Table Of Contents
Vendor Meaning
A vendor refers to an individual or an entity that sells products and services to businesses or consumers. It receives payments in exchange for making items available to end-users. They constitute an integral part of the supply chain management for providing raw materials to manufacturers and finished goods to customers.
A producer delivering final products to distributors and retailers and wholesalers supplying those products directly to consumers can also be a vendor. These immediate sellers can operate as business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and business-to-government (B2G), depending on their clients in the market.
Key Takeaways
- A vendor definition refers to an individual or business selling or supplying commodities and services to end-users.
- They deliver raw materials to manufacturers and finished goods to wholesalers, retailers, and customers as part of the supply chain management process.
- Their size and role vary with the business and client base. They could act as manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, service providers, independent, and operate as B2B, B2C, and B2G.
- Effective vendor management assures on-time product and service delivery, meets required standards, avoids supply chain risks and disruptions, and aids in the development of solid business partnerships.
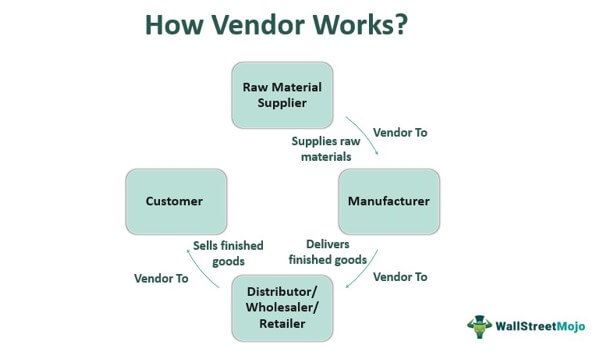
How Does A Vendor Work?
Vendor services differ depending on the company and its nature of business. Furthermore, sellers range in size from individual traders to large corporations. Suppliers of raw materials can be vendors to manufacturers that become sellers to wholesalers and retailers by delivering finished items. These retailers are vendors to customers for selling products to them.
Suppliers usually provide products that are ready to be utilized. Their diverse range may include the supply of drinking water, seafood, IT services, electronic goods, cleaners, outsourcing services, marketing consultants, etc. Besides, a street vendor or hawker sells goods or services in public without having a permanent store. Instead, it holds the sale in temporary structures or on mobile stalls.
The following steps explain how a supplier or seller works:
- The first step in the supply process is the buyer placing a purchase order for a product to the seller. The purchase order contains information about the product, price, delivery date, shipping details, and buying terms.
- Next, the seller collects the product and delivers it to the buyer. It, thus, fulfills the terms of the purchase order.
- At the delivery, the seller provides the buyer an invoice for the ordered product.
- After receiving the ordered product and the invoice, the buyer compares the invoice with the purchase order.
- On ensuring the accuracy of the invoice, the buyer makes the payment to the seller.
Characteristics
A supply chain primarily consists of:
Raw Material Supplier -> Manufacturer -> Distributor/Wholesaler/Retailer - > Customer
In this economic production chain, every party except the customer operates as a vendor at respective stages. Suppliers do not communicate with the manufacturer directly. Instead, they have more direct and personal contact with clients. Their relationships with buyers focus more on price variations.
At times, a supplier may become a business partner. It could assist with cost-cutting, product design advancements, and funding for ongoing marketing efforts.
Importance
Effective vendor management plays a vital role in:

You are free to use this image on your website, templates etc, Please provide us with an attribution link
- Cost management
- On-time delivery of products and services
- Improving customer satisfaction
- Providing better customer support
- Avoiding supply chain risks and disruptions
- Meeting quality standards
- Building stronger relationships with businesses and creating opportunities to negotiate for better pricing
Vendor Selection Criteria
Selecting suitable vendors from different categories is a crucial component of a company's growth strategy, as it paves the path for a positive working relationship. However, doing so will make the supply chain more efficient and cost-effective. Furthermore, choosing the right supplier gives a business competitive advantage and allows new companies to enter the market.
The selection process includes researching, placing a request for quotation (RFQ) and proposal (RFP), and shortlisting. Pricing is also a critical selection criterion for companies. Other deciding factors include reputation, track record, capacity to store and supply, and effective communication from sellers.
In the United States, vendor registration includes providing legal business name, tax classification, address, and tax identification number on the Form W-9. The United States Internal Revenue Service verifies these documents to generate a tax form for tax filing purposes.
Types Of Vendors

Based On Roles In The Supply Chain
#1 - Manufacturer
It refers to a person or company producing finished goods from raw materials or adding value to them for selling. A manufacturer can act as a supplier to wholesalers and retailers that will be selling products to consumers.
#2 - Wholesaler
It is the individual or company supplying products and services to other businesses. Here, retailers buy goods in large quantities and at feasible discounts.
#3 - Retailer
It purchases products directly from the manufacturer or a wholesaler and sells them to individual customers. The individual or business fixes the selling price, thereby making a profit.
#4 - Service and Maintenance Provider
It provides services in the fields of accounting, banking, insurance, consulting, transportation, etc.
#5 - Independent
It could be a person or company or a trade show representative selling products directly to consumers.
Based On Client Base
#1 - B2B (Business to Business)
It deals with products and services sold to other suppliers. An example of B2B is Hyundai Mobis that supplies automotive parts like batteries, tires, electronic systems, door locks, etc., to other sellers.
#2 - B2G (Business to Government)
It sells products and services directly to the government by obtaining a vendor license and special permissions based on contracts. Suppliers having experience in the private sector can also act as government consultants and offer their expertise to the public sector. An example of B2G is Lockheed Martin selling defense equipment to the military.
#3 - B2C (Business to Customer)
It sells product components or final products directly to customers. An example of B2C is Amazon.com selling different products, including clothing, apparel, electronics, furniture, cosmetics, grocery, etc., to end-users.
Examples
Example #1
Cloudtail India Private Limited is one of the biggest online retailers of Amazon India. It sells various goods to customers across multiple categories, including books, media, shoes, beauty products, home appliances, travel accessories, consumables, and so on, across India.
Example #2
EasyLeadz is a crowdsourcing vendor operated by SponsifyMe Technologies Private Limited in India. Its Mr. E by EasyLeadz chrome extension combines machine learning with artificial intelligence to fetch highly accurate B2B contact information. It allows professionals to enrich and verify business profiles with mobile numbers.
The software filters data based on location, industry type, number of employees, etc. Using this online B2B database, sales, marketing, recruitment, and management professionals can connect with their contacts, leads, and candidates. It, thus, results in increased productivity and revenue.
