Table Of Contents
Set Range in Excel VBA
Set range in VBA means we specify a given range to the code or the procedure to execute. If we do not provide a specific range to a code, it will automatically assume the range from the worksheet with the active cell. So, it is very important in the code to have a range variable set.
After working with Excel for so many years, you must have understood that all works we do are on the worksheet. In worksheets, it is cells containing the data. So when you want to play around with data, you must be a behavior pattern of cells in worksheets. So, when the multiple cells get together, it becomes a RANGE. Therefore, to learn VBA, you should know everything about cells and ranges. So in this article, we will show you how to set the range of cells we can use for VBA coding in detail.
What is the Range Object?
Range in VBA refers to an object. A range can contain a single cell, multiple cells, a row or column, etc.
In VBA, we can classify the range as below.
“Application >>> Workbook >>> Worksheet >>> Range”
First, we need to access the Application. Then under this, we need to refer to which workbook we are referring to. Next, in the workbook, we are referring to which worksheet we are referring to. Then in the worksheet, we need to mention the range of cells.
Using the Range of cells, we can enter the value to the cell or cells, we can read or get values from the cell or cells, we can delete, we can format, and we can do many other things as well.
How to Access the Range of Cells in Excel VBA?
In VBA coding, we can refer to the cell using the VBA CELLS property and RANGE object. So, for example, if you want to refer to cell A1, we will first see using the RANGE object.
Inside the subprocedure, we need first to open the RANGE object.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples()
Range(
End Sub
As you can see above, the RANGE object asks what cell we are referring to. So, we need to enter the cell address in double quotes.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples()
Range ("A1")
End Sub
Once we supply the cell address, we must decide what to do with this cell using properties and methods. Now, put a dot to see the properties and methods of the RANGE object.

If we want to insert the value into the cell, we must choose the "Value" property.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples()
Range("A1").Value
End Sub
To set a value, we need to put an equal sign and enter the value we want to insert into cell A1.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples()
Range("A1").Value = "Excel VBA Class"
End Sub
Run the code through the run option and see the magic in cell A1.

As the code mentioned, we have the value in cell A1.
Similarly, we can also refer to the cell using the CELLS property. Open the CELLS property and see the syntax.

It is unlike the RANGE object, where we can enter the cell address directly in double quotes. Rather, we need to give a row number and column to refer to the cell. For example, since we are referring to cell A1, we can say the row is 1, and the column is 1.

After mentioning the cell address, we can use properties and methods to work with cells. But the problem here is unlike the Range object after putting a dot. We do not get to see the IntelliSense list.

So, it would help if you were an expert to refer to the cells using the CELLS property.
Code:
Sub CELLS_Examples()
Cells(1, 1).Value = "Excel VBA Class"
End Sub
Accessing Multiple Cells & Setting Range Reference in VBA
One of the big differences between CELLS and RANGE is using CELLS. We can access only one cell but using RANGE. We can access multiple cells, as well.
For example, for cells A1 to B5, if we want the value of 50, we can write the code below.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples() Range("A1:B5").Value = 50 End Sub

It will insert the value of 50 from cells A1 to B5.

Instead of referring to the cells directly, we can use the variable to hold the reference of specific cells.
First, define the variable as the “Range” object.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples() Dim Rng As Range End Sub

Once we define the variable as the "Range" object, we need to set the reference for this variable about what the cell addresses will hold the reference to.
To set the reference, we need to use the "SET" keyword and enter the cell addresses using the RANGE object.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples() Dim Rng As Range Set Rng = Range("A1:B5") End Sub

The variable "Rng" refers to the cells A1 to B5.
Instead of writing the cell address Range ("A1:B5"), we can use the variable name "Rng."
Code:
Sub Range_Examples() Dim Rng As Range Set Rng = Range("A1:B5") Rng.Value = "Range Setting" End Sub

It will insert the mentioned value from the A1 to the B5 cells.

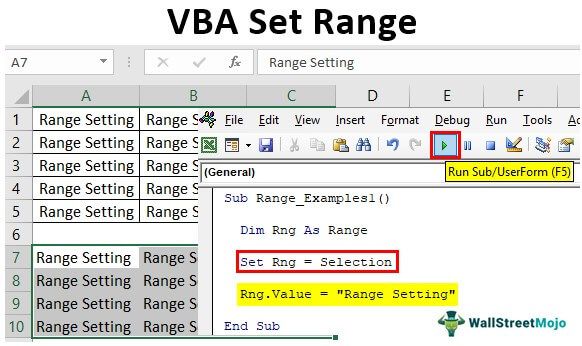
Assume you want whatever the selected cell should be a reference, then we can set the reference as follows.
Code:
Sub Range_Examples() Dim Rng As Range Set Rng = Selection Rng.Value = "Range Setting" End Sub

This one is a beauty because if we select any of the cells and run it, it will also insert the value to those cells.
For example, we will select certain cells.

Now, we will execute the code and see what happens.

For all the selected cells, it has inserted the value.
Like this, we can set the range reference by declaring variables in VBA.