Table Of Contents
What Is The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA)?
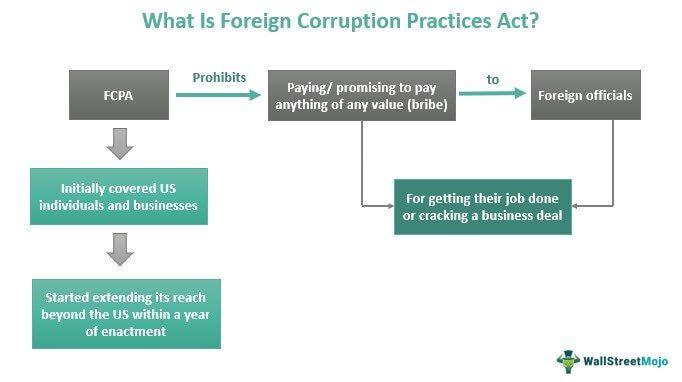
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) is the law that prohibits businesspeople from paying or promising to pay anything valuable to foreign administrative officials or entities for getting a job done or cracking a business deal. In addition, it ensures the prohibitions apply to bribery instances across the globe to prevent violation of law and order.
FCPA prohibits corruption practices concerning both anti-bribery incidents and accounting requirements. It ensures the accounting practices involve no bribes and the company finances are presented accurately without tampering. The publicly traded companies and their direct and indirect stakeholders remain under regular FCPA scrutiny.
Key Takeaways
- FCPA is a law made in the United States to stop businesspeople from making payments in the form of bribes to foreign government officials to secure their businesses.
- For FCPA, the foreign official is quite a broad term, with people from the ministry of finance to professional doctors working in a government-owned hospital
- and employees of any international organization all included in the list.
- It deals with both anti-bribery as well as accounting provisions.
- The act requires the listed corporate entities to maintain transparent books of accounts. It further mandates the said corporate entities to conduct internal audits periodically.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act Explained
The US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, which was enacted in 1977, prohibits businesses from acquiring or retaining deals through illegal ways using bribes. Instead, it introduces a fair platform for corporate players to gain the contracts only on their competitive spirit and merit. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Department of Justice take the joint responsibility of checking FCPA enforcement.
Bribing disrupts the fair economic environment in the country. Therefore, the justified chance of each competitive person is unserved. The act applies to all US persons and issuers of securities belonging to foreign countries. Within a year of its enactment, it extended its applicability to foreign firms and people who make such payments within the US. The act mandates that companies maintain transparent records.
The FCPA restricts companies from paying fines for their officers, employees, directors, agents, etc., making them pay from their pocket. Further, the guilty may be debarred from certain benefits normally available under any government scheme. Such benefits might include obtaining export licenses, participating in federal programs, operating under the securities law board, etc.
Violations
The violation of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977 seriously affects the persons involved in paying bribes or other provisions. Under FCPA, the violation can be civil or criminal per the RICO (Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organisations) Act.
Individuals involved in the case may face an imprisonment of up to 5 years for each violation that falls under the anti-bribery provisions. Furthermore, the imprisonment might extend to up to 20 years if the offense proves to be a willful act. In such cases, the involved individuals are subject to the payment of a fine of up to $1 lac.
Companies are corporate persons with a corporate veil. Therefore, the authorities cannot imprison companies, which are artificial entities and not individuals. The act, however, can make companies pay a fine of up to $2 million for each recorded violation.
FCPA has a provision to increase the fine to up to $25 million for corporate persons and up to $5 million for common individuals involved. However, such penalties may be small for a corporate entity flourishes with cash reserves. The Alternative Fines Act comes into play for such a situation, doubling the penalty amount in criminal fines. However, proving the Act of bribery as a criminal act is the task of the government's lawyers.
Provisions
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act definition can be understood only when the aspects of corruption it covers are properly explored. For example, the FCPA includes anti-bribery and accounting provisions. The anti-bribery provision provides a ban/prohibition on the payment of bribes to foreign officials in the form of money or anything having a monetary value , with the intent of acquiring or retaining an existing business.

On the other hand, accounting provisions require corporate players to maintain appropriate and adequate records and financial statements, confirming the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The provision further requires corporate players to maintain control over internal financial records.
The act requires the listed corporate entities to maintain transparent books of accounts. It further mandates the said corporate entities to conduct internal audits periodically. Thus, many companies are ensuring due diligence compliance at their end to assure fair dealings with foreign officials. In addition, many companies have an FCPA Compliance Program, which summarizes all the transactions.
Examples of Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
Let us consider the two recent Foreign Corrupt Practices Act examples to understand how it works:
Example #1
In October 2021, global investment bank and financial services provider Credit Suisse had to pay around $100 million to SEC for misleading investors and violating the FCPA in a deal involving three financial instruments that helped raise funds on behalf of entities in Mozambique.
Example #2
In June 2022, a global steel pipe manufacturer and supplier had to pay over $78 million for violating the FCPA's anti-bribery and accounting provisions in an instance involving a bribery scheme of its Brazilian subsidiary.
Exception
The FCPA clearly distinguishes between bribery and facilitation. Facilitation also termed grease payment, deals with officials expediting a deal. Here the decision of approval or disapproval of the deal has nothing to do with the decision-making of the foreign administrative officials. Thus, such payments do not fall under the category of bribes.
In short, FCPA is effective only when illegal payments aim to influence foreign officials' decisions in favor of one's business. Conversely, the payments made to the officials to speed up or bring into execution the overall process remain exempted from the FCPA coverage.
