Table Of Contents
What Is A Trust Account?
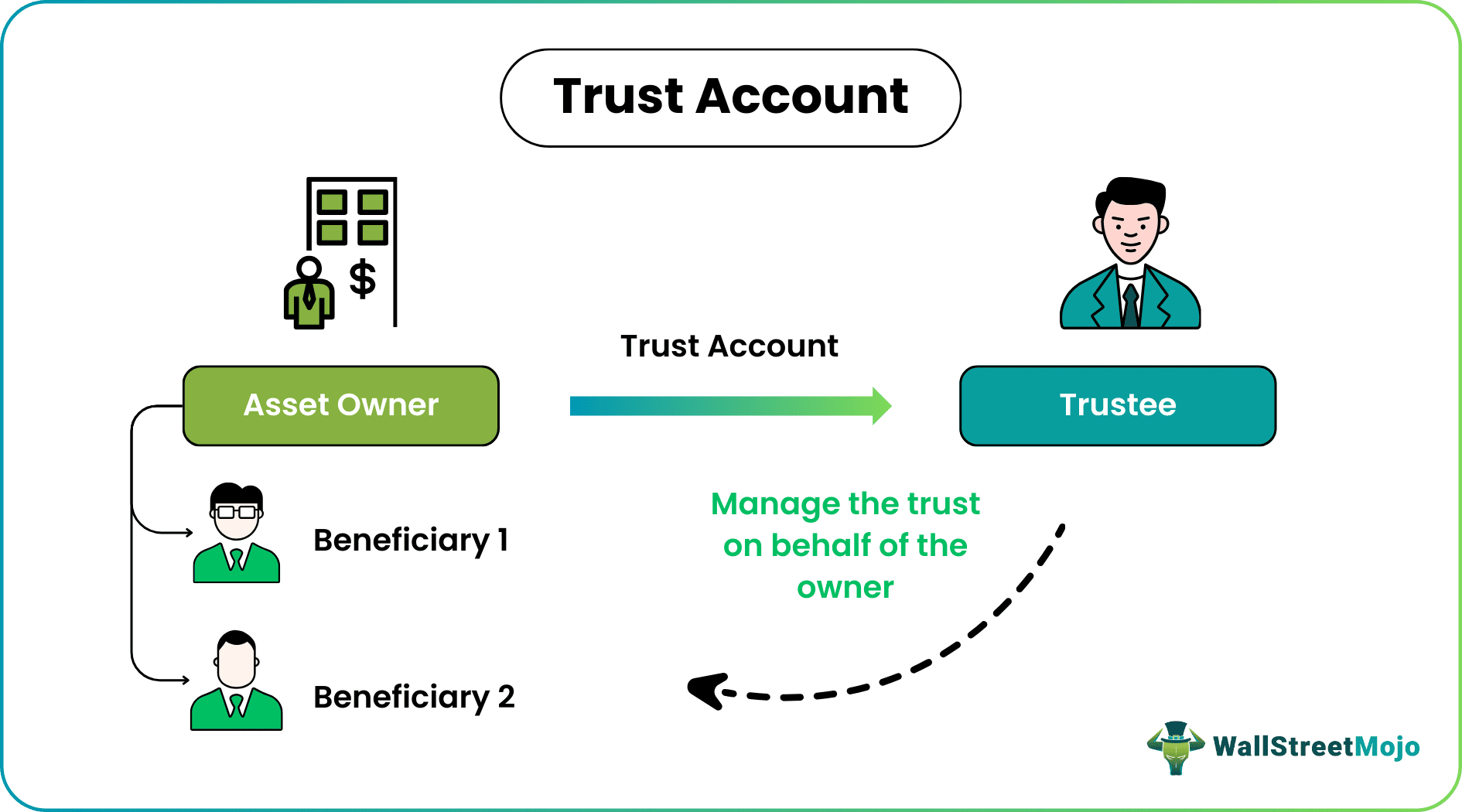
A trust account is created to encapsulate a specific asset or set of assets held in an individual capacity to be managed accordingly for specified beneficiaries. The beneficiary can be a group of any individual. This type of account is expensive to manage.
There can be various uses of this account ranging from paying off mortgages and insurance premiums by the bank on behalf of its customers to handling a real estate property to be inherited. It is a legal process that is arranged for the purpose of managing any assets on behalf of the beneficiary.
Key Takeaways
- A trust account is created to manage specific assets for designated beneficiaries.
- Trust accounts have various purposes, such as handling real estate or paying bills on behalf of the beneficiaries.
- The trust creator is called the settlor or grantor, and the third party managing the assets is the trustee. The beneficiary is the individual who benefits from the trust account.
