Table Of Contents
What Is A Growth Stock?
Growth stocks are stocks of a company's shares with a high price-to-earnings ratio but yield capital gains in the long term for an investor, higher than the market average. Such stocks reflect those companies in a portfolio that generate higher sales and earnings for its investors but do not pay dividends.
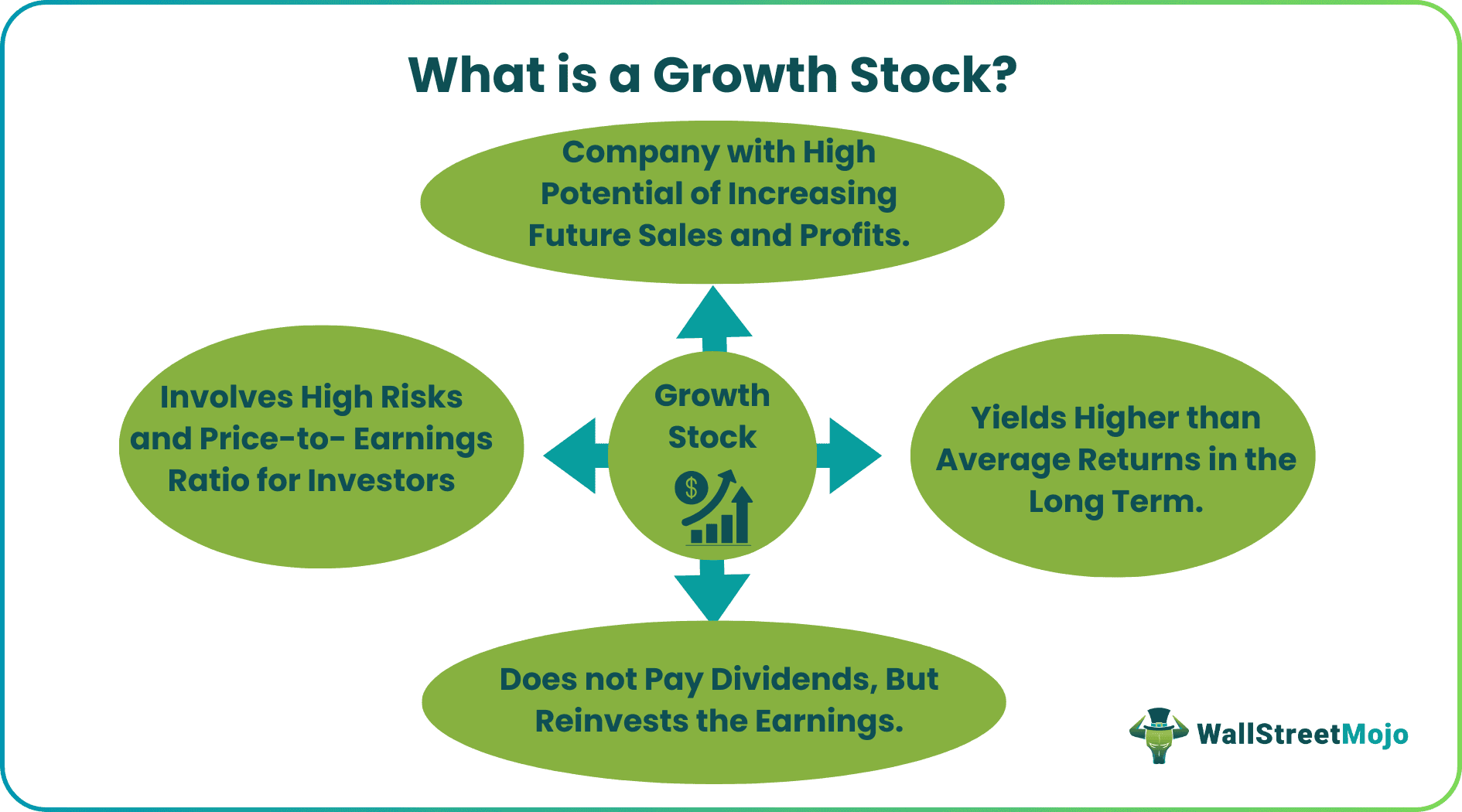
Growth stocks can belong to any company or industry, depending on their ability to grow business and achieve higher earnings. However, from an investor's point of view, investment in a growth company also involves high risk as the investors' returns depend on the sustainability of the company's future earnings and market share.
Key Takeaways
- Growth stock defines the stocks of a company yielding higher returns or capital gains for its investors in the long term when compared to the market average.
- These stocks have a high price-to-earnings ratio. Thus, growth investors pay a high price per share initially but yield higher returns in the future because the company or industry has immense potential to earn increasing profits and returns.
- Growth investors are prone to higher risk, but they might mitigate their portfolio returns with dividend or income stocks that provide regular returns for their investors with lower risks and volatility.
Growth Stock Explained
A growth stock highlights those companies with huge market capitalization and high capital gains. Additionally, investors who invest in these long-term growth stocks expect and rely on increasing future earnings and market capitalization. Consequently, the investor expects the stock value to grow faster and higher than the market average.
Initially, stocks of growth companies have a high price-to-earnings ratio for an investor. It reflects increasing share prices and demand for the company. Thus, in the expectation of higher wealth accumulation from future returns, an investor purchases the highest growth stock.
