Table Of Contents
What is the Preferred Dividend?
Preferred dividends referred to the amount of dividend payable on the company's preferred stock from the profits earned by the company. Preferred stockholders enjoy priority in receiving such dividends compared to common stock, which means the company must first discharge the liability of preferred dividends before discharging any liability of dividends payable to the preferred stockholders.

source: Diana Shipping
Preferred Dividends are fixed dividends received from Preferred stocks. It means that if you’re a preferred shareholder, you will get a fixed percentage of dividends every year. And the most valuable part of the preferred stock is that the preferred shareholders get a higher dividend rate. They are also given more preference than equity shareholders in dividend payments.
Key Takeaways
- Preferred dividends represent the payments distributed to holders of preferred shares based on the company's financial performance.
- Unlike common stockholders, those with preferred shares enjoy priority in receiving these dividends.
- The company is obligated to settle preferred dividend commitments before addressing any obligations to common stockholders.
- Common characteristics of preferred dividends include higher dividend rates, fixed percentages, cumulative dividend options, adherence to legal obligations, and preferential treatment.
- Notably, non-cumulative preferred stocks lack the feature of arrear payment.
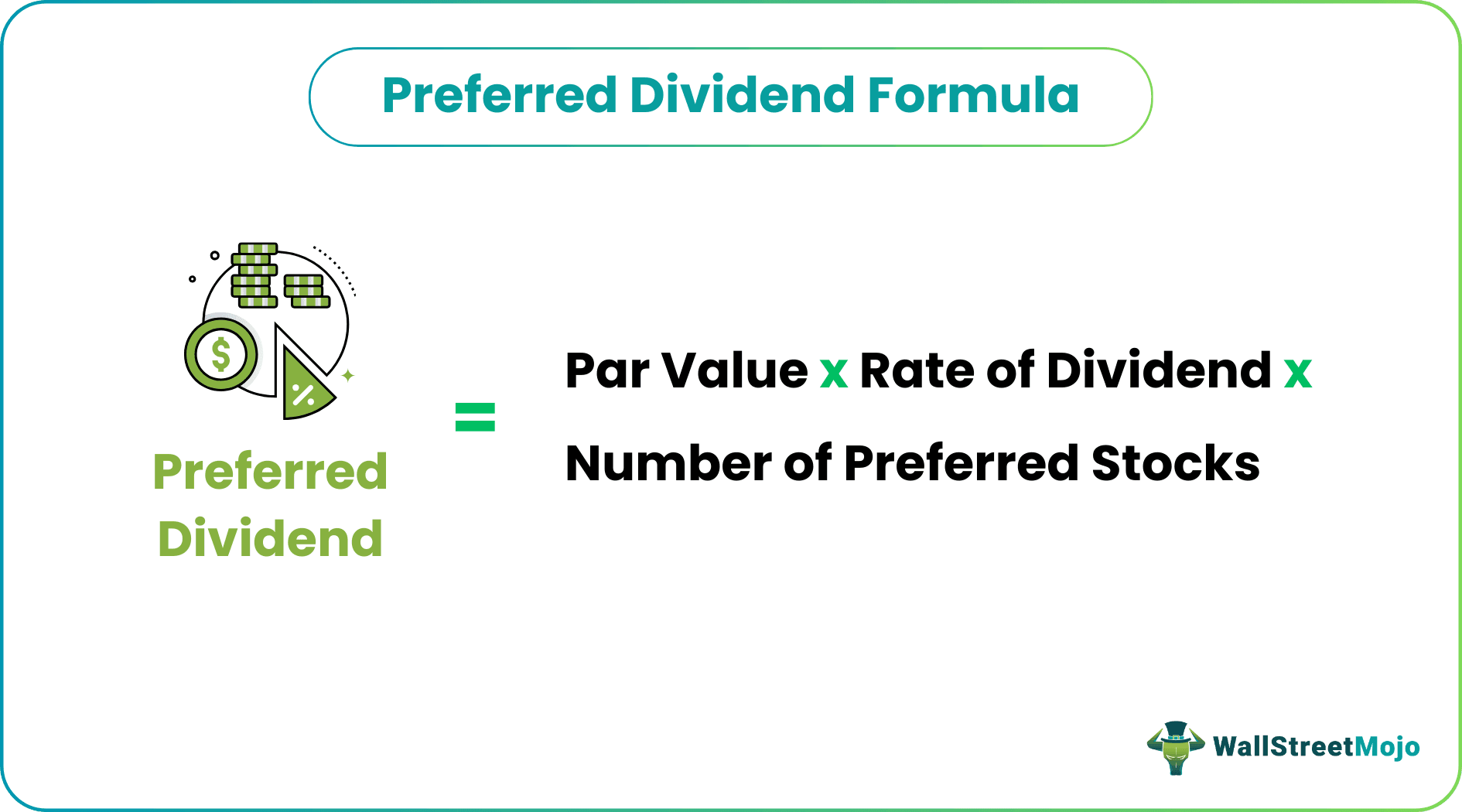
Preference Dividends Formula
Here’s a simple formula for calculating preferred dividends on preferred stock –
Preferred Dividends = Par Value x Rate of Dividend x Number of Preferred Stocks
If preferred shareholders want to invest in the preferred stocks, they need to look at the prospectus.
They need to see two basic things first.
- What is the par value of the stock?
- What is the rate of dividends?
Once they know these two basic things, they can multiply these two components and understand how much they would receive at the end of each year.
The great advantage of investing in preferred stocks is that it is like a fixed instrument. You are assured of a fixed payment every year.