- Setting up a trust account involves selecting the trust type, appointing a trustee, determining assets, drafting and filing relevant documents, and initiating the bank's account setup process.
Trust Account Explained
A trust is a financial account opened and managed by the trustee to overlook and manage the assets or funds of the beneficiary as per the legally binding arrangement.
The creator of the trust is known as a settlor or grantor. A trust account is an important tool for estate planning.
When a trust is created, the party transfers all the legal ownership of the property to the third party (individual or group) responsible for properly handling the property in case of trust account in real estate.
This third party is known as the trustee, and the party for whose benefit the trustee manages the assets or funds is known as the beneficiary.
The trust does not have any of the property’s powers until the beneficiary transfers the assets or the funds into a trust account. Generally, a bank or other financial institution acts as the custodian of the trust’s assets.
These custodians place the assets in the trust account under the name of the trust after opening a trust account. After that, they will only do all the distributions and expenses related to the beneficiary from this account.
Rules
- “Funding the trust” is one of the most important features of opening a trust account. It is the process under which the funds or assets are transferred to a trust. If property ownership is not transferred to a trust, it cannot manage it.
- The trustee must be a mentally competent adult responsible for handling a trust account.
- A trustee has full authority concerning making any changes in the account except if specifically mentioned otherwise in the agreement.
- It is the trustee's fiduciary duty to act in the best interest of beneficiaries.
- According to the state laws prevailing in the particular state, the trustee's responsibility is to file annual tax returns. However, it may have to file regular accounting at the beneficiary's request.
- One must do all the distributions and expenses related to the beneficiary from his trust account.
Types
Many types of trusts somehow have the same functions but serve different purposes. An escrow account, for example, is a type of trust account for real estate, through which a mortgage-lending bank holds funds to pay property taxes and homeowners’ insurance on behalf of the home buyer. The availability of the type of trust depends on the state law prevailing in the jurisdiction. It has basic four classifications, which include: -
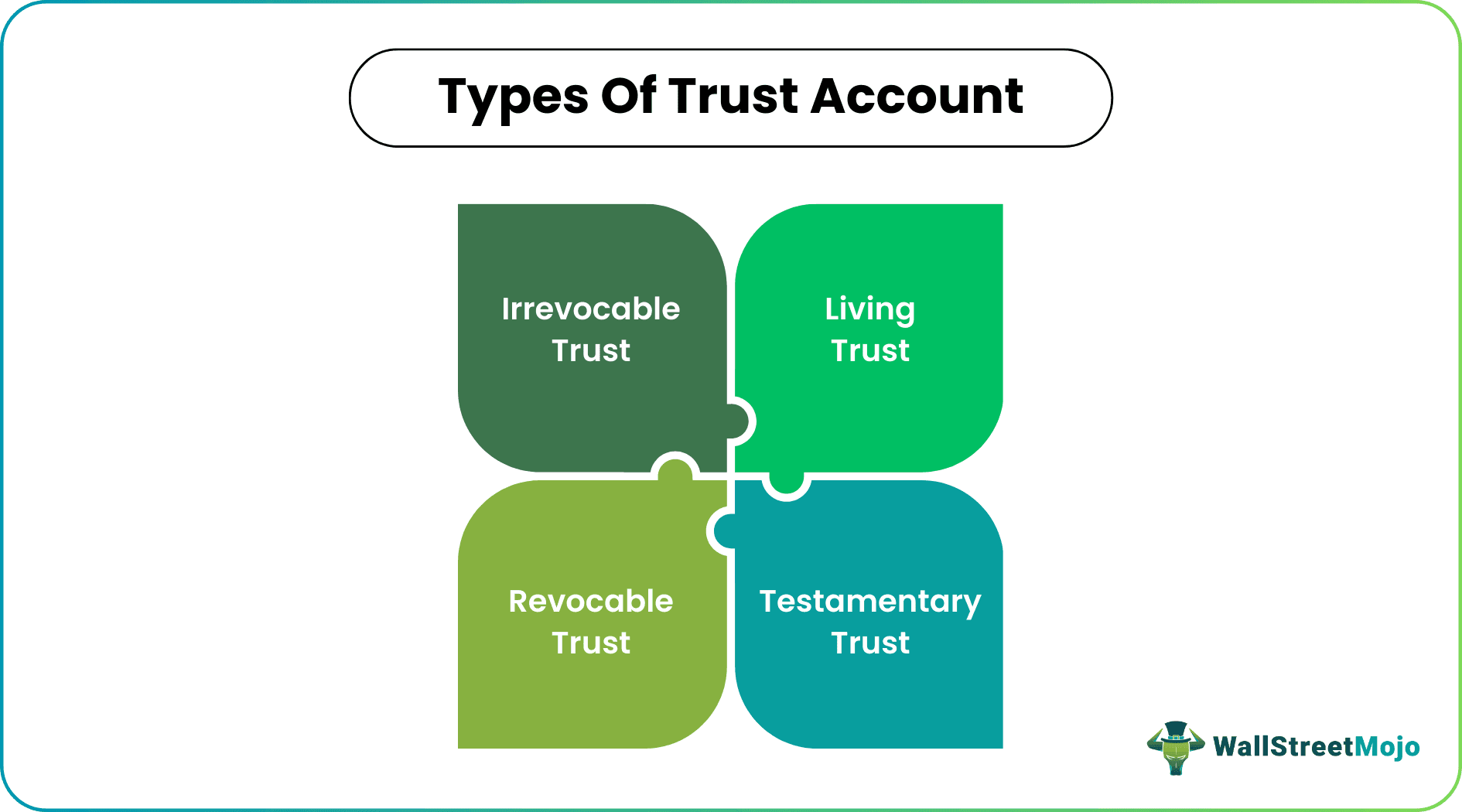
#1 - Living Trust
The trust is enforceable during the lifetime of the trust's creator, i.e., the settler.
