Table Of Contents
What Is A Holding Company?
A holding company is an entity that is not involved in the operational aspects of a business but exercises complete control over it based on its stock ownership. The firms these entities supervise and keep a hold on are referred to as their subsidiaries. As the subsidiaries grow, they have the liberty to decide and begin their journey independently without a controlling authority.
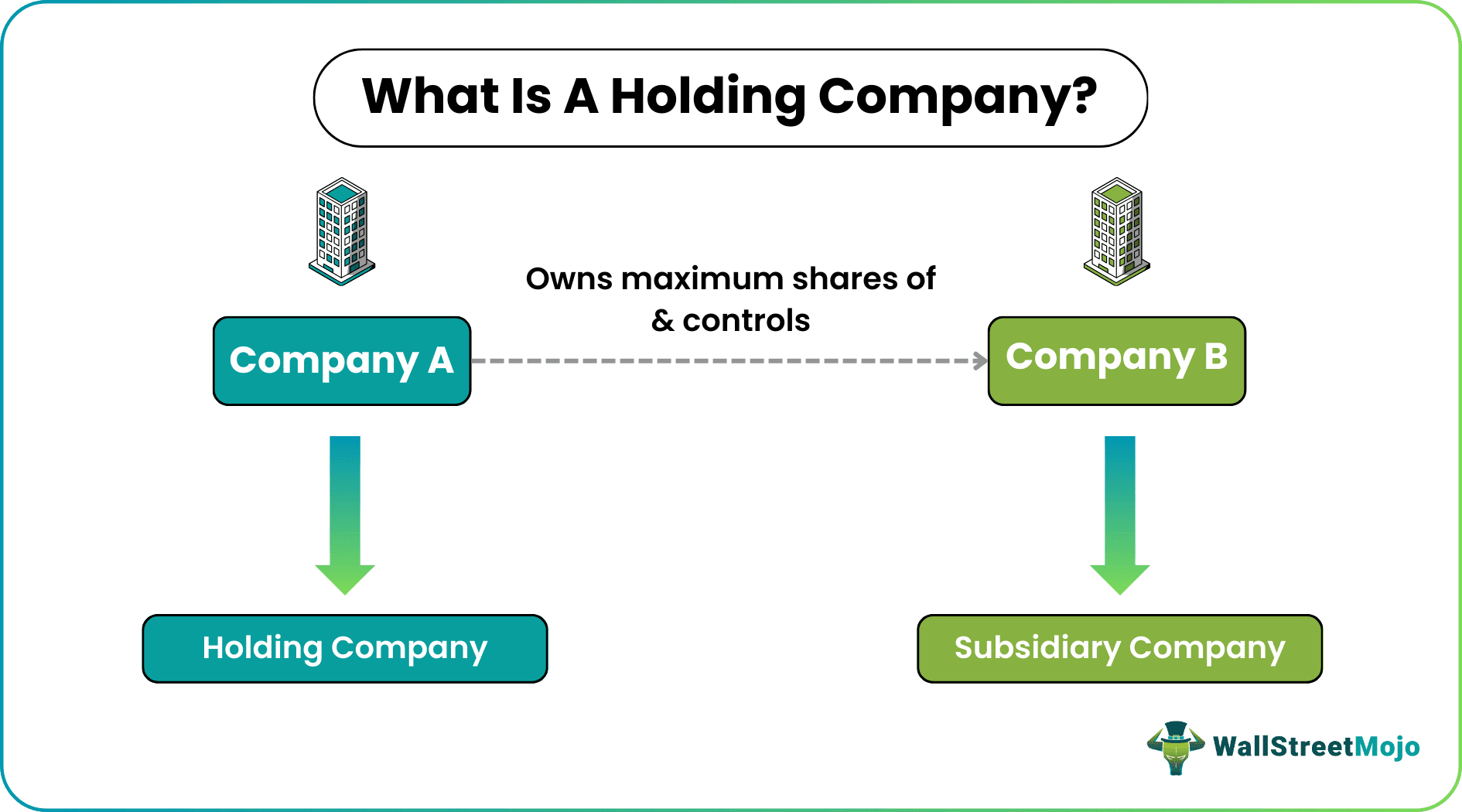
The only motive of the holding firms behind owning maximum shares of another company is to enjoy supremacy. Though these differ from a parent company's roles, responsibilities, and purpose, they are used synonymously in many jurisdictions. The first step in any case is to register the holding company structure, Articles of Association, and other such details with the state authorities.
