Table Of Contents
Kaizen Meaning
Kaizen is a Japanese concept that facilitates constant improvement or betterment. Its principles are self-discipline, common sense, economy, and order. The Kaizen method involves every employee from the highest to lowest ranks to initiate changes, as small changes put together can have an enormous impact on the organization's overall growth.
Kaizen is a culmination of two words, "kai," which translates to change, and "zen," which translates to "good." Therefore, the literal translation of kaizen is to change for the good. By constant improvements and eliminating redundancy, kaizen principles apply to processes, including cross-organizational boundaries in the supply chain, logistics, healthcare, governments, banking, life coaching, and psychotherapy.
Key Takeaways
- Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy developed post-World War II by Masaaki Imai. It believes in constant improvement in an organization.
- A problem is identified and met with solutions involving everybody in the organization, including suppliers and customers.
- This philosophy or process believes in a zero-waste environment where no unnecessary time, energy, or movement is made.
- Following this process helps an organization attain efficiency, waste management and, more importantly, can improve regularly.
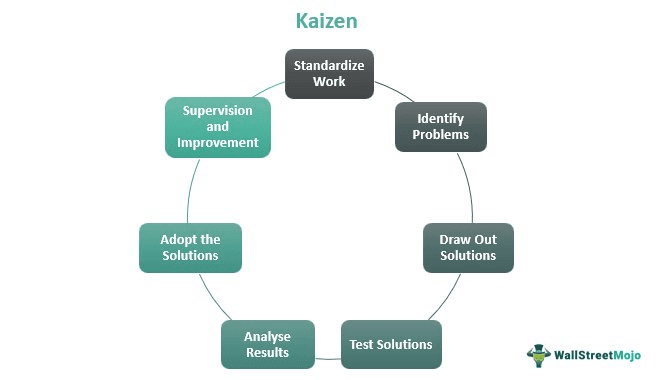
Kaizen Process Explained
Kaizen is a Japanese philosophy that firmly believes in constant improvement and elimination of waste and redundancy to ensure effectiveness and efficiency in an organization.
The kaizen origin has been traced to a period post world war-II when Japan was under economic reform. Most notably, The Toyota company implemented the Kaizen method in 1951, which led to the company's overall development through high productivity from workers and higher product quality.
Masaaki Imai, the father of Kaizen, was a management consultant around the 1980's. Taiichi Ohno was vital in spreading philosophy worldwide along with his friend. As a result, today, organizations across industries implement the philosophy as a daily practice.
It is a daily process whose purpose is beyond just improving productivity. In a larger scheme of things, it helps humanize the workplace, teaches employees how to perform experiments scientifically, finds and eliminates waste or redundancy, and replaces hard work with clever work to a great extent.
The constant development is aimed to be executed in a humanized manner, unlike other process improvement programs. The kaizen method believes in making changes, monitoring results, and adjusting accordingly. Extensive project planning is replaced by assigning smaller tasks or experiments that make change easier to adapt.
In the modern day, it is used to address specific issues in the short run, usually a week or two. This period of implementing kaizen is referred to as the "kaizen event" or "kaizen blitz."
Principles
The kaizen framework involves five important principles. Let us discuss then through the points below:
- Know Your Customer: The core principle believes in finding the interests and wants of the target customer to ensure the organization can create value for its customers. The understanding helps create a better experience for the customer right from purchase to customer support, if necessary, in the future.
- Let It Flow: This principle requires everyone in the organization to strive towards a zero-waste environment. Zero waste refers to raw materials, movement, and time taken to perform a task. Kaizen helps in creating value most efficiently,
- Go To Gemba: Gemba translates to 'the real place.' In the business world. It refers to where work is executed or value is created, such as the office or factory floor. The kaizen principles believe that value can be made only when things happen. Hence, it is crucial to get there physically.
- Empowerment: The team and the management aligning on a set of goals is essential to attain exemplary efficiency. Therefore, setting goals relevant across the organization hierarchy, providing them with tools and systems to execute their tasks, and setting up a developmental feedback mechanism help the cause.
- Transparency: The metrics for evaluating performances must be visible and tangible. Kaizen makes feedback and improvement easier to deal with, as the metrics are for everyone to see. Transparency not only helps with feedback but also with employees remaining motivated and open-minded.
Kaizen 5S
- Sort: Eliminating obstacles and distractions make the environment more conducive to work. The employees must scan the workplace thoroughly to reach a kaizen environment, and only required things are retained. Sorting is a continuous process and cannot be sorted by exercising it once. It requires consistency and supervision.
- Set Up Order: To ensure no time is wasted at the workstation or workplace, on the whole, it is vital to arrange the required tools and equipment in a manner that is readily available and readily accessible. The order aids the smooth flow of work. However, it is also important to note that everything must have a place, and everything in the organization must be in its place. The arrangement makes accessing the tools and equipment prompt.
