Table Of Contents
What Is Employee Stock Options Plan (ESOP)?
An Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) is a retirement or employee benefit scheme that allows employees to own shares of the company and have a financially stable post-retirement life. This provision helps strengthen the bond between employers and employees, encouraging the latter to stick with the former for a longer term.
Any company can offer an ESOP at a discounted rate, which is considerably less than the market price. Hence, employees are willing to invest in these plans and buy shares of their company's stocks, which gives them a feeling of ownership.
Key Takeaways
- An employee stock option plan (ESOP) is an option granted to employees who carry the right, but not the obligation, to buy a promised number of shares at a pre-determined price (known as the exercise price).
- These are complex call options granted by the companies as a part of the remuneration package.
- Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP), Employee Stock Option Scheme (ESOS), Restricted Stock Units (RSU), and Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs) are the types of ESOPs.
- When stock options are exercised in large quantities, it can significantly impact the total number of outstanding shares, diluting the EPS and negatively affecting the firm's valuations.
Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) Explained
An employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) is a retirement plan that gives employees a sense of security and lets job seekers prefer getting employment in companies with ESOP provisions. ESOPs differ from exchange-traded options as they are not traded and don't come with a put component. Though these options remain unlisted, they allow employees to invest and own the shares.
The employers issue stock options under the stock options compensation plan. Employees can exercise these options if the market price exceeds the exercise price or the strike price, executing in-the-money trade.
Once stock options are exercised, the company issues shares to the option holder. This, in turn, increases the total number of outstanding shares. As a result, earnings per share (net profit/number of shares outstanding) decreases as the denominator increases.
Thus, in this process of employee stock option plan for private companies, the employees get equity as part of their compensation plan which not only motivates them to work harder and contribute more towards the business, but also give them a share of the company’s success. The business is able to attract better talent and retain them for a longer period, fostering loyalty and long-term growth. It is a financial incentive where the employees are benefitted by buying stocks at lower prices, when the actual market price is more.
However, the tax treatments may vary depending on the type of options. Some tax consequences are there while selling them.
Employee Stock Option Plan Video Explanation
Types
The employee stock option plan meaning becomes clearer as one explores its types. Employers can provide ownership of stocks in various forms – Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP), Employee Stock Option Scheme (ESOS), Restricted Stock Units (RSU), and Stock Appreciation Rights (SARs).
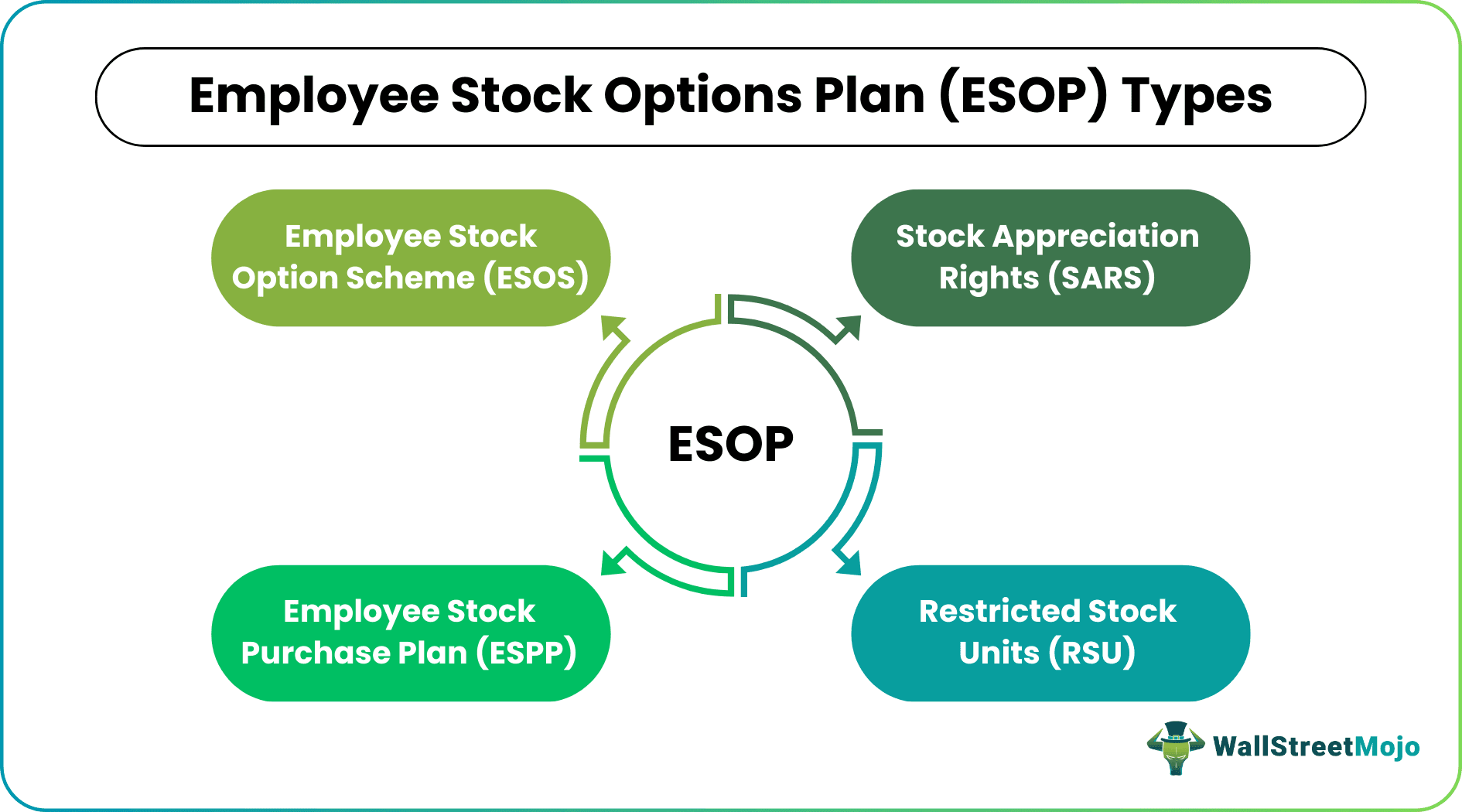
ESPPs are schemes wherein companies offer shares to employees who complete a minimum service period. Then, they sell them at much lower than the market price. An ESOS, on the other hand, is a plan where employers offer options based on a pre-defined valuation. This works concerning the vesting period and the overall performance of employees. Employees can exercise the options at the pre-defined strike price as soon as they achieve the minimum vesting period.
