Table Of Contents
Book Building Meaning
Book building is a process that helps companies discover the price of their security when their shares are being offered for sale in an IPO with the help of investment bankers. Major stock exchanges and regulators recommend it because it is the most efficient mechanism to price securities in the market.
Key Takeaways
- Book building is a method that helps companies discover the security price when their shares are offered for sale in an IPO with the investment banker's help. Most stock exchanges and regulators recommend it since it is the most effective way to price securities in the market.
- Accelerated and incomplete book building is the different varieties.
- In comparison to the fixed-price system, this method has substantial expenses.
- The period is more critical in book building than the fixed-price system.
How Does the Book Building Process Work?
When a company has planned to list its shares on the stock exchanges for the first time via IPO, the company management decides various things to get its share listed on the stock exchange, such as issue size, share price, etc. Firstly, company management must appoint an underwriter to help with this listing process.

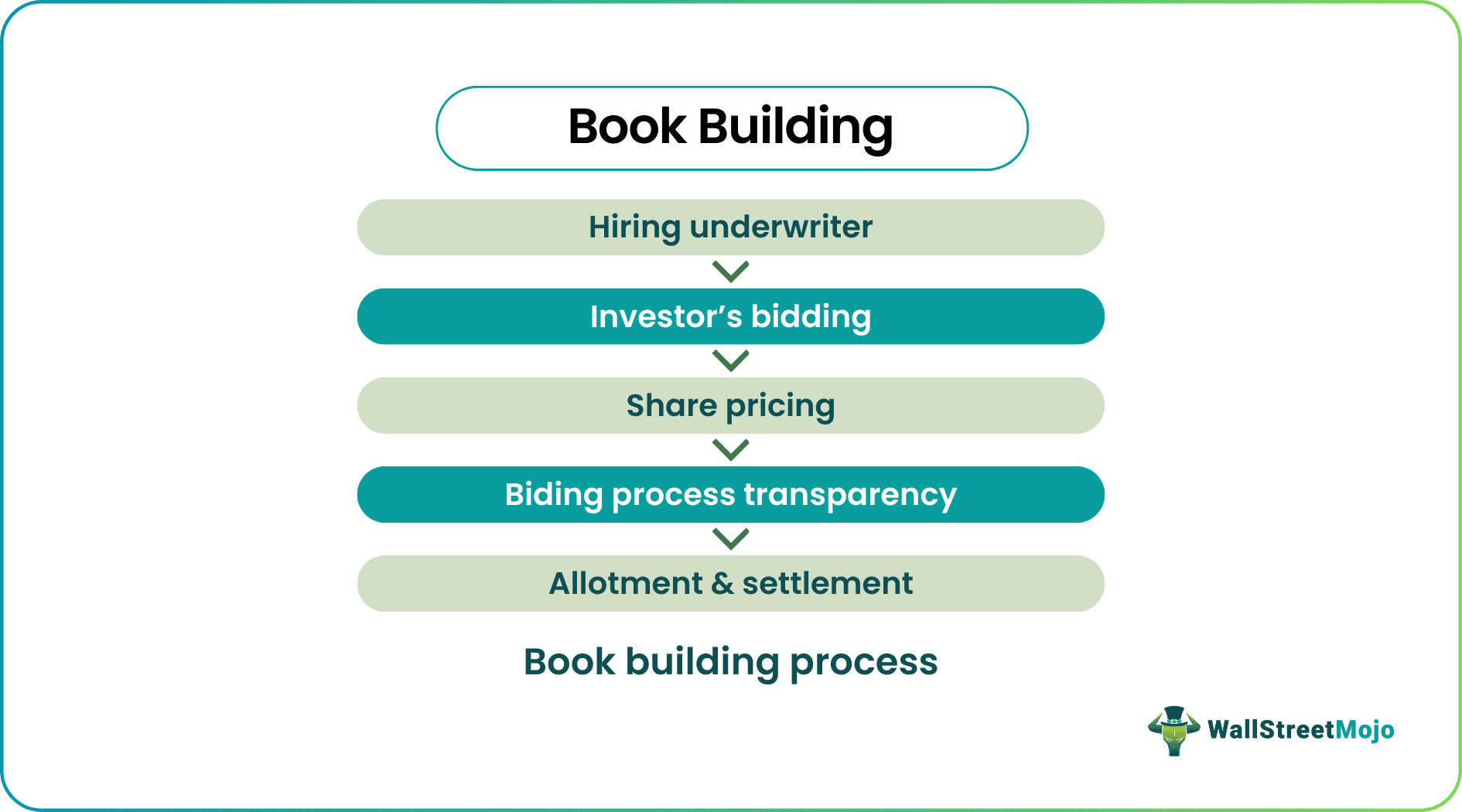
Let us see in detail each step involved in the book-building process.
