Table Of Contents
What Is Business Law?
Business Law, also known as commercial law, controls the rules and regulations associated with the business. It specifies the codes related to business deals, the conduct of people associated with the industry, and laws related to any organization's rights, order, and dispute settlement.
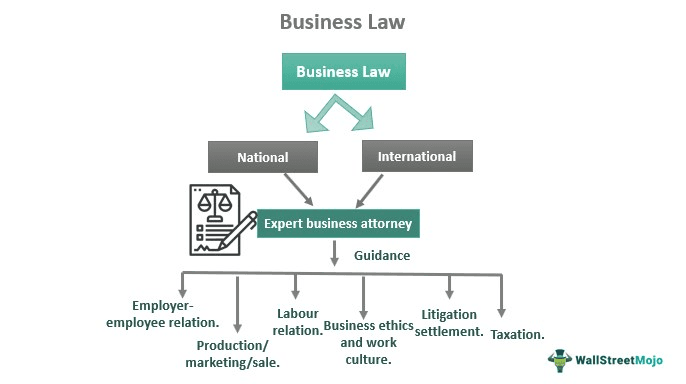
Every country has its own rules and laws of business. Organizations should know such laws and strictly abide by them to have a healthy and responsible business practices. They are taught in business or law schools and fall under civil law. It also deals with licensing and legal or regulatory provisions and applies to companies and individuals.
Key Takeaways
- Business law or commercial law states the rules and regulations associated with any business at both company and individual levels.
- A business law attorney identifies laws related to business deals, administrative rights, orders, or dispute settlement at any business entity level.
- National and international business law is taught in law or business schools, and it is essential for every company to know them and follow them correctly.
- This law will ensure a responsible and healthy work culture at all levels of the organization.
Business Law Explained
Business law, also called commercial law, governs every business operation area, including formation, daily operation, employee and labor relations, purchase and sales, marketing and advertising, sale, bankruptcy, etc. Therefore, it is necessary to strictly follow them to ensure a transparent and efficient company working.
Any national and international business law has two different areas. One is commercial entity regulation, and the other is commercial transaction regulation. However, the above types fall under either common law (some rules implemented based on court decisions) or statute law (formulated by elected officials). All business or commercial law aims to protect stakeholders’ interests and lead the company toward growth and expansion.
A business entity might be a sole proprietor, a small partnership firm, a registered limited company, or a multinational corporation (MNC). Such entities, while working, will face financial issues, employee and customer dissatisfaction, market competition, natural or artificial calamities, etc., for which commercial laws should be in place to guide them.
Objectives
Some objectives related to business law are as follows:
- Defines taxation law – This kind of law gives details and procedures of the business-related tax system.
- Defines employee rights and duties – An organization's employees have some legal rights and responsibilities towards their employers. The business law notes provide the details of the same.
- Make business environment friendly – Any business entity becomes a great place to work if the domain is friendly and has good work culture. This law of a business ensures such an environment.
- Defines roles of various entities – It elaborates on the parts of different types of businesses like sole proprietors, partnerships, big corporations, or LLCs.
- Define laws on various business cases – A business might face many situations like contract drafting, work delegation, contract breach, the penalty for agreement violation, etc. Each of them is dealt with in different ways. However, the business law notes give details of the same.
- Ensure healthy competition – Any law or rule ensures that things run smoothly, healthily, and transparently.
- Formulate legal and ethical rules – It formulates business-related legal and ethical regulations, procedural and substantive laws, court structure, etc.
- Define property or technology-related matters – This law analyses the effect of technology and property-related matters in business. A business law attorney can give expert advice regarding this.
- Formulate bankruptcy laws – Formulating laws related to bankruptcy is essential because it is a crisis where a company has more liabilities than assets. As a result, the court declared that the company could not manage its business, and there are several ways to deal with it.
- Sale and reorganization laws – A company may sell its business to another organization or reorganize it for better management or the company’s infrastructure development. The laws of a business state the rules related to such situations.