The next is RSU, where employers grant company shares to employees with no particular vesting period or exercise price. Instead, the latter can exercise the right over the shares only when a local event occurs.
SARs, on the contrary, may or may not be considered an ESOP. This is because few companies prefer offering cash in exchange for shares to employees on meeting the specific criteria or conditions.
Accounting
While allotting shares, companies calculate the difference between the fair market value at the exercise date and the price the employees pay at the time of subscription or at the time of exercise. This is the prerequisite value, eligible for tax deduction at the source.
On the other hand, the profit becomes a capital gain when an employee opts to sell their share. This is because taxes apply to capital gains - the difference between fair market value on the exercise date and the sale value of shares.
Example
Let us consider the following employee stock option plan for private companies example to understand how the concept works:
ESOP taxation – while exercising the option – The first condition for taxation
- Prerequisite value of ESOP (at the time of allotment)
- Market value = 120
- Exercise price = 70
- and the number of shares allotted under ESOP is 6000
Calculation of Prerequisite value of ESOP

Prerequisite value of ESOP = (fair market value- price at the time of exercise) * No of share
= (120-70) * 6000 =300,000
The above value of 300,000 is the prerequisite value of ESOP, which is a part of the employee's salary. Therefore, it is taxable at the time of allotment of shares.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The concept has certain advantages and disadvantages as given below:
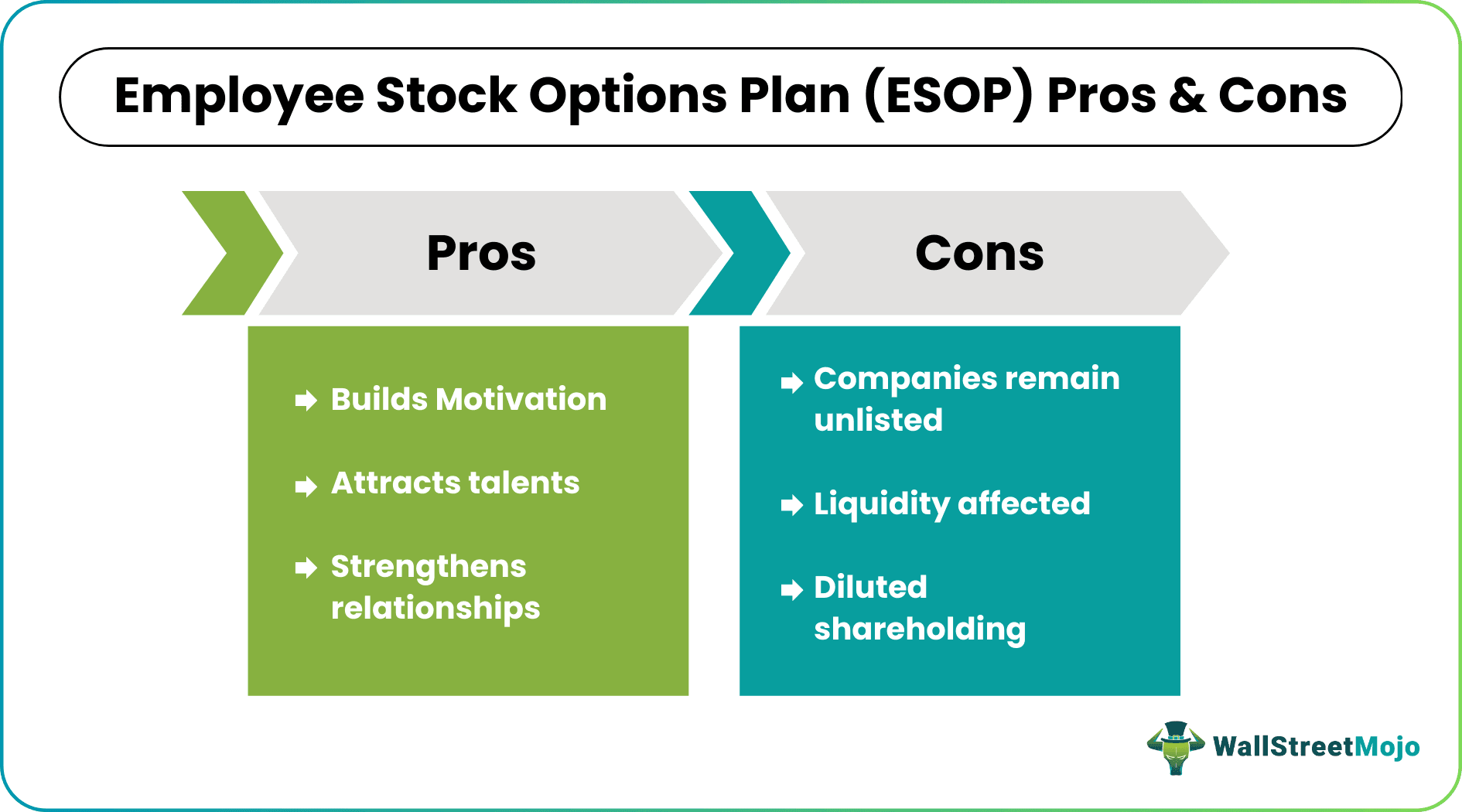
Advantages
- When companies offer Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP), it builds motivation among employees. They own a share in the company's stocks, which offers them a sense of belongingness, making them work even harder for the company's progress.
- The ESOPs motivate employees and strengthen the relationship between employers and employees. This is because the interest of the employees are aligned with that of the business. The employees are able to get a share of the success of the business and thus, it is obvious that they will take more initiative towards the growth and expansion of the company in future.
- In addition, these programs attract the best talents to join the company, which ultimately adds to its strength.
- Among employee stock option plan benefits, it is a good option in terms of retirement benefit which helps them in the future as the company’s performance improves.
- Employers often receive tax benefits for the ESOP scheme that they provide to their employees, providing tax advantages to them. The employees also get benefits related to tax due to this process.
- The employees get a stability in terms of their job because due to this process, the businesses are not able to suddenly terminate the jobs of employees who are under this scheme. If the companies do so, they need to cash out a huge financial compensation, affecting their cash flow.
- Sometimes the owners of the company may plan to sell of their stake and move out. In such cases, this method provides a ground to give away their shares, which already has a ready market. This is one of the employee stock option plan benefits.