#2 - Testamentary Trust
It is the trust that is enforceable after the death of the settlor.
#3- Revocable Trust
The trust having the clause gives the settler the right to change or terminate the trust agreement.
#4- Irrevocable Trust
Under this, the settlor is restricted from making any changes in the agreement or terminating the trust. Once the settlor transfer property under this account, the right of ownership is given up in case of trust account in real estate or any other property.
Thus, one has to first decide about the type of trust account it is interested in, then it has to decide who should be the trustee, who all will be the beneficiaries, and all the assets that one can transfer into the trust account.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept.
Stella is 40 years old and is the owner of Star Industries, a fast growing cosmetics manufacturing company and has two kids. She wants to make financial plan for her kids and wants to set up two trust accounts for each of them. Thus, it is a trust account for minors in this case.
After consulting her trust account lawyer, she decides that each account will start disbursing the college fees once they take admission, which will be directed paid to the institution. Later the trusts will also manage the expenses for any professional level education.
How To Open?
The following are the steps that are followed while setting up a trust account: -
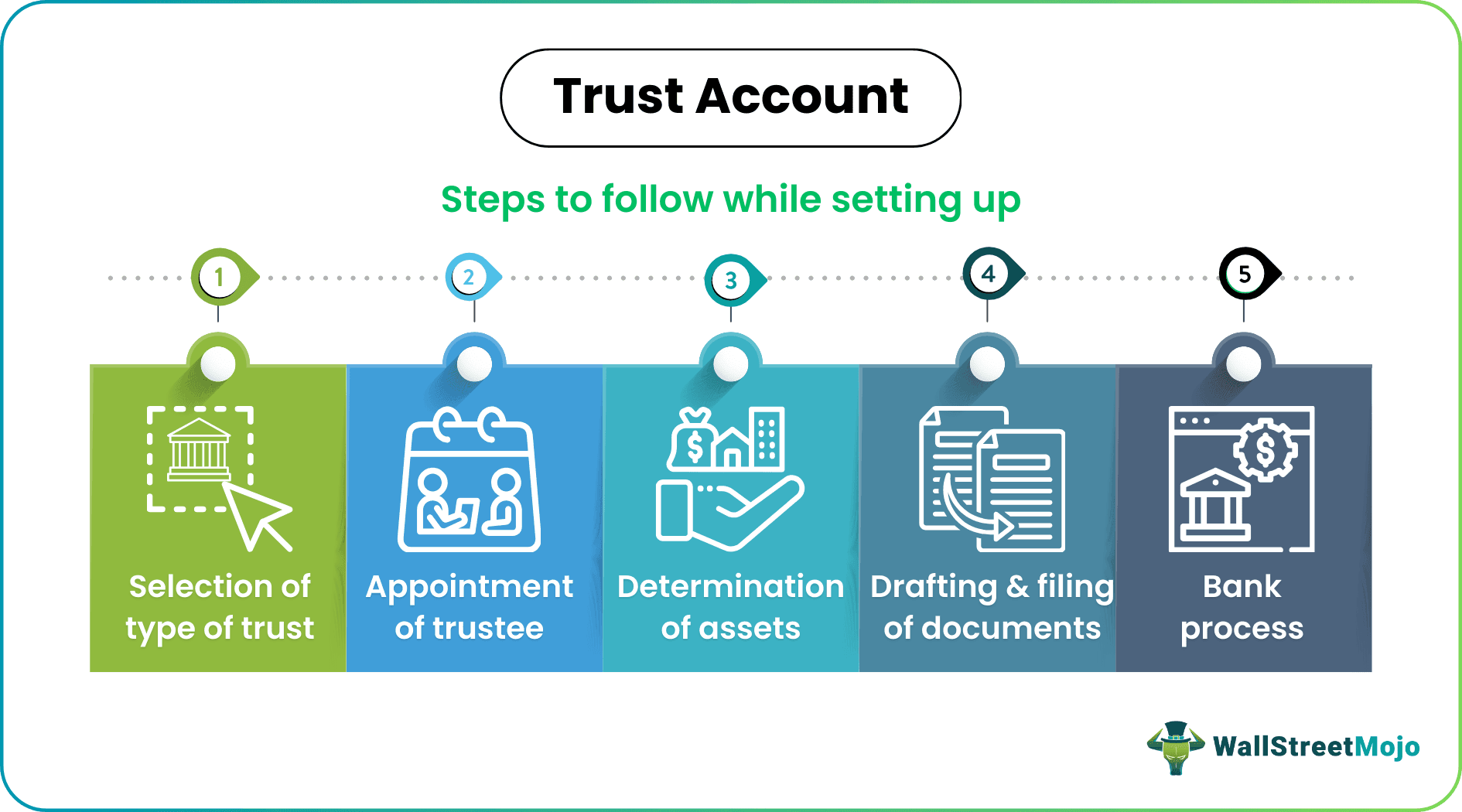
#1 - Selection of Type of Trust
The first step in setting up a trust account is to decide the type of trust that suits the particular person best. As stated above, a trust may be living trust, testamentary, revocable, or irrevocable. The type of trust one chooses determines the trust account form it should open.
#2 - Appointment of a Trustee
The appointment of a trustee is the second step. A trustee is a person who is responsible for managing your trust assets and executing the terms and conditions of trust especially in case of trust account for minors. A trustee can be any mentally competent person. One must remember that alternate trustees should also be designated who can act as trustees in case of death and incapacity of a trustee.
Generally, a trust department in law firms or banks serves as trustees or become the trust account lawyer. However, if one is appointing an individual as a trustee, that person should be capable enough to understand the nature of trust and perform his duties efficiently.
#3 - Determination of Assets
The third step is the determination of the assets in which a person wants to get placed in a trust. There are few assets such as bank accounts, cars, stock, a real estate whose legal title should be changed in the name of a trustee as the trustee is the legal owner of trust property.
