Table Of Contents
What is a Trust Receipt?
A trust receipt is a short-term finance-like promissory note to the bank where they would repay the loan on the sale of goods (local or export) to the customer.
Key Takeaways
- A trust receipt is a form of short-term financing, similar to a promissory note, where a borrower repays a loan to the bank upon selling goods (locally or for export) to the customer.
- The advantages of a trust receipt include it being an easily accessible source of finance and the ability to utilize available liquidity for other investment or capital investment purposes.
- The disadvantages of a trust receipt include increased control by the bank over the customer and the requirement for excessive documentation.
Explanation
- Usually, companies may not have adequate cash and cash equivalents to purchase inventory from a vendor to affect sales but may have sale orders from customers. They approach the banker for short-term credit like trust receipt in these cases. The banker would pay the goods to the foreign exporter or the domestic seller. Then, using the inventory purchased from the vendor, the company can make a further sale to the customer; on realizing the receivable, the loan availed from the bank is repaid with a nominal interest rate.
- The borrower (i.e.) the person who approached the bank for the trust receipt must have adequate segregation of the goods obtained. The banker also issued the periodical report based on a trust receipt agreement.
Format of Trust Receipt
These are used throughout the world with no uniform format. In other words, this issued by a bank in the UK may not be the same as practiced in the USA.
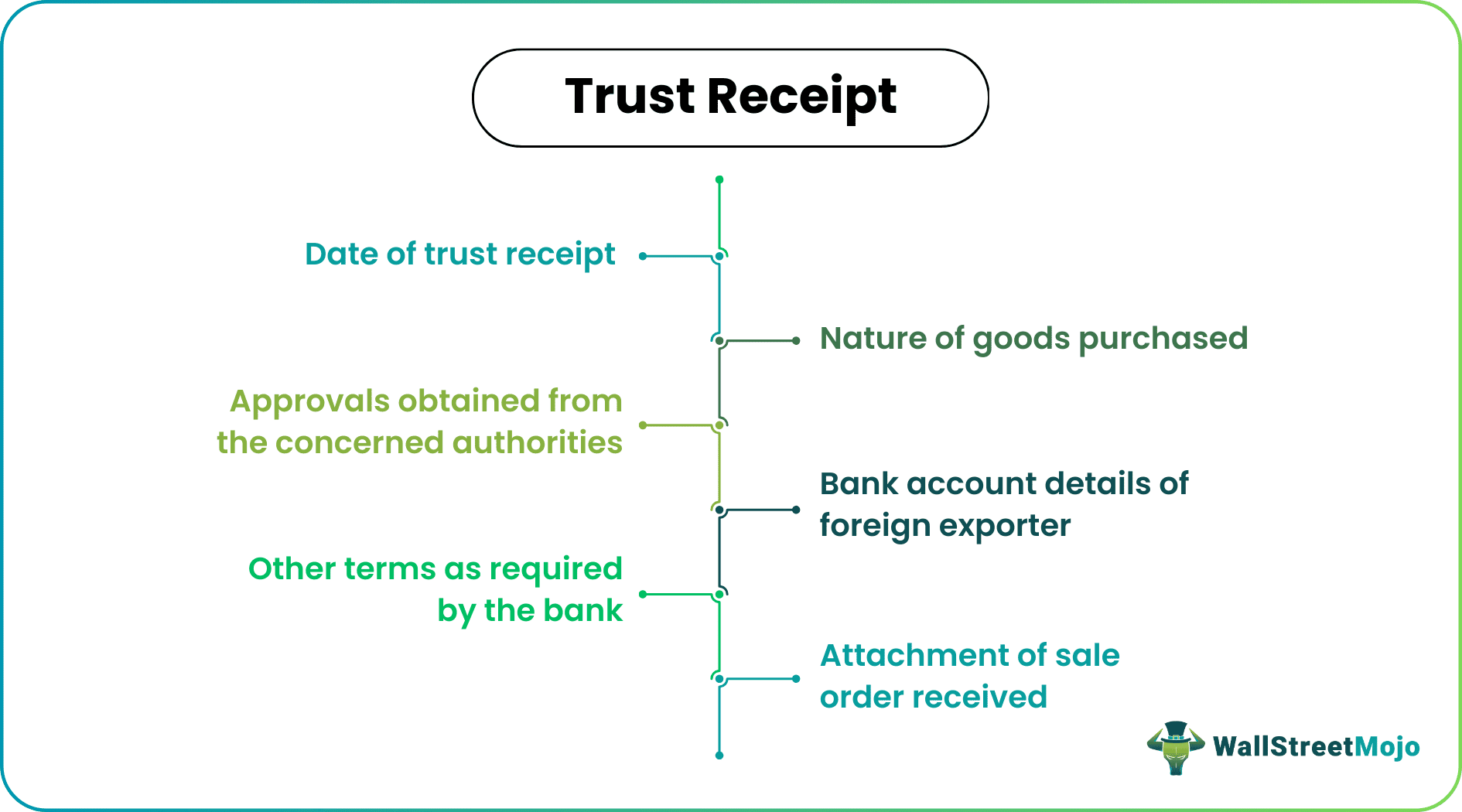
The basic requirements are as follows:
- Date of the trust receipt.