Disadvantages
Besides the employee stock purchase plan benefits, there are a few disadvantages too that ESOPs are subject to.
- As the employees get a chance to own company shares, it dilutes the founders’ shareholding proportions.
- In addition, as the companies offering such schemes are unlisted, the shares’ liquidity is limited or non-existent. This, however, might lead to disputes between employers and employees.
- The share of every business is subject to certain amount of fluctuation in prices due to either internal or external factors. This is a huge risk from the point of view of the employee because the value of the shares may go up or down and lead to changes in the retirement benefit and savings amount in future.
- However, if the employees are too much dependent on this method to invest their money, they will not channelize their funds into other investment opportunities with better returns and this will lead to lack of portfolio diversification.
- Very often the employees are not fully aware of the important employee stock option plan rules and laws that come with this scheme. They often find the process unsuitable for them in the future, leading to dissatisfaction.
- The entire process definitely involves some good amount of legal requirements and complex rules. There are some administrative cost responsibilities that come with it from the point of view of the employers.
- Since these stocks can be sold only in case of employment termination or retirement, there is a rigidity in terms of sale ability. Thus, as per the employee stock option plan rules, the employees have very limited option of selling their shares or accessing their money during their employment period.
Thus, even though they are very useful tool for employee retention and company growth, they also come with their own share of limitations. Both advantages and limitation should be carefully analysed before adopting this process in order to understand its long term effects.
Employee Stock Option Plan Vs Employee Stock Ownership Plan
The above are two different types of stock ownership opportunities that companies provide to their employees. But there are some differences between them as follows.
- The former is the right to buy a certain number of stocks of the business at a price fixed beforehand within a particular time period. But the latter is a benefit where the employees become partial owners through purchase of the stocks.
- In case of the former, the employee can directly buy the stocks at a fixed value which is known as the exercise price. But for the latter, the employers can either give the stocks to employees or put money in a common fund from where the stocks are bought and allocated to employees based on their years of experience or salary levels.
- The main purpose of the former is to provide incentive or compensation to work better and continue showing their loyalty towards business performance. But the main aim of the latter is providing ownership and motivation. It is also a source of retirement fund for the employees.
Thus, both are powerful tools that attract and retain good talent of the industry through encouragement and participation.