Plus, if the firm gets bankrupt any day, you will be given preference over equity shareholders. If the company becomes bankrupt before equity shareholders are paid a buck, you will get the amounts due to you.
Once you know how to calculate the preferred dividend per share, you need to multiply the number of shares with the preferred dividend per share. And you would know how much you would get each year.
Video Explanation of Preferred Dividend
Example of Preferred Dividend
Let’s take a simple example and see how it works.
Urusula has invested in the preferred stocks of a firm. As the prospectus says, she will get a preferred dividend of 8% of the par value of shares. The par value of each share is $100. Urusual has bought 1000 preferred stocks. How much dividend will she get every year?
The basic two things to calculate the dividend are given. We know the dividend rate and the par value of each share.
- Preferred Dividend formula = Par value * Rate of Dividend * Number of Preferred Stocks
- = $100 * 0.08 * 1000 = $8000.
It means that every year, Urusula will get $8000 as dividends.
Common features of preferred dividend
#1 - Higher dividend rates
- Rates are much higher than the rates of equity or common stock.
- This is because preferred shareholders do not have ownership control over the company; hence, higher dividends rates are offered to them to attract investors.
#2 - Fixed percentage
- Unlike the dividend on common or equity stock, which keeps on fluctuating every year depending on the company's profitability ratios, preferred dividends do not fluctuate. Their rate remains unchanged throughout the maturity life of preference share.
- There is also another major reason for the fluctuation of dividends on common stock.
- The shareholders recommend dividend rates on common shares during the company's annual general meeting.
- Hence it keeps on fluctuating since the shareholders decide on rates keeping in mind the profitability and future outlook of the Company.
#3 - Cumulative or arrears in dividend
- Shareholders are entitled to a dividend every year irrespective of the profitability of the Company.
- But sometimes, on account of business exigencies, a company may not be in a position to pay to shareholders.
- In such circumstances, dividends are accumulated and are paid in a subsequent year.
- Let’s understand the impact of one of the business difficulties on the payment of preference dividends with the help of a practical illustration.
Cumulative Preferred Dividend Example
Company X Inc. has 3 million outstanding 5% preferred shares as of December 31st, 2016. The par value of preference shares is $10 each. The cash balance available with the Company is $1 million.
Preference dividend to be paid for the year 2015 = 1,500,000 (3,000,000 *10*5)/100
Available cash balance =1,000,000
In the above case, the company can’t pay a dividend to shareholders since the total available cash is less than the total amount of preferred dividend liability. In the above case, a dividend will accumulate and must eventually be paid to preferred shareholders in a subsequent financial year. Since the dividend is always paid in cash, its shortage will force the company to withhold dividend payments for 2016.
Please note that the above illustration highlights just one single business exigency. Various other business exigencies might force the company to withhold the preferred dividend payment.
#4 - Legal obligations
- Preferred dividends, like interest on debts, create a legal obligation on the company. These will be paid to shareholders in preference over any common stock dividend.
- The liability of the company to pay dividends is unconditional and absolute.
- Various jurisdictions impose penalties if the company does not pay an outstanding preferred dividend.
- These penalties range from fines and imprisonment of directors to prohibition on the company from raising additional finances from the public till the liabilities are paid out.
#5 - Preferred treatment
- It is paid out to shareholders in precedence over other types of dividends. i.e., shareholders pay dividends before the common stock, or equity dividends are issued.
- In case of liquidation of the company, shareholders with preferred shares are entitled to be paid from company assets first.
- All this feature of the preferred dividend gives it preferential treatment over other types of dividends.
- The above features highlight some of the common features in most preferred shares. In the corporate world, there are various types of preference shares.
- These may or may not have some of the features mentioned above and may contain some additional unique features.
- Now, let’s look at the different types of preference shares that are issued by the company to raise capital in the primary and secondary markets.
Uses
The preferred stock pays a fixed percentage of dividends. However, a firm can skip the equal payment of preferred dividends to preferred shareholders. And the firm can choose to pay the dividends in arrears. That's why we call it perpetuity because the dividend payment is equal and paid for an infinite period.
It means that a firm won’t pay a dividend each year. Rather the due amount of dividend would accumulate over the period. And then, the firm will pay the accumulated preferred dividends to the preferred shareholders. This feature of arrear payment is only available with the cumulative preferred stock. And the firm is legally obligated to pay off the previous year’s preferred dividend before paying the current year’s dividend.
In the case of non-cumulative preferred stocks, this feature of arrear payment is not available.
Preferred Dividend Calculation in Excel (with Excel Template)
Let us now do the same example above in Excel. This is very simple. You must provide the two inputs of Par value, Rate of Dividend, and Number of Preferred Stocks.
You can easily calculate the ratio in the template provided.

You can download this template here - Preferred Dividend Excel template.
Advantages
- Higher dividend rate – TThis is one of the most important advantages of holding preference shares. Amongst all the debt instruments like bonds, commercial papers, Government T-bills, etc., the return received by an investor by holding a preference share is far greater than received through holding any other debt instrument. The reason is pretty obvious since the cost is directly related to return. The higher the cost of holding any instrument, the higher the return received and vice versa.
- Preferential treatment - As highlighted above, preferred shareholders have the right to preferential treatment regarding dividends. In the event of liquidation of the Company, the shareholders with preferred shares are entitled to be paid from company assets before Common stock shareholders.
- Assured minimum return - Preference shares have a fixed dividend rate, whereas, on the other hand, common stocks do not have a fixed dividend. Fixation of the dividend rate in advance guarantees the minimum return to shareholders. Shareholders do not have to depend on the company's general economic conditions or profitability. If the company suffers a loss, the dividend accumulates for the subsequent year.


