Table Of Contents
What is a Long Data Type in VBA?
Long is a data type in VBA used to store the numeric values. We know that integer also holds numeric values, but Long differs from integers as the data storage range is very big. In the case of the Long data type, we can hold decimal values too. So, it is a built-in data type.
“Long,” as the name says, should hold the value of something big. “Long” is a numerical data type in VBA Excel.
The Long data type in Excel VBA can hold the values from 0 to 2, 147, 483, 647 for positive numbers, and the negative number can hold from 0 to -2, 147, 483, 648.
VBA Long data type requires 4 bytes of memory storage of your computer. It is the double Integer data type, variable memory (2 bytes), and half of the double data type variable memory (8 bytes).
In my short career, we have never seen a scenario where we want to utilize the limit of a VBA Long data type fully. But, we will show you some examples to better understand it.
Examples of VBA Long Data Type
Below are the examples of excel VBA Long data types.
VBA Long Example #1
As soon as you declare the variable data type as “Long,” you can assign the values from -2, 147, 483, 648 to 2, 147, 483, 648.
For example, declare the variable as a Long data type.
Code:
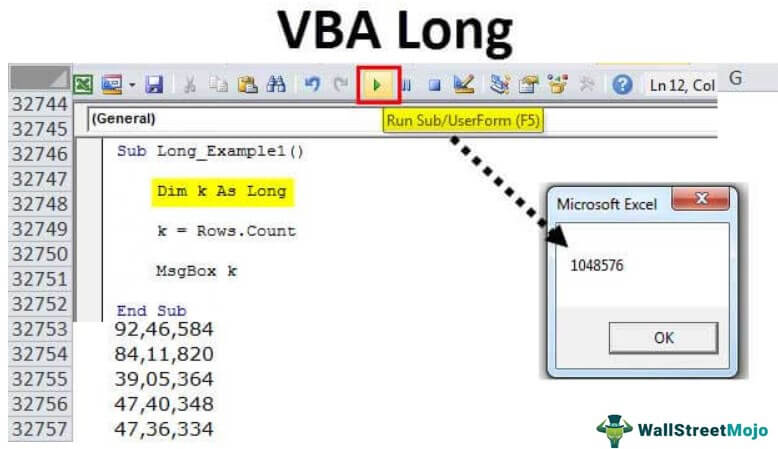
Sub Long_Example1() Dim k As Long End Sub

Let us assign the value as a total row count of the worksheet.
For getting the total count of rows in the excel worksheet, the code is “Rows. Count.”
Code:
Sub Long_Example1() Dim k As Long k = Rows.Count End Sub

Now, show the value in the message box.
Code:
Sub Long_Example1() Dim k As Long k = Rows.Count MsgBox k End Sub

Run this code and see what the total rows count in the worksheet is.

It says we have more than 1 million rows on the worksheet.
For better understanding, we will change the data type from LONG to INTEGER.
Code:
Sub Long_Example1() Dim k As Integer k = Rows.Count MsgBox k End Sub
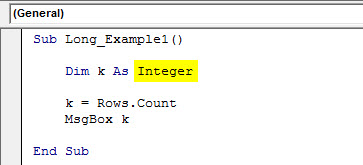
If we run the VBA code, we get the error message “Overflow.”
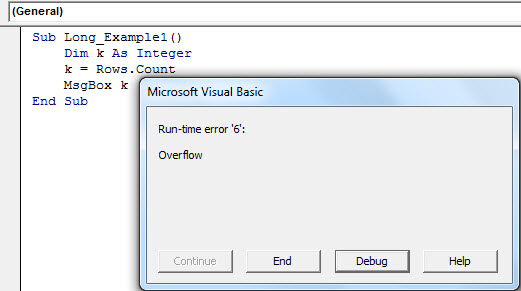
We got this error in VBA because the data type “Integer” can only hold the values from -31768 to 32767. In this case, “Rows. Count” will return the number exceeding the limit of the “integer” variable.
Assigning the value of over 1 million to the variable which can hold only 32767 causes the overflow error here.
VBA Long Example #2
Find the Last Row Using Long Variable
Finding the last used row of the worksheet is the most important of the coding. To find the last used row of the worksheet requires a variable to be declared. While declaring the variable and assigning a data type requires some common sense.
As shown in the image below, assume you have data that ends at 25,000 rows.

Now, we know the last used row number is 25,000. So, for this, we do not need the “LONG” data type because the “INTEGER” data type can give me the last row.
Look at the below code for your information.
Code:
Sub Long_Example1() Dim k As Integer k = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row MsgBox k End Sub

If we run this code, we will get the last used row number of the worksheet we are working on now.

Knowing the size of the data you will have in the future is important as a coder. Because at the moment, data may end at the 25,000th row, but if the data increases beyond the “Integer” limit, i.e., 32767, it causes an overflow error.
For example, I will increase the data to 32768th rows.

We will not get the value if I run the same code again. Rather, we will get the error below.

Remember, we have increased the limit by just 1, beyond the limit of the "Integer" value, so we got an "Overflow" error.
So, it is important to know the size of your data before you assign a data type to the variable. Therefore, it is always better to declare the variable as "LONG" without considering your future data size.
Alternatives to Excel VBA Long Variable
You must already be thinking about what if we want to hold the value more than the limit of a long variable. For this, we need to use different data types: VBA "String" or "Variant."
Remember, when it crosses the number 2147483647, we will get an overflow error in VBA with the LONG data type. So, we need to use the "String" or "Variant" data type to store more than this number.
For String
Code:
Sub Long_Example2()
Dim k As String
k = 2147483648
MsgBox k
End Sub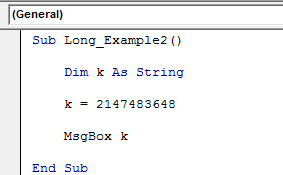
For Variant
Code:
Sub Long_Example2()
Dim k As Variant
k = 2147483648
MsgBox k
End Sub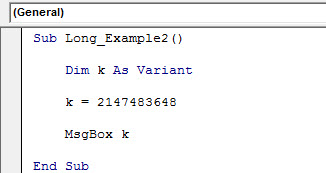
When we run the above codes, it will show the mentioned number.


