Table Of Contents
S Corporation Definition
S corporation refers to a special status entity exempted from paying corporate tax, which allows shareholders to be taxed only once when they receive the benefits by follow-through taxation, thereby avoiding double taxation at the corporate level under a special chapter of the IRS so that all the rules specified in the chapter shall be complied with.
There are different types of business entities formed for conducting trade or business. The structure of their business categorizes business entities. An S Corporation business is one such category. The name stands for ‘’small business corporation’’. The structure or features of a business entity help distinguish it from other types.
To begin with, let us first understand some of the basic features of the S corp. Mentioned below are the following key features:
- The entity must be a “domestic corporation.” A domestic corporation refers to an entity that cannot have non-resident shareholders as its owners.
- An entity must have its shareholders to be less than or equal to 100.
- All shareholders must be individuals. However, certain aspects of this requirement need to be discussed further.
- Trusts and estates considered charity organizations get exemptions from taxation and can be regarded as shareholders.
- Partnerships or other corporations are not eligible to be shareholders. Family members are treated as a single shareholder in S corp. This implies that spouses or individual descendants of the elected shareholder will be considered as a single shareholder.
- An entity that owns one class of stock (Profits and losses are distributed to owners/ shareholders in proportion to their interest in the business).
The entity must comply with all such requirements as listed above. If it fails, the entity will no longer be granted the S corp status.
S Corporation Explained
S corporations, also known as S-corps, are a type of business entity commonly used by small and mid-sized businesses in the United States. They are named after Subchapter S of the Internal Revenue Code, which governs their formation and operation. S corporations offer a hybrid structure that combines the limited liability protection of a corporation with the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship.
One of the key features of S corporations is pass-through taxation, where the profits and losses of the business "pass through" to the individual shareholders. This means that the business itself does not pay federal income taxes at the corporate level.
Instead, shareholders report their share of the corporation's income or losses on their personal tax returns and are taxed at their individual tax rates. This avoids the double taxation that occurs with C corporations, where the corporation pays taxes on its profits and shareholders pay taxes on dividends received.
An S corporation qualification requires a business must meet certain eligibility requirements set by the IRS, including having no more than 100 shareholders, all of whom must be individuals, estates, or certain types of trusts. Additionally, S corporations can only have one class of stock, and shareholders must be U.S. citizens or residents.
While S corporations offer many advantages, such as pass-through taxation and limited liability protection for shareholders, they also have some limitations. For example, S corporations are subject to strict eligibility criteria and operational requirements set by the IRS.
Additionally, shareholders of S corporations are generally prohibited from deducting corporate losses beyond their basis in the corporation, and there may be restrictions on transferring ownership interests. Despite these limitations, S corporations remain a popular choice for many small businesses seeking tax advantages and liability protection.
Requirements
To begin with, let us first understand some of the basic features of the S corporation business. Below are the a few key features:
- The entity must be a “domestic corporation.” A domestic corporation refers to an entity that cannot have non-resident shareholders as its owners.
- An entity must have its shareholders to be less than or equal to 100.
- All shareholders must be individuals. However, certain aspects of this requirement need to be discussed further.
- Trusts and estates considered charity organizations get exemptions from taxation and can be regarded as shareholders.
- Partnerships or other corporations are not eligible to be shareholders. Family members are treated as a single shareholder in S corp. This implies that spouses or individual descendants of the elected shareholder will be considered as a single shareholder.
- An entity that owns one class of stock (Profits and losses are distributed to owners/ shareholders in proportion to their interest in the business).
The entity must comply with all such requirements as listed above. If it fails, the entity will no longer be granted the S corp status.
Losing S Corporation Status
There are various scenarios under which an entity can lose this status. Let us look at a particular case as S Corporation examples.
- Suppose, for instance, if any of the shareholders elected is a “foreign national,” i.e., a non-U.S resident, or if the number of shareholders exceeds 100 due to the transfer of shares to a new shareholder, then the entity stands to lose its S corp status.