Key Takeaways
- The holding company is the company that holds the majority voting shares of another company, referred to as its subsidiary. The former, however, enjoys full control over the management of its subsidiaries.
- All the directions and policies of the subsidiary are directed by these companies that typically do not produce anything or provide any service themselves but control it.
- Pure, mixed, immediate, and intermediate are some forms of holding firms found in the business sector.
- Such holding companies are not necessarily the parent companies of the subsidiaries.
Holding Company Explained
A holding company aims to gain control over more and more companies. They do it by owning stocks and assets belonging to the latter. These entities neither participate in selling the products and services that the firms under control manufacture and market nor are involved in any other business operations or activities. Instead, the sole purpose of those firms is to control and keep a watch on the subsidiaries.
It is important to learn how they are classified to understand the holding company's meaning. These entities are categorized as – pure, mixed, immediate, and intermediate – based on their function in the business sector.
- A pure holding firm is one whose only motive is to gain control over another company with no interest and participation in any other business.
- Mixed ones are those that already have a business and still look forward to controlling other companies.
- An immediate one is a holding entity under another holding firm's control.
- Intermediate holding companies are those that are themselves the subsidiaries of large corporations besides being held by another entity at the same time.
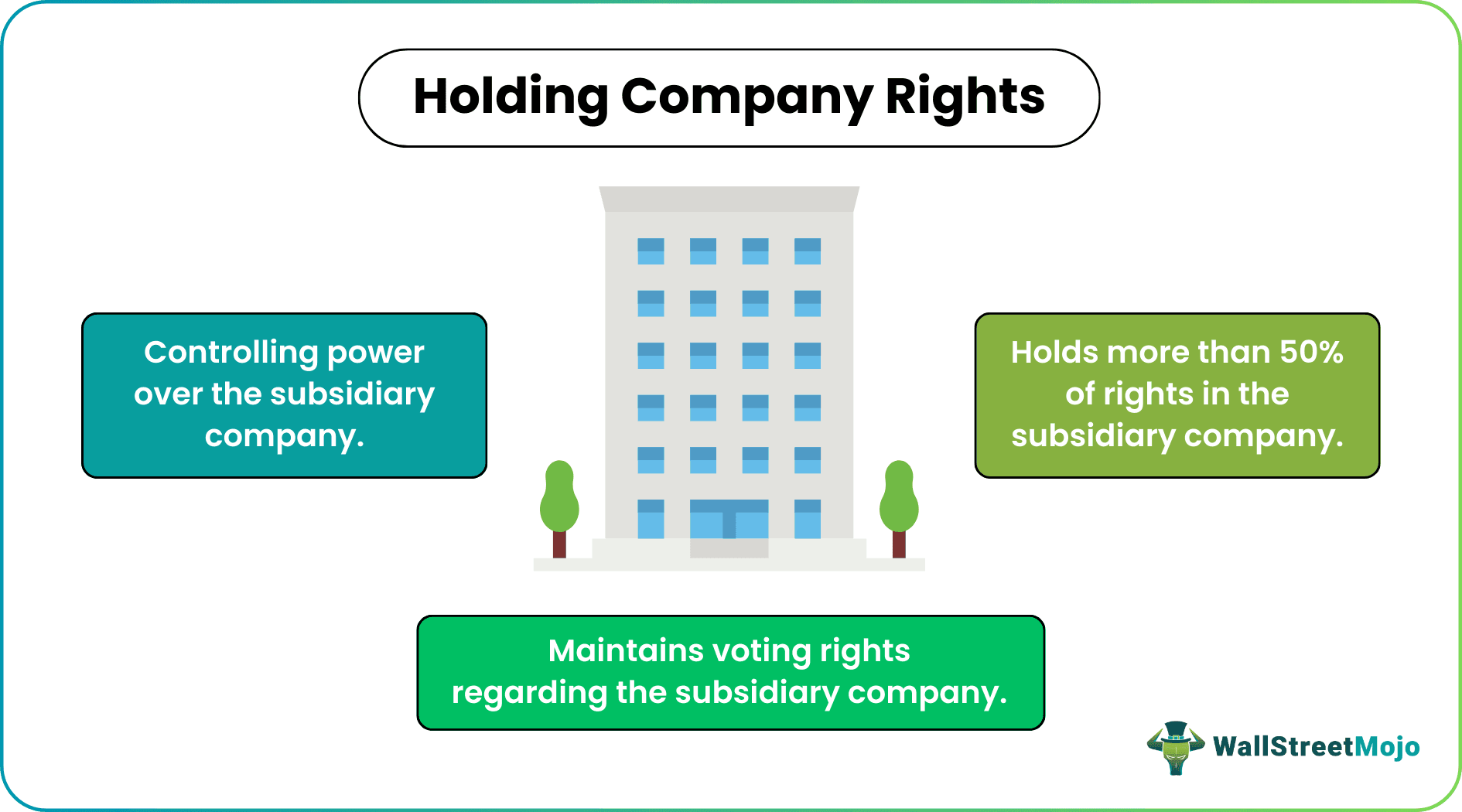
In most cases, these companies may act as the parent company and hold over 50% of rights in the subsidiary company through stock ownership. They may maintain voting rights in the companies they exercise control over and hold responsibility for tax obligations of the subsidiary and business operations and management of the sister concerns in the respective jurisdictions. As parent companies, if so to their subsidiaries, they could also become a guarantor for the latter in their financial requirements.
