Table Of Contents
Initial Public Offering Definition
An initial public offering (IPO) occurs when a private company makes its shares available to the general public for the first time. IPO is a means of raising capital for companies by allowing them to trade their shares on the stock exchange. Initial public offering stocks become a source of generating more visibility and credibility in the market.
During an IPO, employees who have been loyal to the company for a significant period also benefit through stock options. However, there are some drawbacks, too. Firstly, it is an extremely costly affair to get a company listed on the exchange. Also, the existing owners may lose control over the direction of the businesses.
Table of contents
- Initial Public Offering Definition
- Initial public offering (IPO) is defined as the debut of a private company on the stock exchange by issuing its shares for the first time to the general public.
- The shares are first issued in the primary market. Thereafter, they get listed in the secondary market which contains stock exchanges and over-the-counter (OTC) market. Once listed, the newly listed shares start trading amongst investors.
- For holding an IPO, the company typically has to file the S-1 Registration Statement with the SEC in order to comply with the authority's requirements.
- It is a kind of exit strategy adopted by angel investors, venture capitalists, and other early-stage investors of a business to make high returns on their investment.
- The general public makes gains from IPOs by acquiring shares at a low cost and selling them to other investors when the price rises.
Initial Public Offering Explained
The initial public offering helps startups and growing businesses in acquiring extensive capital from the market. A business can raise funds from relatives, angel investors and venture capitals to only an extent. Besides, most of these sources invest intending to grab massive gains from appreciated share values when the startup goes public.
With an obligation to enable investors a fruitful return and to further expand themselves by raising funds from the most coveted source, businesses go public. A private company becomes public by offering its shares to the general public. However, there are many established companies such as State Farms, IKEA, etc., that remain private.
The Initial Public Offering model is desirable as it opens avenues for scalability with extensive funds. The process of IPO initially involves issuing shares in the primary market through the help of investment banks. After legal filings, marketing and price computing, the shares are finally allocated. In due time, they begin trading on the stock exchange in the secondary market.
A company has to file an S-1 Registration Statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to issue the IPO as per the federal laws. In addition, it encompasses legal requirements to attain IPO eligibility. Also, post Initial Public Offering, stock exchanges hold distinct criteria to remain listed. For example, the NYSE requires the market value of post-IPO shares to be at least $40 million.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Process
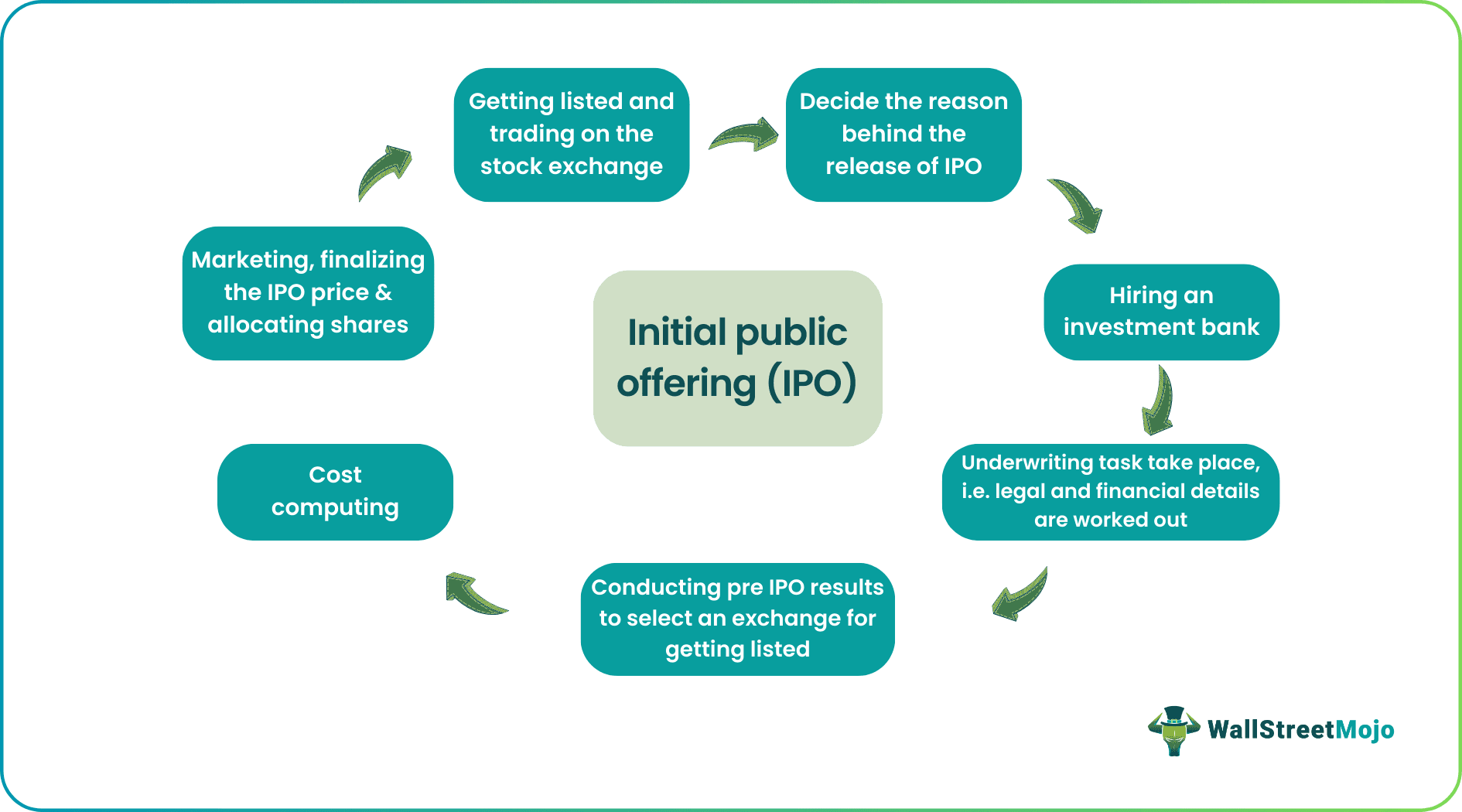
The IPO process is a complicated business. Usually, a company takes the services of an investment bank that first sells the company’s shares to certain investors in the primary market. Following which, the shares debut on a stock exchange and start trading amongst investors. Another route is direct listing, when a company enlists itself on an exchange without an investment bank. Let us look at the step-by-step process of Initial Public Offering.
1. Deciding the reason behind the release of the IPO
At the initial stage, the company needs to ascertain the purpose of raising funds. Whether it is expansion, integration or diversification, the company should be clear.

2. Hiring an investment bank