- Now that we have listed down the features of an S corp, let us dive deeper into the concept of what an S corp means.
Examples
Now that we understand the basics and intricacies of S corporation qualifications, let us understand its practicality through the examples below.
Example #1
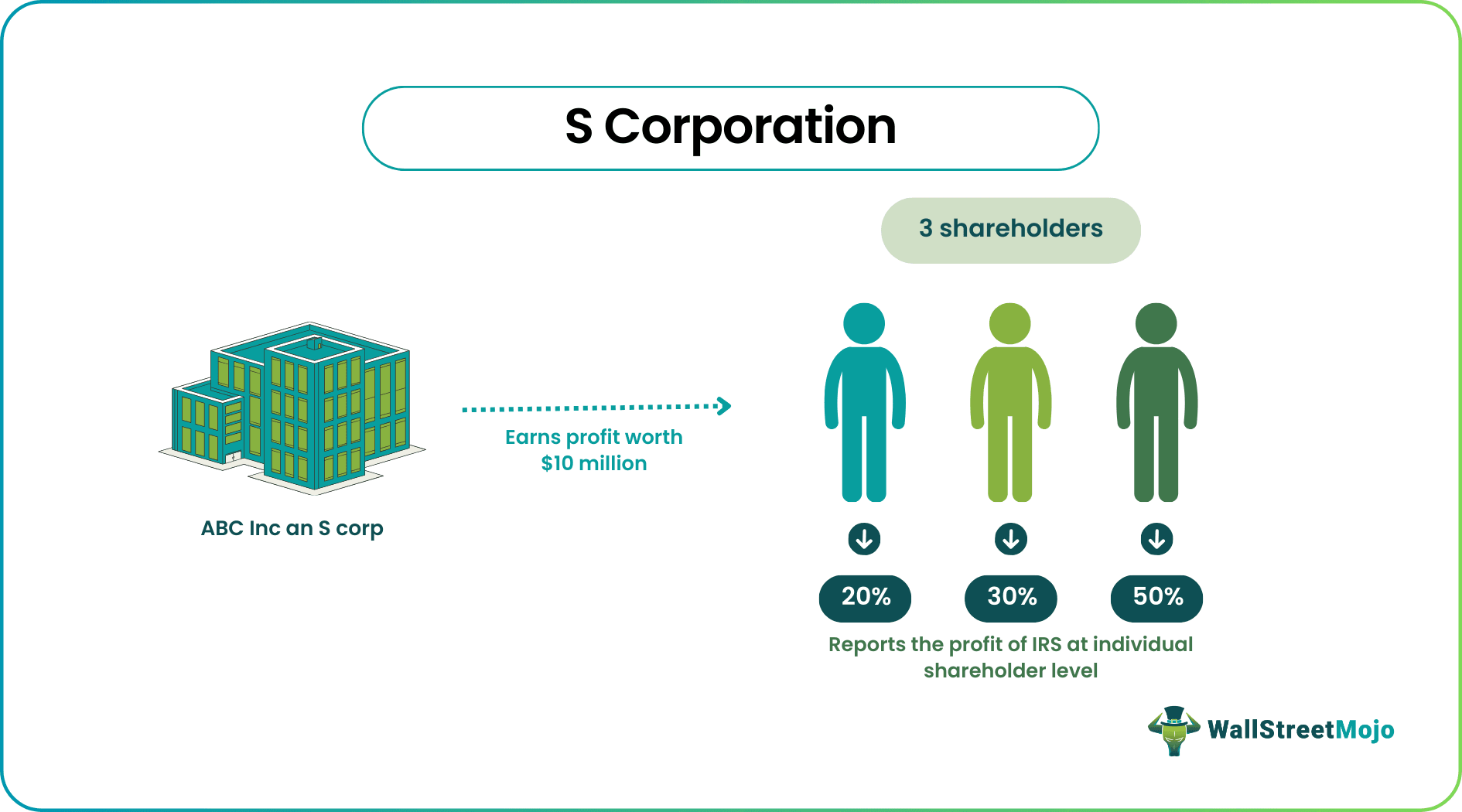
Let’s suppose an entity “ABC Inc” is an S corp with three shareholders in 2016. In the year 2016, it earned a profit worth $10 million. Depending on the percentage of shares owned by them initially, each of the three shareholders will draw incomes equivalent to that percentage.
