Table Of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Shareholder structure refers to the composition of a company's ownership, including the number and type of shareholders, the percentage of ownership held by each shareholder, and any shareholder agreements in place.
- Dual-class and multi-class share structures are the two types of shareholder structure.
- The shareholder's structure is a valuable tool for management to keep track of the company's ownership and decision-making powers.
- It helps diversify the company's ownership by not letting a group control significant decision powers.
Explanation
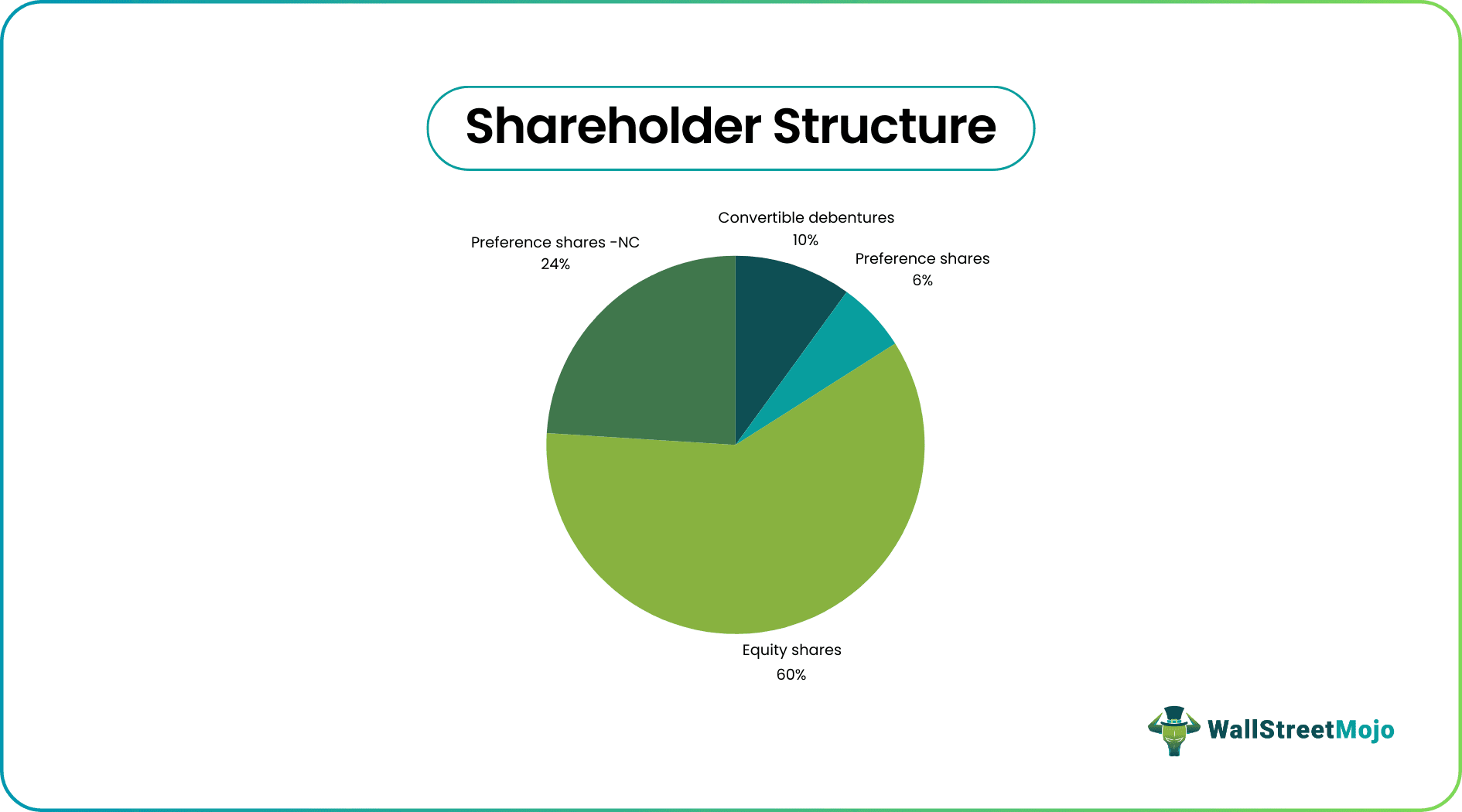
Shareholders Structure Report classifies the different classes of shares issued by the company i.e., common shares, preference shares, convertible shares, ESOP, etc. where preference share can also be of two types i.e., preference shares without voting rights or preference shares with restricted voting rights. After classifying the different shares issued, Share Structure then retains the records of shareholders with the number and percentage of shares held by them at the end of the reporting period. But the percentage of shareholdings only provides the owner of the company which does not define the overall decision making power of the shareholders which can only be provided after declaring the voting rights available to the shareholders.
Maintaining the Shareholding Structure of a Company helps the management to diversify the ownership of a company and not letting a group control or having exclusive decision power. It is maintained at the acquisition of the company when the shares are issued to Promoters of the company and then the same is updated at the issue of new shares. This could be done by recording the name of the shareholders subscribing to the issue of shares of the company and recording the respective holdings of the shareholders. After recording this much, the percentage of the capital hold by every shareholder is calculated and the percentage of voting rights available to the shareholders is also evaluated and mentioned.
While preparing the Shareholder Structure of the company, the list of potential shareholders can also be mentioned, which will be holding common shares after dilution of the company or after conversion of their convertible securities.
It also helps the management during the liquidation of the company. It provides the owner of the company and provides the rights of the shareholders in the profit or value of the company. After paying off Creditors and preferential creditors, the remaining realization from the company’s assets are to be paid to the shareholders of the company according to the rights of the individual shareholders.
Conclusion
The shareholder's structure is a useful tool for management to keep track of the ownership of the company and the decision making powers in the company. The structure can be of two types- Dual-class share structure or Multi-class share structure; which help the management to maintain decision power in the hands of the management and promoters so that the management could focus on the vision of the company and could work towards the future prospects of business without thinking about the hindrance from the decision making of shareholders. Shareholder structure helps during the time of liquidation in deciding the liabilities & the rights of the stakeholders.