Few assets like jewelry and art do not have any legal title, and in such a case, one must transfer the investment to the trustee. Remember that the trustee’s powers over the trust’s assets must be clearly stated in the trust documents.
#4 - Drafting and Filing of Documents
The fourth step is drafting and filing the documents. The trust shall be written per the state laws, and the papers should be properly signed and notarized. If in one's region it is mandatory to file the trust documents with the state, then it should file all the documents.
#5 - Bank Process
Lastly, one will go to the bank with the trust documents as these documents will instruct the bank about setting up a trust account which includes the name and the designation of a trustee.
Thus, a solid understanding of the state’s trust laws is required. One should properly research the trust that the state laws permit and the rules governing the trust’s operations. It is risky to transfer the assets in improperly formed trusts as they can be voided and sent your assets into probate. Therefore, it is always good to consider all the factors and consult a professional before creating a trust account.
Trust Account Vs Estate Account
Trust Account is the one that has the responsibility of distributing assets to beneficiaries whereas estate account contains all the assets of the owner.
| Trust Account | Estate Account |
|---|---|
| It is in operation even when the owner is alive. | It is operative after the owner is no more. |
| The assets are distributed over a period of time. | The estate is distributed only one time. |
| It helps in distributing assets as per the owner’s instructions. | It protects the asets from getting distributed against owner’s wish. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The earning of interest on a trust account depends on various factors, including the terms of the trust and applicable laws. Sometimes, a trust account may be structured to generate interest or investment income, while others may not.
A trust account refers to a specific financial account that holds assets for the benefit of one or more beneficiaries according to the terms of a trust. It is a bank or investment account where trust assets are held and managed. On the other hand, a trust fund refers to the total assets (which may include various accounts and properties) held in trust for the beneficiaries.
A trust account is established as part of a trust agreement to hold and manage assets on behalf of the beneficiaries. On the other hand, an estate account is a temporary account that is typically opened during the probate process to hold and manage a deceased individual's assets until they are distributed to the rightful heirs or beneficiaries according to the terms of the will or applicable laws.
