Table Of Contents
What Is An Acceleration Clause?
An Acceleration clause in a contract gives the lender a right to demand full repayment of the unpaid borrowed sum if the borrower has failed to fulfill certain contract conditions. Such clauses are frequently used in mortgage loans and real estate lending.
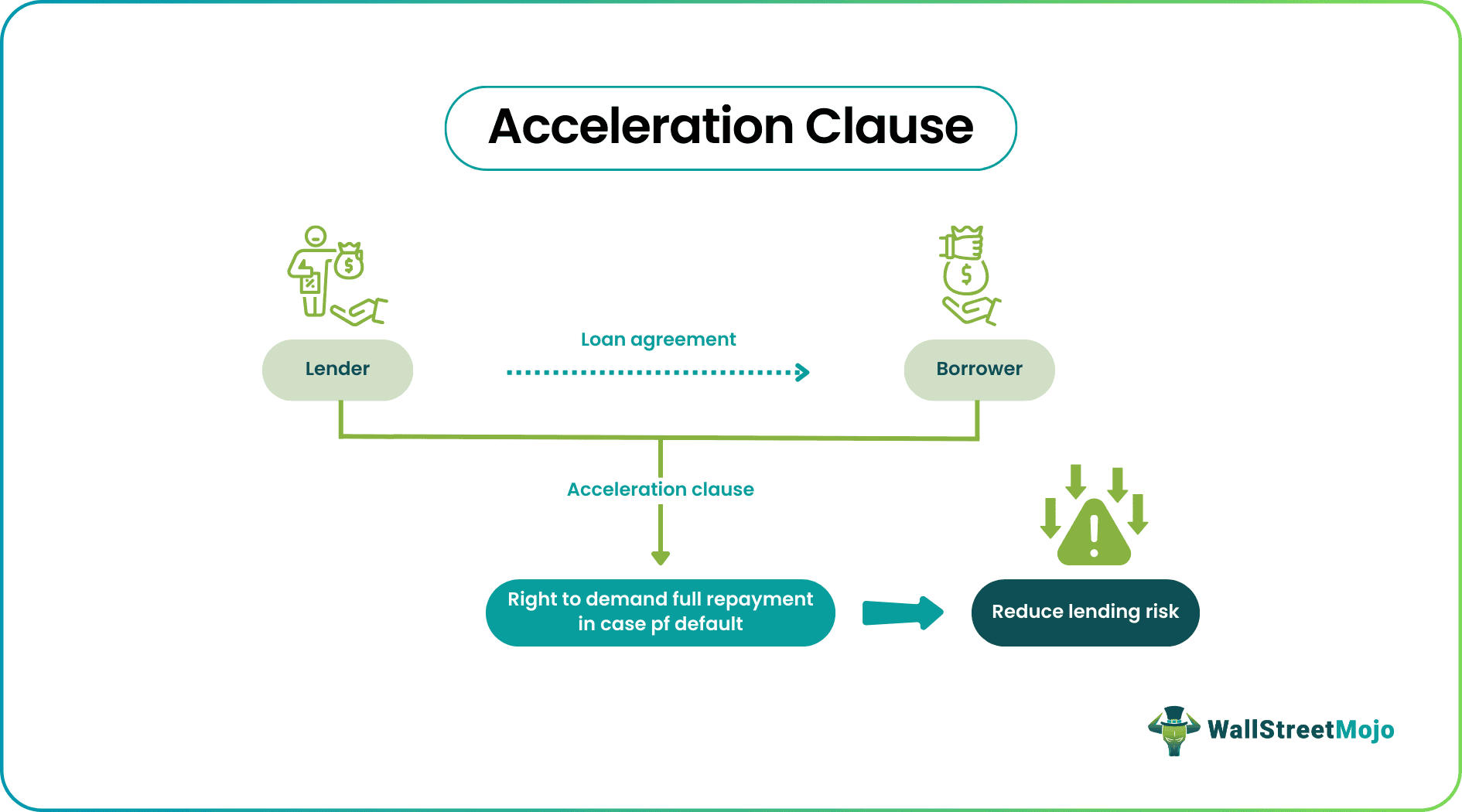
As such, these provisions protect the interests of lenders by reducing the lending risks. The lender of funds get the right to demand the entire payment that is pending from the borrower. Thus, the lender is assured that they will get the money back in various situations like unpaid interest, violation of loan agreement terms or selling off the asset backing the loan.
Key Takeaways
- An acceleration clause is a condition in a contract that permits the lender to demand full repayment of the outstanding loan amount if the borrower fails to comply with certain contractual obligations.
- It is commonly used in mortgage and real estate lending.
- The acceleration clause can be triggered by events such as failure to pay interest, default on the mortgage payment, violating debt covenants, or selling the property without the lender's consent.
- The acceleration clause is typically beneficial for lenders as it enables them to demand full repayment of the loan amount if the borrower fails to comply with the contract.
Acceleration Clause Explained
An acceleration clause in mortgage gives the lender a right to demand full repayment of the unpaid borrowed sum if the borrower has failed to fulfill certain conditions of the contract. As such, these provisions protect the interests of lenders by reducing lending risks.
