, when there is international trade, this taxation is applied in two different countries.
For example, when earned, corporate profits are taxed as corporate tax and then taxed again as personal income when distributed as dividends among the stockholders.
An owner must pay the tax levied on the earnings of an entity. Plus, if the owner is also the shareholder who receives the dividend from the company, the tax at the personal level gets levied, next.
Video Explanation of Double Taxation
Types
Double taxation is observed to exist in two forms – corporate and international.
#1 - Corporate Dual Taxation
For corporate taxation, when an organization earns a profit and an income, the tax is levied on the overall income it generates as a business unit. After the tax deduction, when the remaining amount is distributed among shareholders, they are taxed at an individual level as well for the share profits they receive on a personal level. This is how tax payment occurs twice for a corporation.
So far as corporate taxation is concerned, only C-corporations have to pay double tax. This is because S-corporations are similar to partnership ventures as they facilitate the distribution of profits between partners, taxed only on a personal level and not as an entity.
Similarly, Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) and sole proprietorship ventures remain exempted from the double tax payment as they represent pass-through entities. In such firms, profits pass through the owners and co-owners as individuals, thereby making them liable for taxes on an individual level only.
#2 - International Dual Taxation
In international trade, where two countries exchange goods and products for money, the parties dealing in the items must pay the taxes levied on those products in both countries. This is how twin taxation applies when purchasing and selling products involving two nations.
Countries that want to avoid dual taxation have the alternative of signing a double taxation treaty with the required nations. Such treaties set certain guidelines and rules that govern all taxation matters concerning the trade and investment of the countries involved. For example, nation A and nation B can mutually agree upon specific clauses and sign an agreement to avoid paying dual taxes within each other's boundaries.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the meaning of double taxation better:
Example #1
Company SRP recorded a profit of $500 million in the year 2022. A tax of 21% was levied on it as a corporation in the first place. The company distributed the remaining amount among the three shareholders of the company. Each share of profit or dividend was then subject to a 37% tax at an individual level. This is how these taxations are levied on corporates and the players.
Examples #2
The United States and Croatia signed a double taxation avoidance agreement in December 2022. This came as an assurance that they do not have to pay double taxes for their international trade. This treaty would reduce the withholding taxes that the source country imposes on the taxable income. In addition, this agreement sets both countries free to do business with the companies operating within each other's boundaries. This, thereby, increases employment opportunities for Americans in Croatia and Croatians in America.
Benefits & Problems
Let us have a look at the pros and cons of this dual taxation system:
- While double taxation helps the governments of the countries earn significant revenue, it increases the tax burden of the citizens.
- In short, this taxation system is a source of additional revenue for the nations, but it imposes additional tax liability on people on individual levels.
- In corporate taxation, the businesses pay taxes on an income first. Then, the shareholders pay taxes on an individual level against the dividends distributed from the same income. Hence, it's an additional tax for the same source of earnings.
- In foreign trade, the businesses pay taxes to the source country, where the income generates. Then, they pay the tax in their nation for the products they bring back.
How To Avoid?
Formulating legislation in the form of treaties or agreements is the best way to get double taxation relief. The firms can also opt to register themselves as ventures other than Corporations. This means if the ventures register as a sole proprietorship firm, partnership unit, or LLC, there will be no system of dividends. And where there is no dividend, there is no dual taxation.
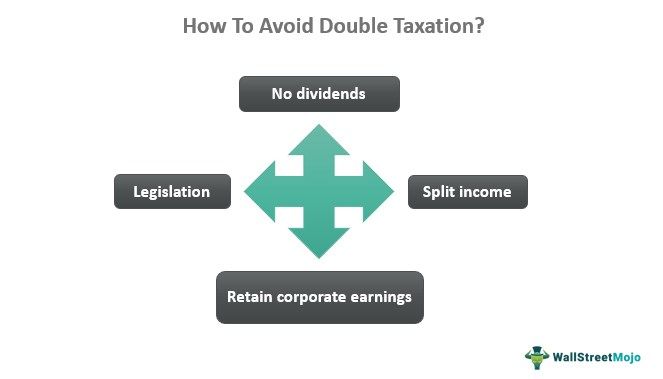
If businesses want to avoid dual taxation, they can retain their earnings and not distribute them further. Lastly, they can split their income and pay wages and salaries to the employees to cut their tax burden.