The earnings for an investor are through capital gains, and there is no growth stock dividend. The stock's initial price is expensive; however, if the company continues to grow at an increasing pace, the stock prices will increase in the future. Thus, investing in growth companies is suitable for investors prone to risky investments. But these stocks do not yield high current earnings.
As a result, such investors maintain a balanced portfolio to have a cushion in case high-growth companies yield poor returns in the future and the company's earnings and market capitalization fall. Additionally, maintaining a balanced portfolio may assist the investor in having stable current earnings through dividend stocks.
An investor shall bear huge losses if the growth companies do not yield the expected returns or profitability in the long run. However, to offset such losses, an investor can determine the growth companies through their price-to-earnings ratio on any stock exchange.
Higher growth stocks usually have a high price-to-earnings ratio and belong to companies in a booming industry. Examples of such industries with profitable long-term returns are biotech, software and information, technology, or innovation-based industries.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Characteristics
An investor shall determine the higher growth stock or those with high profitability by the following traits,
- Price to earnings or P/E ratio – It indicates the value of a company that compares its current per share price to its relative earnings per share. The initial returns for the investor will be low due to the high price per share. However, it is also important to note that stocks reflecting a higher P/E ratio may not always belong to growth companies.
- No dividends – Growth companies usually do not distribute dividends to their shareholders as the company aims to reinvest profits and earnings into the business. The high potential for increased future revenue and earnings of the company incentivizes the growth investors to invest for the long run with hopes of capital gains in the future.
- Booming Industry – An investor can determine growth companies trading on any exchange. A growth company or industry will yield higher than average returns and substantial cash flow in the long term. In addition, a company's balance sheet assists in determining its earnings and profitability to estimate future returns.
- Technology and Patent – Such factors may set a company or industry apart from others due to its innovative potential. Deciphering technologies through research and development can significantly increase the trust of customers, investors, and other stakeholders. Simultaneously, it can increase the future value of the stocks of a growth company.
- Price earnings to growth (PEG) ratio – The price to growth ratio shows a more honest picture of investors' returns. The PEG ratio accounts for the annual increase in total earnings per share for a business.
Examples
Let us look at a few examples of growth companies to understand the long-term growth stock and its characteristics better,
Example #1
According to Forbes advisor, one of the best growth stocks of 2022 is Alphabet. It is the parent company of Google, YouTube, and other popular enterprises. The company has a three-year annualized earnings per share of 37%.
Additionally, its class A stock (GOOGL) also its highly profitable stocks yielded $16.4 billion in net income. This trend reflected in the stocks of Alphabet has set the company apart from other high-profile growth stock companies in the same industry, struggling to create a profitable business model.
Example #2
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, has proven to be an excellent investment for any focused growth investor, especially those who invest in one company. The company's mind-boggling growth of 1500% over the last decade while its stock prices increased 65% from 2020-2021.
However, investing in one company as a growth investor is also risky, irrespective of the large market capitalization. Risk factors like natural calamities, pandemics, adverse market environment, loopholes in operations, or loss in customer and other stakeholders' trust can quickly throw a company's growth stock into volatility and lead to a crash.
Growth Stock vs Dividend Stock vs Income Stock
The growth stock definition explains the stocks which yield substantially high returns and cash flows for investors in the long term. In contrast, the dividend stock or value stock yield normal but continuous dividends for its investors.
The value stock companies share the earnings and returns with their investors, unlike the growth companies. Growth companies focus on increasing the company's potential by reinvesting their earnings.
Value companies have a low risk and volatility profile as they are unwilling to undertake any major risks or investments to increase their potential earnings. Thus, stocks of value companies are in demand and are easily available on exchanges, with normal but continuous earnings.
However, in the case of a bull market, the stocks of value companies lag behind the growth companies. Thus, a balanced portfolio of both stocks is a safer investment option.
An income stock defines security that yields regular and increasing returns or dividends for its investors. These types of stocks generally have a low-risk profile and less volatility. As a result, income stocks generally belong to companies with increasing annual profits, good market reputations, and trust amongst stakeholders.
Thus, the income stocks' shareholders receive continuous and higher than average yields. Unlike growth investors, income stock companies have sustainable business models and extremely low volatility. Like growth companies, income stock companies compensate their investors for rising inflation that may eat into future cash earnings.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Growth mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are a compilation of growth stock companies of an industry that have an edge over other competitors due to higher earnings and profits. These factors promise capital gains to growth investors against long-term investment but also involve high risks. These are categorized based on small, mid, and large market capitalization.
These stocks have various characteristics, such as a high price-to-earnings ratio and a high price earnings-to-growth ratio which highlights increasing share price returns for investors annually. At the same time, a company's balance sheet or annual financial statement also reflects its profitability and earnings status. Thereby, growth investors can identify such stocks in any of the top exchanges and make capital gains.
Value stocks are stocks of a company that provides regular dividends to its investors. These are different from growth stocks, as value stock companies don't reinvest all their earnings and profits into the business, unlike growth companies. Instead, as the growth companies show immense potential for higher future earnings and profits, it reinvests their earnings, ensuring investors of future capital gains.