- Hiring Underwriter - Firstly, the issuing company needs to hire an Investment bank that acts as an underwriter. With the help of issuing company management, the investment bank identifies the size of the issue and determines the price range of the securities. An investment bank drafts the company prospectus, including all the relevant details about the issuing company such as financials, issue size, price range, future growth perspectives, etc. The share price range consists of floor price (lower end of the price range) and ceiling price (upper end of the price range).
- Investor’s Bidding - Investment banks invite investors. Usually, these are high net-worth individuals and fund managers to submit their bids on the number of shares they are willing to buy at different prices. Sometimes, not a single investment bank underwrites the entire issue. Rather, the lead investment bank is engaged with other investment banks who use their networks to tap many investors for the bidding process.
- Share Pricing - After the investment bank collects all the bids at different price levels, they evaluate the aggregate demand for the issue from the submitted bid. To price the share of the issue, the underwriter uses the weighted-average method to arrive at the final price of the share. This final price is also known as the ‘cut-off price.’ If investors have a good response for any issue, the ceiling price is usually a ‘cut-off price.’
- Biding Process Transparency - Most of the regulators and the stock exchanges in the world require companies to make public the details of the bidding process. An underwriter must publicize the details of the bids submitted by the investor to purchase the shares of the issue.
- Allotment Settlement - Lastly, the allotment process begins by allocating the shares of the issue to the accepted bidders. Now, as you know, initially, investors had bid for this issue at a different price range, but the settlement process ensures that all allotments happen at the cut-off price of this issue. An investor who had bid in excess to cut off cost, their excess money is returned, and investors who had bid less than the cut-off price, investment bank ask them to pay the difference amount.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Other Subtypes of Book Building
The following are subtypes of book building: -
#1 - Accelerated Book Building
The companies can use an accelerated book-building process to acquire quick capital market. That can be the case when a company cannot finance its short-term project via debt financing. So, the issuing company contacts several investment banks that can act as underwriters the evening before the intended placement. Under this process, the offer period is open only for a day or two days, and you have no time for marketing for an issue. So, instead, the underwriter overnight contacts their networks and details the current topic to institutional investors. If this investor finds this issue interesting, then allotment happens overnight.
#2 - Partial Book Building
As the partial book building says, that issue book is built partially, where the investment banker only invites bids from the selected investors. Based on their bids, they take the weighted average of the prices to finalize the cut-off price. Then other investors, such as retail investors, take this cut-off price as a fixed price. So, the bidding happens with a selected group of investors under the partial book-building process.
Advantages of Book Building
The following are the advantages of the book-building process over a fixed price mechanism: -
- The most efficient way to price the share in the IPO market.
- The share price is finalized by investors' aggregate demand, not by the fixed price set by the company management.
Disadvantages of Book Building
The following are the disadvantages of the book-building process over the fixed-price mechanism: -
- High costs are involved in the book-building process compared to the fixed-price mechanism.
- The period is also more in the book booking process than the fixed-price mechanism.
Video Explanation - Book Building
Important Points to Remember
- Book building is a process of discovering the security price offered for sale in an IPO market.
- The security price range consists of ceiling price (upper end of the price) and floor price (lower end).
- The final price at which shares are allocated to investors is known as the ‘cut-off price.’
Conclusion
Book building is one of the most efficient mechanisms by which companies, with the help of investment bankers, price their share in IPOs. In addition, all the major stock exchanges and regulators also recommend them. It also helps investors value the shares by submitting the bids to the underwriter, which is impossible if the company chooses a fixed-price mechanism to price its share.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Book building is utilized in Initial Public Offer (IPO) for effective price discovery. It is a mechanism where bids are collected from investors at prices above or equal to the floor price during the period the IPO is open.
Reverse book building is for effective price discovery. In this process, as a company declares a delisting plan, public shareholders can tender their shares at or above the floor price. Moreover, shareholders can perform this through an online bidding system on the stock exchanges that stays open for five days.
Book building is how an underwriter attempts to estimate the price it will offer an initial public offering (IPO). The price discovery process involves creating and recording investor demand for shares before arriving at an issue price. Then, Book Running Lead Manager assigned by the issuer intimates the exchange of the eligible members to participate in the issue. Finally, these members can bid in the IPO.
Book building in accounting is how an underwriter determines the price at which one must sell the shares in an Initial Public Offer (IPO).

