Table Of Contents
What is Type Statement in Excel VBA?
VBA Type Statement is used to define variables under one single group name with different data types assigned to each variable. This helps us to group together multiple variables under a single object to use them under the defined type name.
We can avoid using Class modules in VBA by declaring the Type statement. It does not need any string modules because we can embed it into existing modules, saving us space.
In one of the earlier articles, we discussed the “VBA ENUM” to group all the variables under a single group name.
For example, if you have a group called “Mobiles,” we have group members like Redmi, Oppo, Vivo, Samsung, LG, etc. So, the Enum statement we can group with their respective values.
Enum Mobiles
Redmi = 12000
Oppo = 18000
Vivo = 18000
Samsung = 25000
LG = 15000
End Enum
Like this, we have created enumerations in that article. The problem with the Enum statement as it can hold only a LONG data type. We can use the VBA TYPE Statement to group variables with different data types. This article will show you how to construct a Type statement in VBA. Read on.
Syntax
Before you declare variables by using a Type statement, take a look at the syntax:
Type Group Name as Variable Data Type as Variable Data Type as Variable Data Type as Variable Data Type as Variable Data Type End Type
These statements can be declared within and at the top of the module, like our Global Variables in VBA.
VBA Type can hold object variables. It can hold arrays. However, it cannot contain procedures or functions.
Type Statement Example in VBA
Let us start the process of declaring variables with the Type statement. Then, we will see the same example of declaring mobile brands as we used in VBA Enum.
Step 1: At the top of the module, start the word “Type” and give a name to the Type of group.
Code:
Type MobileBrands End Type

Step 2: What are the things we usually see in mobile brands? We see names first so declare the variable as Name as String.
Code:
Type MobileBrands Name As String End Type

Step 3: After the name, we check the LaunchDate. Declare the variable as LaunchDate as Date.
Code:
Type MobileBrands Name As String LaunchDate As Date End Type

Step 4: Next, we check storage capacity to declare the variable as storage as Integer.
Code:
Type MobileBrands Name As String LaunchDate As Date Storage As Integer End Type

Step 5: The next thing is we check RAM capacity.
Code:
Type MobileBrands Name As String LaunchDate As Date Storage As RAM As Integer End Type

Step 6: At last, we check about the price.
Code:
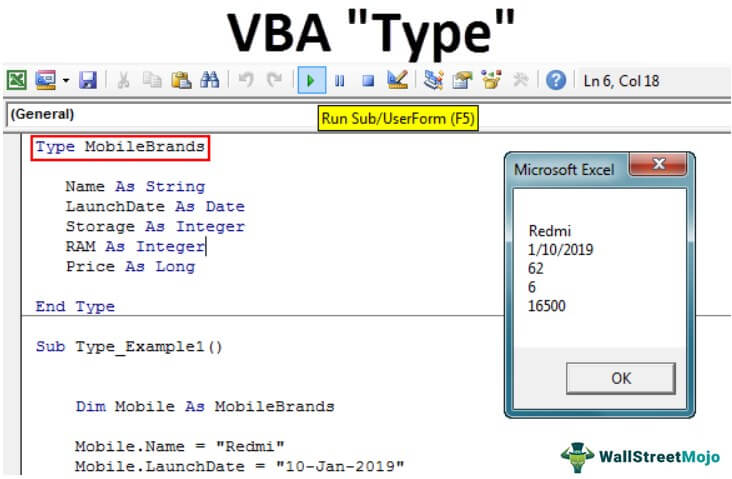
Type MobileBrands Name As String LaunchDate As Date Storage As Integer RAM As Integer Price As Long End Type

Now, in the sub procedure, we can access all these variable data types by declaring the variable as Type, Name, i.e., MobileBrands.
Step 7: Create a subprocedure.
Code:
Sub Type_Example1() End Sub

Step 8: Now, declare the variable “Mobile” as MobileBrands.
Code:
Sub Type_Example1() Dim Mobile As Mob End Sub

Step 9: Now, with the variable name “Mobile,” we can access all the variables of “MobileBrands.”
Code:

Step 10: Now, store each value like the below.
Code:
Type MobileBrands Name As String LaunchDate As Date Storage As Integer RAM As Integer Price As Long End Type Sub Type_Example1() Dim Mobile As MobileBrands Mobile.Name = "Redmi" Mobile.LaunchDate = "10-Jan-2019" Mobile.Storage = 62 Mobile.RAM = 6 Mobile.Price = 16500 MsgBox Mobile.Name & vbNewLine & Mobile.LaunchDate & vbNewLine & _ Mobile.Storage & vbNewLine & Mobile.RAM & vbNewLine & Mobile.Price End Sub

Finally, show the result in a VBA message box like the below one.
Code:
Sub Type_Example1() Dim Mobile As MobileBrands Mobile.Name = "Redmi" Mobile.LaunchDate = "10-Jan-2019" Mobile.Storage = 62 Mobile.RAM = 6 Mobile.Price = 16500 MsgBox Mobile.Name & vbNewLine & Mobile.LaunchDate & vbNewLine & _ Mobile.Storage & vbNewLine & Mobile.RAM & vbNewLine & Mobile.Price End Sub

Run the code using the F5 key or manually and see the result in a message box.

Like this, we can use the VBA Type statement to define new data types in the sub procedure.
VBA Types vs. VBA Class
Often, VBA Type compares to VBA Class modules. However, there are certain differences between them. Below are the common differences.
- Difference 1: VBA Type can contain only Public variables. VBA Class can contain both Public as well as Private variables.
- Difference 2: VBA Type cannot contain procedures and functions. VBA Class contains both of them along with properties.
- Difference 3: One may declare VBA Type in any modules and procedures. One can only declare VBA Class in dedicated class modules.