Holding Company Explained in Video
Purpose
Let us understand the very purpose of forming the basis of holding company accounting through the points below.
- Asset Protection: A holding company provides a layer of separation between the assets of different business entities it owns, shielding them from potential liabilities and risks.
- Risk Management: By holding multiple subsidiaries, each operating under its legal entity, a holding company diversifies risk. The failure of one subsidiary does not necessarily impact the others.
- Tax Efficiency: Holding companies can optimize tax strategies, leveraging tax incentives, and consolidating financial activities for improved efficiency in tax planning.
- Acquisitions and Investments: Simplifies the process of acquisitions and investments as the holding company can use its shares or capital to acquire or invest in other businesses.
- Facilitates Financing: Holding companies can raise capital more effectively by using the combined financial strength of subsidiaries for borrowing or attracting investors.
- Estate Planning: Facilitates estate planning by allowing for the smooth transition of ownership and control within the family or among stakeholders.
Types
Understanding the distinctions among the different types of holding company structures is crucial for businesses to adopt the most suitable structure aligned with their strategic objectives and industry considerations. Let us do so through the discussion below.
- Pure Holding Company: Holds the stock of other companies but does not engage in operational activities. Its primary purpose is to own and manage investments.
- Operating Holding Company: Not only owns the stocks of its subsidiaries but actively participates in their management and decision-making processes. It engages in operational activities alongside its subsidiaries.
- Intermediate Holding Company: Positioned between the parent and subsidiary companies, it serves as an additional layer for specific strategic reasons, often related to tax planning or regulatory requirements.
- Mixed Holding Company: Engages in both investment activities and operational activities, blending characteristics of a pure holding company and an operating holding company.
- Financial Holding Company: Primarily engaged in financial activities, such as holding the assets of financial institutions like banks and insurance companies.
- Diversified Holding Company: Holds interests in subsidiaries operating in various industries, providing diversification of investments and risk.
- Subsidiary Holding Company: Functions by holding the stock of other companies, and its primary purpose is to control and manage its subsidiaries.
- Minority Interest Holding Company: Holds a minority stake in another company, typically with no controlling interest, and may or may not actively participate in its management.
Examples
Let us consider the examples below to understand how and why such firms come into existence:
Example #1
In 2015, Google underwent a corporate restructuring and became a subsidiary of Alphabet, Inc., a newly formed holding entity for Google and many other related subsidiaries. It owns substantial intellectual property through its subsidiaries and is entirely driven by its earnings, cash flows, and assets. Over 85% of its total revenue in 2018 was generated from its primary business, i.e., advertising.
Alphabet, Inc. was formed with the underlying intention of narrowing Google's business scope, focusing on its core business, and creating a better management scale by running Google's subsidiaries separately.
Example #2
JPMorgan Chase & Co., one of the largest global investment banking and financial services holding companies, has over 40 subsidiaries worldwide in investment banking, asset management, and wealth management, which include JPMorgan Chase Bank, JPMorgan Asset Management Holdings Inc., JPMorgan Securities LLC, and Chase Bank USA.
Benefits
The concept of holding companies encourages the owners to make smaller investments and enjoy greater control over the subsidiary companies. The holding company and subsidiary company have a stake in the assets. While they share profits, they also enjoy limited liability in case of losses. The holding entity has multiple ownerships, and hence its liabilities remain divided, which makes it easier for them to handle the losses.