The next step is to find an investment bank that can work as an underwriter for your IPO process. An underwriter helps the company fulfill financial and legal obligations. It also arrives at the company's value, IPO price and sells the shares to the initial investors in the primary market. It is essential to select an investment bank that holds expertise and proven experience in conducting Initial Public Offers.
3. Underwriting Tasks
- Financial details - The underwriter helps the company prepare its financial statements, and reports required for registration. It involves compiling revenues, profits, total asset size, and other business figures including the company valuation.
- Legal requirements – A company can go public only after registering with the SEC. For this, the underwriter undertakes more paperwork to adhere to the regulatory compliance including clearly specifying the reason behind the IPO issue and risk factors. If the SEC sends revisions, the company has to make necessary changes. Once approved from the SEC, the company can go public.
4. Conducting pre-IPO analyst research
- Here the company conducts extensive research for a successful Initial Public Offer. It indulges in primary research and records IPOs viability from the perspective of investors and competitors. Based on the trend it zeroes in on the right time to get listed.
- Looking for a stock exchange that is suited to one’s business capabilities is also a part of the research. Some options are NYSE (New York Stock Exchange), AMEX (American Stock Exchange), NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations), OTCBB (Over the Counter Bulletin Board) and Pink Sheets.
5. Cost Computing
Throughout the process, the company has to keep a tab on its finances as going public takes a lot of capital. The company has to restrict the process within its means lest it offsets the gains from the initial public offering model.
6. Marketing, finalizing the IPO price and allocating shares
- Marketing – Starting from marketing, the following are most important stages in initial public offering. During marketing, the management team promotes the IPO by connecting with prospective investors. A prospectus is shared. The prospectus or offering document discloses the terms and conditions of the IPO, financial health, earnings, etc. Therefore, it is a crucial element for attracting investors.
- Finalizing the IPO price – After marketing, investors send their indication of interest which reflects that they are interested in buying the company shares. The price per share can be modified as per the investors' response. The IPO price is finalized here and also the share lot.
- Allocating shares - Lastly, the Initial Public Offer becomes good to go. The shares are allotted to initial investors who are predominantly institutional buyers in many cases. Retail investors also take part.
- Getting listed and stock trading – After initial allotment, the shares are debuted on an exchange where they trade between investors.
Initial Public Offering Video Explanation
Types
Each type of initial public offering stock has a distinct implication in terms of pricing, investor participation, and demand. Let us understand them through the detailed discussion below.
- Fixed Price IPO: The issuing company and their underwriters discuss and set a fixed price for the shares before they are up for offering. The investors who are willing to subscribe to the IPO do so at the pre-decided price.
- Book Building IPO: Initially, a price is not fixed. A price range is provided instead. Investors bid for these shares within the range and the final price is set based on the demand for the stock.
- Over-Allotment (Green Shoe Option): This is the type of scenario where the underwriters allow the issuance of additional shares if the demand or subscription to the IPO exceeds their expectations. This stabilizes the price of the stock in the secondary market by covering excess demand.
- Rights Issue: Existing shareholders are given the right to purchase additional shares of the said company before the IPO is open to the rest of the public. This makes sure that the existing shareholders have the opportunity to maintain their ownership stake in the company.