- Shine: Constant use of machinery and infrastructure is bound to attract wear and tear. To ensure the deterioration is slower, the machinery is in pristine condition, and safer for the workers, it is essential to clean and maintain the workplace regularly, if required. Kaizen maintains the working condition of the machinery and equipment and helps workers feel pleased with their workplace.
- Standardize: This part of 5S refers to the best practices chosen by the organization for the work area and ensuring those practices are followed. To maintain high standards across functions of the organization, it is crucial to ensure the items are in order and the standard for each activity is written down.
- Sustain: Sustain in this regard refers to discipline and training. To ensure every item is placed in its place, cleaned regularly, and employees are free of distraction, it is pivotal for the employees to be trained to an extent where these activities become their second nature. Furthermore, regular feedback contributes to the sustenance.
Types
The essence of the work and the concept of kaizen is a continuous improvement or constant development. However, how it is interpreted in the modern business world highly depends on the nature of the business, place of implementation, and management style. Let us understand the different types of kaizens through the points below:
- Point Kaizen: This interpretation is one of the most widely used types of kaizen as it requires minimal planning and can be implemented quickly. In this practice, as soon as something incorrect or broken is found, immediate measures are taken to correct them. Generally, these corrections or implementations are small and easy to teach but have a massive impact on the process. For example, a worker believes that a change in place for the equipment can increase efficiency in terms of time consumed. It is a small change, but overall downtime is cut down significantly, making the production process smoother.
- Line Kaizen: The line kaizen refers to the movement of communication upstream and down the stream of an organization. Kaizen can be layered in multiple ways and extended within departments.
- System Kaizen: System kaizen is an upper-level planning method implemented quickly. It is implemented to cater to system-level problems within the organization.
- Plane Kaizen: Plane kaizen is another extension of line kaizen, where several organization lines are connected. In modern terms, it is usually synonymous with a value stream where product families and value streams replace traditional departments.
- Cube Kaizen: A cube kaizen describes a situation where every plane in the organization is connected without any irregularities. This connection involves the suppliers and customers, which might require the business to modify the standard business procedures.
Examples
Let us understand the concept better through the examples below:
Example #1
Core Forging Company is an organization that makes steel fences and other items in its factory. Each dye's average weight ranges from 75 kgs to 150 kgs.
The floor workers must lift the dye from the store area to the machinery. Each time a dye is changed, it takes up to 25 minutes.
Therefore, the management decided to purchase a forklift which not only makes lifting heavy weights easier but also saves 20 minutes every time a change in the dye is required.
Example #2
When the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted the healthcare system bred by the utter chaos on a global level, the healthcare sector exhibited an exemplary display of Kaizen practices. The collaboration at a cross-organization level to ensure patient care calmed the environment.
Telecommunications, patient care, housekeeping, Disease Control, and Prevention Foundation, and London Hospital formed a system that constantly found problems and solved them on different levels to cater to the ever-growing inflow of patients.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Just like any other concept or ideology, kaizen also has its share of advantages and disadvantages. Let us understand the pros and cons of this concept through a brief comparison below:
Advantages
- Teamwork: One of the main advantages of kaizen principles is it facilitates better teamwork because it involves everyone in the business and believes in solving problems collectively.
- Targets: This philosophy of constant improvement includes everyone involved in the business, from the top-level managers to the floor laborers, suppliers, and customers. The kaizen method applies to most types of businesses. It provides the employees with a sense of belonging and worth by rewarding and recognizing their efforts.
- Efficiency: Since all distractions are eliminated and processes are standardized, everyone involved in the business can concentrate on their respective tasks efficiently. In addition, restricting any time, effort, or movement waste ensures more work is done without excess or extra effort.
Disadvantages
- Disrupts Current Flow of Work: Even though kaizen is an efficiency-building practice, it becomes a hurdle when it is implemented by replacing an existing work system. Therefore, it is easier to implement this practice in a new establishment rather than in an organization that has a current way of operating.
- Training: Implementing a system that constantly promotes improvement is ideal for any organization. However, it comes at the cost of training employees on the new ways of operation and can cost more for the organization.
- Friction: Especially in an organization with an existing framework of daily activities, a sudden shift in operating style could cause frictions that might take time for the employees to get used to and managers to be able to motivate and supervise them.
Kaizen vs Six Sigma vs Lean
| Basis | Kaizen | Six Sigma | Lean |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | The kaizen origin traces back to Japan post World War II. | These are a set of tools and techniques developed by Motorola in 1986 for improving processes. | The founders developed this management philosophy based on the Toyota Production System (TPS). |
| Program | Bottom-up approach | Top-down approach | Top-down approach |
| Founded By | Masaaki Imai | Bill Smith from Motorola | Womack, Roos, and Jones from MIT |
| Primary Focus | Constant improvement. | Process Efficiency | System Efficiency |