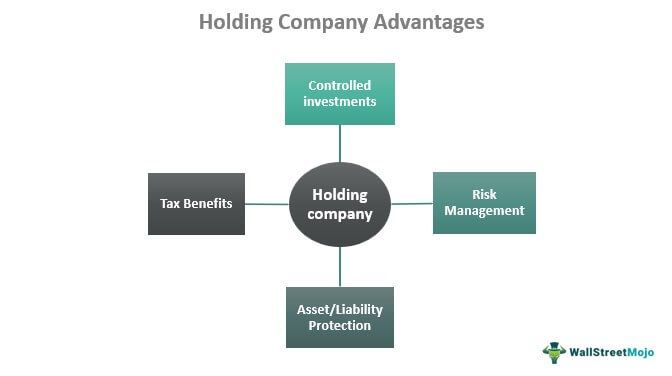
Holding companies that own 80% or more ownership in another firm can have significant tax benefits. First, they can file consolidated tax returns. As the name implies, this form helps add up the finances of all the acquired companies and a parent company for the holding firm. As a result, these companies get an opportunity to reduce their tax liability. On the other hand, the parent companies can enjoy tax advantage under the regional taxation laws by declaring the holding firm and its subsidiaries as entities of different jurisdictions.
In the UK, however, holding company accounting accounting for tax is different. There, it does not engage in operations and only takes an interest in holding the companies' assets. As these companies could only earn by leasing the owned assets to the subsidiaries, they hardly have any additional corporate tax liability.
Disadvantages
As holding companies do not confine themselves to owning one firm, it is difficult for the stakeholders to assess their financial health. The confusion that arises further due to multiple ownerships creates a rift between the parties involved. Moreover, the dispute between the holding firm and its subsidiaries makes the latter separate itself if its growth is significant enough to run a setup independently.
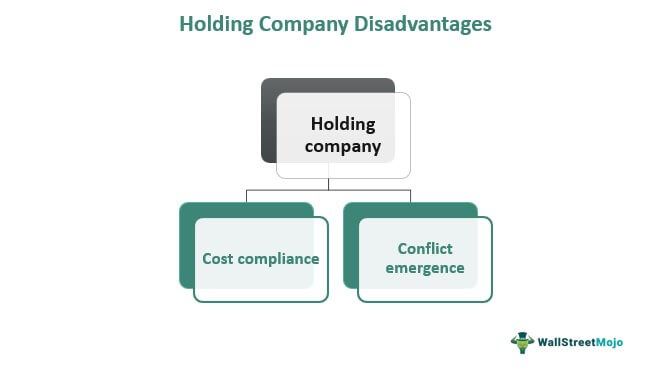
The formation of these entities involves various payments to multiple authorities. Hence, it becomes an expensive and complicated affair for the entities involved. Bearing compliance costs, therefore, becomes one of the major cons of setting up holding firms.
Holding Company vs Subsidiary Company
While the holding firm is the controller, the subsidiary is the one that is controlled. This is the basic difference between the two terms. In addition, the former is the one that owns more than 50% share of another company. In contrast, a subsidiary firm has more than 50% shares owned by another entity or corporation.
However, the holding and a subsidiary firm are not confined to remaining the controlling and the controlled entity forever. Instead, one holding firm can become a subsidiary of another holding entity, and if it grows significantly, a subsidiary company can hold shares of another firm.
Holding Company Vs Parent Company
Let us understand the distinctions between holding company structure and parent company through the comparison below.
Holding Company
- A holding company is a type of business entity that primarily exists to hold and manage investments in other companies. It owns the stock or assets of other businesses but often does not engage directly in day-to-day operational activities.
- Holding companies typically have a passive role, with limited involvement in the operational aspects of their subsidiaries. They are designed to oversee and coordinate strategic decisions rather than manage daily operations.
- The primary focus of a holding company is on investment management and risk diversification. Its purpose is to create a structure that allows for the efficient management of a portfolio of companies or assets.
- Holding companies usually have limited liability, meaning the risks associated with individual subsidiaries are isolated, and the holding company's assets are protected from the liabilities of its subsidiaries.
Parent Company
- A parent company is a business that directly owns and controls other companies, known as subsidiaries. It holds a majority stake in these subsidiaries, providing it with significant decision-making authority.
- Unlike holding companies, parent companies are actively involved in the day-to-day operations of their subsidiaries. They have a direct role in managing and overseeing the business activities of each subsidiary.
- The primary focus of a parent company is on the operations and success of its subsidiaries. It actively participates in the business activities of its subsidiaries and is responsible for ensuring their overall success and alignment with the parent company's goals.
- A parent company assumes more direct liability for the actions and obligations of its subsidiaries. It is actively engaged in the decision-making processes and management responsibilities., making it more directly accountable for the overall performance and risks associated with its subsidiaries.