- Attachment of sale order received.
- Nature of the goods purchased (PO attached if obtained).
- Approvals obtained from the concerned authorities (if import).
- The bank account details of the foreign exporter.
- Other terms as required by the bank.
How does Trust Receipt Work?
The process practically is quite complicated, especially in import or export transactions, as the provisions of the local customs act and the rules (if any) made thereunder are also to comply.
The basic process is as follows:
- The customer approaches a bank for want of trust receipt by filling the required forms and completing the necessary process.
- On being satisfied with the documentation, the Bank appoints the customer as its agent to purchase the goods he needs.
- On receipt of goods, the bank pays the purchase consideration to the supplier within the agreed timelines.
- The trust receipt document mentions that the payment is made only to the bank account.
- The goods obtained are segregated and stored in the warehouse of the borrower until sold.
- The bank is intimated periodically about the closing balance of the good and its condition.
- The purchase consideration is first used to settle the trust receipt’s principal and interest when sold.
How is Trade Receipt different from the Letter of Credit?
So the next question is, How is trade credit contrast with the Letter of Credit?
- A letter of credit is a guarantee given to the foreign party by the local banker for payment of transactions’ consideration. It is not an instrument whereby the bank pays the amount and then collects it as a trust receipt from the borrower. In international transactions, the parties may not know each other.
- In these cases, the foreign vendor has not been protected from the risk of default of his overseas customer. Hence, the vendor would want the buyer to give him a guarantee from his banker, stating that the bank would be liable to pay his consideration if the customer defaults. The bank, for this purpose, would charge a commission from the customer for guarantee and not interest in case of trust receipt.
- In other words, the bank acts as the principal in trade credit, and the borrower is its agent. On the other hand, in the Letter of Credit, the bank guarantees the payment to the foreign vendor and is liable only if the local customer defaults. Hence, the bank has the first charge in the case of a letter of credit but the second charge in trust receipt.
So, the first and initial step is to ensure that the borrower has the documents to avail of the trust credit. Therefore, the basic prerequisites would be: –
- The buyer accepts a bill of exchange (BOE) (A sale order is mere intention to buy, but BOE is acceptance to pay!).
- Invoice if already raised on the buyer.
- Approval of customs authorities (if obtained – in exports)
Also, the above is general and is common across countries. The banks, based on local laws, seek additional documents.
Advantages
#1 - Easy Source of Finance
Usually, banks do not hesitate to give trust credit. One would certainly repay the money with interest once the goods are sold. It is a win-win situation for the bank and the borrower since the bank gets to cash in the form of interest, and the company earns money without having to invest initially.
#2 - Instant Liquidity
One can use the cash otherwise available for other working capital and investment purposes. That enables the company to effective treasury management.
Disadvantages
#1 - Excessive Control
Banks lay a lot of conditions on the customer. A few of them are: -
- To maintain the inventory about trust credit separately.
- Maintain and issue a report to the bank periodically.
- The clause that “banks may conduct a stock audit if required.”
- Cost constraint.
The company may incur additional costs in terms of interest and to comply with the banks’ other conditions. Accordingly, a cost-benefit analysis of this extant is to be conducted.
#2 - Excessive Documentation
You do not get a trusted credit unless the minimum of the above documents is submitted. Practically, it is impossible to get customs clearance to export goods to the customer without actually manufacturing the goods.
(Note: You first buy the goods and then process them for sales)
Conclusion
Trust receipt is the cheapest source of finance with a comparably flexible maturity period. One can select the start with the requisite cost-benefit analysis by submitting the requisite documents.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Trust receipts can be used in various industries and sectors. They are commonly utilized in trade finance and commercial transactions involving the movement or financing of goods. Industries such as manufacturing, import/export, retail, and distribution often use trust receipts as a financing mechanism.
Trust receipts are primarily used for tangible goods, such as inventory, equipment, or commodities with a physical presence. They involve a borrower holding the goods on behalf of a lender until the loan associated with the goods is repaid. However, trust receipts are generally not used for intangible assets, such as intellectual property, patents, or copyrights, as these types of assets do not have a physical form that can be held as collateral.
Yes, a trust receipt can be used as collateral for additional financing, depending on the terms and conditions agreed upon between the borrower and the lender. For example, the lender may consider the trust receipt and the underlying goods as security when evaluating a borrower's eligibility for additional financing.