It is the reason based on which the lender can demand to get back the amount pending from the borrower, which might be interest payment, asset backing the loan that the borrower sold without the knowledge of the lender, or violating any other terms of the loan agreement.
This clause facilitates risk management, especially in the field of acceleration clause in real estate, where the lender’s financial interest lies in the property.
Thus, if the borrower is not able to meet the required conditions of the mortgage agreement, the lender has the right to invoke the terms of payoff immediately.
Example
We will now take the help of acceleration clause example to explain this concept thoroughly.
- John takes a home loan that has a tenure of ten years. He has been paying the loan dues in installments. Unfortunately, he fails to pay the installment in the fifth year.
- The loan lender has put an acceleration clause in real estate in the lending agreement. It states that the borrower will have to repay the remaining amount immediately if one or more installment is missed.
- If John successfully pays the unpaid principal amount of the loan, he will get ownership of the house.
- But if he fails to make the payment, it will be considered a breach of contract. As a result, the lender will gain the right to cease John's property.
- House ceasing comes from the levy, which the contract will also mention. Levy gives the lender a right to cease the debtor's property upon failure to pay the debts.
Thus, the above acceleration clause example gives a clear insight into the process. It is important to note that the acceleration clause will not get triggered on its own if the borrower fails to pay an installment. The trigger happens after the lender decides to invoke the clause.
Trigger
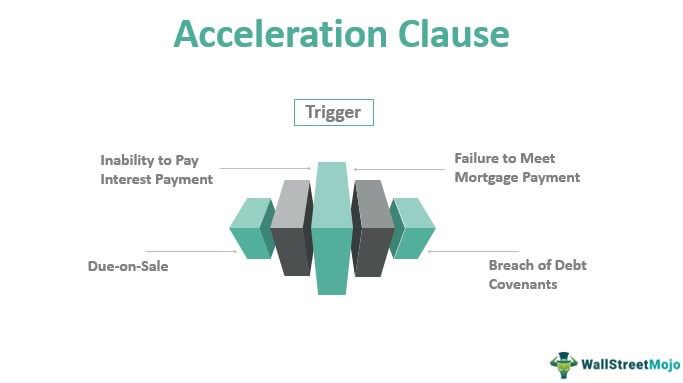
Let us list out some situations that can make the lender invoke the acceleration clause in mortgage.
Let us list out some situations that can make the lender invoke the acceleration clause in mortgage.
#1 - Inability To Pay Interest Payment
The lender on the principal amount usually charges interest rates. The contract would spell out how many missed payments would trigger the acceleration clause.
#2 - Due-On-Sale
The borrower uses a property to mortgage the loan in mortgage loans. In other words, the loan is secured against this property. So, if the borrower fails to repay the loan amount, the lender has the right to sell off this property to recover the borrowed sum. But what if the borrower has already sold the mortgaged property?
For such cases, Due-on-Sale comes as a rescue. It is a covenant used in mortgage loans. It helps the lender demand full repayment of the principal amount of the loan if the borrower sells off the property with which the loan had been mortgaged
#3 - Failure To Meet Mortgage Payment
This sample acceleration clause trigger occurs mostly in real estate loans where massive loan sums are involved. Therefore, the repayment is usually made in fixed intervals using mortgage payment and interest payment in such cases. If any of these payments are not honored, it triggers the clause.
#4 - Breach Of Debt Covenants
Debt covenants are restrictive covenants imposed by the lender to combine the lender and borrower's interests. These clauses in the agreement specify specific rules which the borrower must follow. If the borrower does not adhere to the terms specified under this covenant, the lender can fully repay the outstanding loan amount. It will also lead to a breach of covenant.
Advantages
Is this clause a boon for lenders? Does it hold any benefit for the borrowers? We will give such insights on this concept by highlighting its ups and downs.
- Let's take a sample acceleration clause of a case of Bad debts that are a common occurrence in the lending business, we see that it helps a lender recover the borrowed sum if a borrower fails to make timely payments.
- Therefore, the lender is at a lesser risk of losing the lent money. As we mentioned above, if an acceleration clause is triggered, it would demand the borrower to repay the loan or sell/mortgage his property to the lender.
- Once the payment is processed, the borrower gets relieved of any future payments before the loan's maturity.
- Some such clauses provide relief to the borrowers as they state that the clause will be triggered after two or three installments are missed.
Disadvantages
- This is usually unfavorable for the borrower as it demands to pay a large sum of money at once, which may be impossible to materialize at short notice.
- The terms and conditions of the acceleration clauses may seem overwhelming to understand. As such, people often take the help of a lawyer to understand the nuisances of the provisions and trigger points.
- When triggered, it makes borrowers prone to losing their property in addition to losing the money they had paid previously.
Acceleration Clause Vs Alienation Clause
- Understand that the two provisions are different. Apart from mortgage loans, the Alienation clause is found in insurance and finance contracts.
- This clause pertains to the transfer or sale of a particular asset when the borrowing party fails to fulfill the financial obligation mentioned in the contract.
- This clause acts in favor of the borrowers. If the lender has sold their mortgaged property and utilized it to recover the outstanding loan amount, it releases the borrowers from future payments.
- Here the borrowers are released from the contract only after the property is transferred to the new owner.