In this case, let us say that Sam, Todd, and Sara own 20%, 30%, and 50% of shares, respectively. Given that ABC Inc. is an S corp, the profits earned will not be reported to the IRS at the company or corporate level. Instead, they will report at the individual shareholder level. Each of the three shareholders will report this profit while filing their individual income tax returns. Hence, Sam, Todd, and Sara will report $200,000, $300,000, and $ 500,000 for their incomes, respectively.
Example #2
If ABC Inc. were to undergo losses of a certain amount, all three shareholders would have to file for losses on their personal income tax returns in the same proportion of shares owned by them.
Another major of S corporation’s advantages is that such entities can avoid double taxation. Given that S corporation tax at the shareholder level, as explained above and not at the corporate level, will pass on income directly to its shareholders. Only income is given out as salaries to shareholders are subject to taxation. Other business entities do not enjoy this advantage because any income/profit earned is filed and taxed at the corporate level. The net income/ profit is distributed to the shareholders, who are taxed on their earnings. This constitutes double taxation. Therefore, it is advantageous for small businesses to register as an S corp to enjoy the tax benefits associated with it.
Tax Rate
Let us understand the different tax rates applicable to S corporation businesses through the points below.
- Pass-through Taxation: S corporations are not subject to federal income tax at the corporate level.
- Shareholder Taxation: Profits and losses of the S corporation are "passed through" to individual shareholders.
- Individual Tax Rates: Shareholders report their share of the corporation's income or losses on their personal tax returns.
- Taxation at Shareholder Level: Shareholders are taxed at their individual income tax rates on S corporation income.
- Avoidance of Double Taxation: Unlike C corporations, where corporate profits are taxed at the corporate level and again when distributed to shareholders as dividends, S corporations avoid double taxation.
- Potential for Tax Savings: Pass-through taxation allows S corporation shareholders to potentially save on taxes by utilizing individual tax deductions and credits.
Advantages
Let us understand the advantages of adhering to S corporation qualifications through the discussion below.
- One of the major advantages enjoyed by an S corporation is that it is not subject to income taxes.
- This is subject to taxation, similar to partnerships wherein all income or losses are shared among all its owners or shareholders. This implies that the IRS taxes such entities at the shareholder level, not at the corporate level.
Disadvantages
Despite the various advantages, there are a few points of concern that cannot go unaddressed. Let us discuss the disadvantages of S corporation qualifications through the points below.
- S corporations have strict eligibility requirements, including a limit of 100 shareholders who must be individuals, estates, or certain types of trusts. This can limit the ability to raise capital or attract investors.
- They can only have one class of stock, which restricts the flexibility of ownership arrangements and may deter potential investors.
- While they offer limited liability protection to shareholders, they may not provide as much protection as a traditional corporation in certain legal scenarios.
- These corporations must adhere to various operational and regulatory requirements set by the IRS, which can be burdensome for small businesses with limited resources.
- S corporations may face restrictions on the types and amount of passive income they can generate, which can affect their ability to diversify income streams and grow wealth.
S Corporation Vs C Corporation
Let us understand the distinctions between an S corporation business and a C corporation through the comparison below.
S Corporation
- Pass-through taxation.
- Limited to 100 shareholders, who must be individuals, estates, or certain trusts.
- One class of stock.
- Shareholders report income on personal tax returns.
C Corporation
- Subject to double taxation.
- No restrictions on the number or type of shareholders.
- Can issue multiple classes of stock.
- Pays corporate taxes on profits, and shareholders pay taxes on dividends received.