Types
The various types of business law are given below:
- Employment law- An employment law covers the rights and duties of the employer and employee. It deals with issues like health and safety, workplace harassment, wages, workplace discrimination, etc. The law establishes employment rules to adhere to and deal with such circumstances.
- Tax law – All businesses must pay taxes to the government, regardless of type. If not paid on time, there are serious consequences.
- Antitrust law – Antitrust laws ensure there is healthy competition in the market without unnecessary dominance. It helps to avoid market allocation, which creates a geographic area for operation so that other similar firms can also operate. Antitrust law also avoids price fixing and monopoly.
- Litigation law – A company might face litigation due to consumer complaints due to dissatisfaction or any other adverse situation. These legal actions are expensive, and settling them with a formal agreement is necessary.
- Bankruptcy law- Bankruptcy happens when the liabilities are more than the assets. Thus, a business cannot pay the dues, and the court declares it bankrupt. There are methods to reorganize or file for bankruptcy detailed in the law.
- Formation law – Promoters should follow some legal steps to form or set up a new company, which are detailed in the formation law of a business.
- Intellectual Property law – Intellectual property is related to any invention or innovation the business might make to expand in this rapidly changing digital world. Thus, any trademark, logo, design, or creative art the company uses for its growth is intellectual property that it should protect from exploitation.
- Negotiation law - The company may enter into a contract or merger with another company to grow, expand, or reduce competition. Such rules are elaborated in the contract in business law.
Examples
Let us understand the concept with some examples.
Example #1
Mark has been working as a software expert in a firm that designs software for commercial and educational purposes. However, he now plans to open his firm, through which he can cater to software demands in the growing technologically advanced market.
He decides to take the service of an attorney who is an expert in commercial law and knows the rules of setting up a firm. Thus, the attorney helps him complete all legal formalities and the step-by-step company formation process related to taxation, financing, structure, etc.
From the above example, we see that commercial law is an integral part of business formation, and it is necessary to know and strictly abide by them.
Example #2
The workers at Amazon, who work in a small outlet in New Jersey, have shown interest in voting for union creation, as reported by the US National Labor Relations Board (NLRB).
Many workers at the facility have agreed to this arrangement to organize themselves in a trade union. Amazon has shown flexibility in encouraging workers to go ahead after resisting the process for many years. Thus, the existing business or commercial law in the state will govern the formation of this union to help workers gain more cooperation and efficiency.
Importance
Knowing and implementing laws related to business is very important due to the following reasons:
- Business set up – It helps to set up a business in a legal and planned way by following the law step by step.
- Rights of stakeholders – It helps to meet stakeholders’ ownership and requirements by maintaining a transparent and healthy operation, thus keeping stakeholders happy and satisfied.
- Compensations – Business law helps settle compensation for management and employees. Violation of such laws may lead to severe legal consequences.
- Drafting contract – This helps to draft a contract in business law by following the rules. In such contacts, one party agrees to exchange for some consideration, signed by both parties and made legally enforceable.
- Litigation settlement – Court cases may be due to reasons like employment or contract-related disputes, workplace discrimination, intellectual property violation, etc.
- Labor management – Any business has several laws related to labor relations. Laborers are an integral part of a company, and it is necessary to look after their utmost welfare.
Business Law vs Corporate Law
Business law deals with the legal requirements for running smoothly, whereas corporate law emphasizes the rules related to day-to-day business operations. However, some differences between them are as follows:
| Business Law | Corporate Law |
|---|---|
| It focuses on the legal rules of marketing, sales, production, employee relations, safety, health, etc. | It focuses on the legal rules of formation, merger, acquisition, sale, bankruptcy, etc. |
| It concentrates on policy enforcement. | It concentrates on avoiding litigation through peaceful and transparent settlement. |
| It incorporates how the business functions will affect its growth. | It incorporates how the business will function. |
| The Uniform Commercial Unit (UCU) establishes it. | The federal and state government establishes it. |
| Any change alters the way a company operates internally. | Any change will alter the company's relationship with the outside world. |
