Table Of Contents
What Is Personal Income?
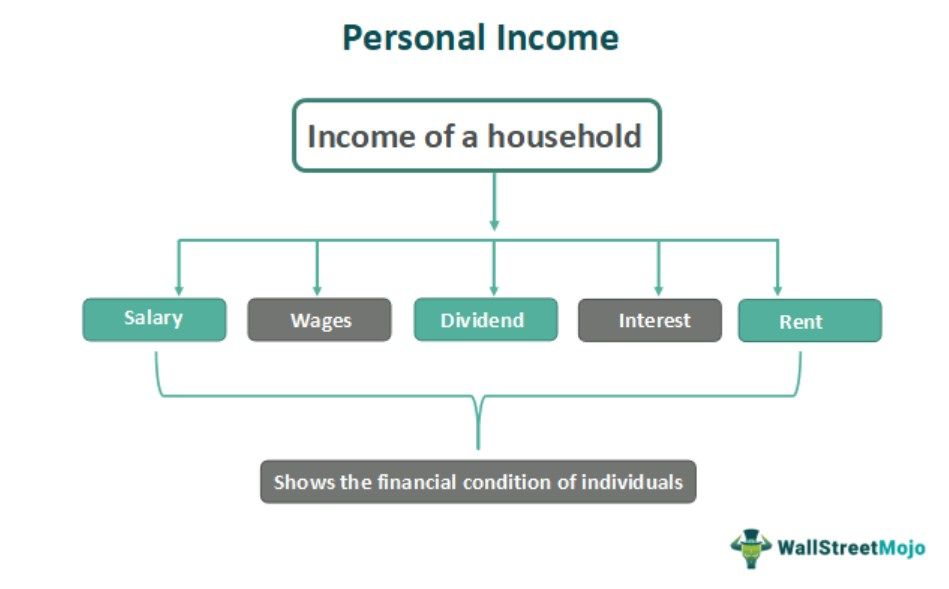
Personal income refers to all the earnings made by a household in a given year. It includes various sources of revenue like salaries, wages, investment, dividends, rent, contributions being made by an employer towards any pension plan, etc.
This concept has been used in computing the adjusted gross national income in economics. As a result, it has become a major tool for investors to predict future demand for goods and services easily. There are three measures of national income, of which personal income is the one reported to the national income and product accounts being maintained by the Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Personal income means all a household's earnings in a given year. It involves different revenue sources such as salaries, investments, wages, dividends, contributions by an employer towards any pension plan, and similar things.
- One uses this concept in estimating the adjusted gross national income in economics.
- As reported by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, personal income is among the three measures of income.
- Disposal income and national income are the other two measures. In addition, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Net Domestic Product (NDP) are interrelated production measures.
Personal Income Explained
Disposable personal income is the household's measure of income and includes income not necessarily earned by them. It may take the form of social security benefits, unemployment benefits, welfare compensation, etc.
The undistributed share of profits not received by the individuals, indirect business taxes, and employers' contributions towards their employees' social security are some additional examples of personal income.
Revenue vs Income Explained in Video
Types
A major portion of disposable personal income cropped up from factors of production like land, labor, capital, and entrepreneur, which includes rent, salaries, wages, interest, and profits, respectively. We will describe each component in detail now.
#1 - Salaries/Wages
Salaries and wages earned by individuals and households form 60% of personal income. Therefore, according to the national income and products accounts, the official term for labor is wages, salaries, and other labor incomes.
#2 - Rent
The rental income received by the individual household members forms part of the personal income statement. The owners collect the rent from the properties, land, plant, or any equipment given on rent. The rent forms around 2 to 3% of personal income.
#3 - Interest
According to national income and product accounts, maintained by the Bureau of Economic Standards, the official term used for interest as a component in personal income statement is personal income. The interest comes from bank accounts, fixed income securities or bonds, or any other loan form. Interest forms 10% to 13% of PI.
#4 - Profit
Profit is the entrepreneur's share of his capital in the business. The dividend is the official entry for the profit in the personal income formula. The dividend varies from 2% to 4% in the personal income. In addition, there are other forms of business profit not distributed called retained earnings and corporate taxes on the gains.
#5 - Proprietor’s Income
In proprietorship and partnership, owners do not receive salaries or wages. Instead, they receive a share of profits from the league, known as the proprietor's income. It forms around 10% of PI.
#6 - Transfer Payments
The components mentioned above are the income that is earned and received. The relative forms around 80% to 85% of personal income. The rest of 15% to 20% comes from transfer payments. Transfer payments are the income that has been received but not earned by the factors of production. Major examples of transfer payments are social security benefits, welfare payments, and unemployment compensation.
Formula
Let us look at how to calculate annual personal income.
Where,
- PI = Personal Income
- NI = National Income
We can also express it in the following forms: -
OR