- Employee IPOs: As the name suggests, it is reserved for the company’s employees, giving them the opportunity to purchase shares at a discounted price. This improves employee loyalty and makes sure the interests of the company and its employees are on the same page.
Examples
Let us take a look at some examples to elucidate the process of the initial public offering model.
Example #1 - Facebook
Facebook had registered its IPO documents by filing an S-1 document with the SEC. The company had 845 million monthly users as of December 2011, with $1 billion in profit. After intense marketing, Facebook shares debuted on NASDAQ in May 2012 at $38 each.
The offer price resulted in a sky-high company valuation at $104 billion, becoming the first US company at the time to go public at over $100 billion. The shares opened up at $45, 11% up from IPO price. However, experts suggest that technical delays and high valuation led the price to fall sharply. At last, Facebook’s underwriters jumped in and bought some shares, closing them at $38.23 on the first day.
Due to the huge demand, Facebook had decided to release more shares. As a result, a record shares 576 million shares were traded on the first day. Mark Zuckerberg had retained 28% of company shares at the IPO, which came down to 14% in 2020.
After a rocky start at the IPO, the company continued to rise by trading at over $300 per share in 2021 and its quarterly revenue being $26.17 billion.
Example #2 - Coinbase
Cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase got itself listed on NASDAQ in April 2021 with an impressive IPO. It had filed form S-1 Registration Statement to the SEC quoting 43 million retail users and the December 31, 2020 revenues at $1.3 billion. Shunning the traditional IPO process, Coinbase undertook direct listing.
While the pre-emptive reference price of the Coinbase IPO as declared by NASDAQ was $250 per share, it opened at $381 on the first day. Then, the price further climbed to $429.54. Finally, however, it closed at $328.
Some anticipated upcoming initial public offerings of 2021 are Robinhood, Traeger, and Weber, among others.
Pros and Cons
Through Initial Public Offering stocks, a company can avail colossal capital from the public. But, like everything, initial public offerings also come with its own pros and cons. Let us have a look at the major ones.
Pros
- Monumental earnings arising out of the IPO help businesses expand themselves and address monetary issues if any.
- Also, original investors such as venture capitalists and angel investors who had been holding certain shares of the startup make their exit. After the IPO, they sell their shares at a tremendous profit.
- Sometimes, the value of pre-IPO shares is higher than the company's expectation due to hyping. It helps the company enter into accessible acquisition deals and minimize the capital cost.
- It allows favorable credit terms due to quarterly reporting of financial statements. Executives and workers are compensated after the IPO when the business sales and revenue grow.
Cons
- A significant risk is not getting a positive response from the investors towards the IPO and thus chances of inability to raise the desired capital.
- In addition, since the company becomes public, it has to reveal all its business information such as finances, team, revenue, tax, accounting, etc. This, in turn, may help the competitors gain an edge over the company.
- IPO is a costly business since a public company has to incur various non-operating expenses. Also, the overheads related to marketing, accounting, management and legal matters go up. Moreover, it consumes excessive managerial efforts and time to maintain the quarterly financial reporting as the company goes public.
- Other drawbacks are stringent legal and regulatory compliance requirements, loss of control, higher accountability towards shareholders, and changes in the board of directors.
- Companies are also thrown into adverse effects when their stocks are subjected to constant speculation post the initial public offering.
How Can Investors Trade Safely?
The SEC often advises investors to exercise caution around stock trading, especially with initial public offering models. Given below are some of the points an investor should consider before jumping into IPO trading -
- Thoroughly go through the company prospectus to understand its business, IPO purpose, dividend policy, risk factors, dilution, and financial condition.
- A public company needs to furnish Forms 10-K and 10-Q to disclose its annual and quarterly financial statements for transparency. It reveals the company’s financial health to shareholders which the investors must keep a tab on.
- Figure out the underwriter and company's mindset behind setting a specific offering price. Look into market analysis, interpretation, condition and negotiation.
- Other essential elements to keep an eye on include hype, limited trading volume, non-traded outstanding shares, company's stage, emerging growth companies, separate classes of common stock and selling shareholders (who receive proceeds of their stocks sold in Initial Public Offer).
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
An IPO is a method adopted by a private company to debut its shares to the general public. As part of the IPO, the shares are initially sold in the primary market, following which they are made available for public trading on the stock exchange.
An initial public offering (IPO) involves high risks; therefore, you must always overlook the speculation of exceptional returns since they often hype up even non-potential stocks. However, if you go by the facts, i.e., conducting due diligence on the company's background, scope, profitability, past performance and plans, it can reap terrific returns in the long run.
Retail investors can apply for the pre-IPO shares, either online/offline or through a stockbroker. It is mandatory to have a Demat account for such an application. The underwriter does the allotment of shares according to the bidding size (oversubscription or under subscription).
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is Initial Public Offering (IPO). Here we discuss how it works and which factors you need to consider before conducting an IPO process. You may learn more about Investment Banking from the following articles -