How To Calculate?
The following are the two approaches that are used to calculate annual personal income.
1) In the first approach, personal income can derive by taking the sum of all the income received by the household members.
PI = Salaries/Wages Received + Interest Received + Rent Received + Dividends Received + Any Transfer Payments
2) The second approach can be derived by adjusting the national income with the income received and earned and income not earned but received.
PI = NI + Income Earned but not Received + Income Received but not Earned.
#1 - Income Earned but not Received
The three major incomes earned but not received are undistributed profits, taxes on social security, and corporate taxes. The social security taxes are the contribution being made by laborers; undistributed profits are the business's share of earnings for future business opportunities. Finally, the corporations pay corporate taxes on the business's profits.
#2 - Income Received but not Earned
The three major sources of income received but not earned are social security benefits, unemployment benefits, and welfare payments. The household members receive these three incomes from the government. Social security benefits are paid to elder citizens, disabled people, and retired citizens.
Unemployment compensation is being paid to the unemployed members of the household by the government to maintain the normal standard of living. Lastly, welfare benefits are being paid by the government to the poor sections of families.
Examples
Now, we will explain the concept with the following examples.
Example #1
Let us assume individual James has the following sources of income: -
Solution:
Use the given data for the calculation:-

PI = Salaries + Interest Income + Rent Income + Dividend Income + Transfer Payment
The calculation can be done as follows:-

- PI = $1,00,000 + $8,000 + $7,500 + $3,000 + $2,000
PI will be -

- PI = $120,500
Example #2
In this example, we will calculate the personal income of the United States of America as a whole by considering all the household members of the United States. Following are the data related to United States national accounts: -
Solution:
Use the given data for the calculation: -

The calculation can be done as follows: -

- PI = $8,500.00 + $1,350.00 + $700.00 + $1,550.00 + $2,800.00 + $1,518.00
PI will be:-

- PI= $16,418.00
Example #3
In example 3, we will calculate the personal income in economics by adjusting the national income.
Solution:

We can use the following formula to calculate personal income in this example.
PI = National Income – Income Received But Not Earned + Income Earned But Not Received
The calculation be done as follows: -

- PI = $25,000.00 - $2,800.00 + $2,000.00 + $1,200.00 + $2,000.00 + $30.00 + $500.00
PI will be: -

- PI = $16,470.00
Uses
- As mentioned above, personal income in economics is among the three measures of income being reported by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. Disposal Income and National Income are the other two measures. In addition, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Net Domestic Product (NDP) are two interrelated production measures.
- It is primarily used to measure the income being shelled out to members of the household sector and provides the basis for consumption expenditure in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) after adjusting income taxes.
Personal Income Vs Business Income
- The former comes from sources like rent salary, commission, wage etc, whereas the latter comes from businesses and corporations.
- For the former, tax is paid on the amount an individual earns whereas for the latter, the tax is paid on the annual returns of the corporation.
- The former pay taxes per their income according to the income tax slab, whereas the latter calculation depends on the amount of profit.

