Table Of Contents
What Is A Security Interest?
A security interest refers to a legal right granted to a lender or creditor over a borrower's property or assets. It allows the lender to take possession of the property or assets in the event of a default, ensuring they can recover some or all of the money they lent.
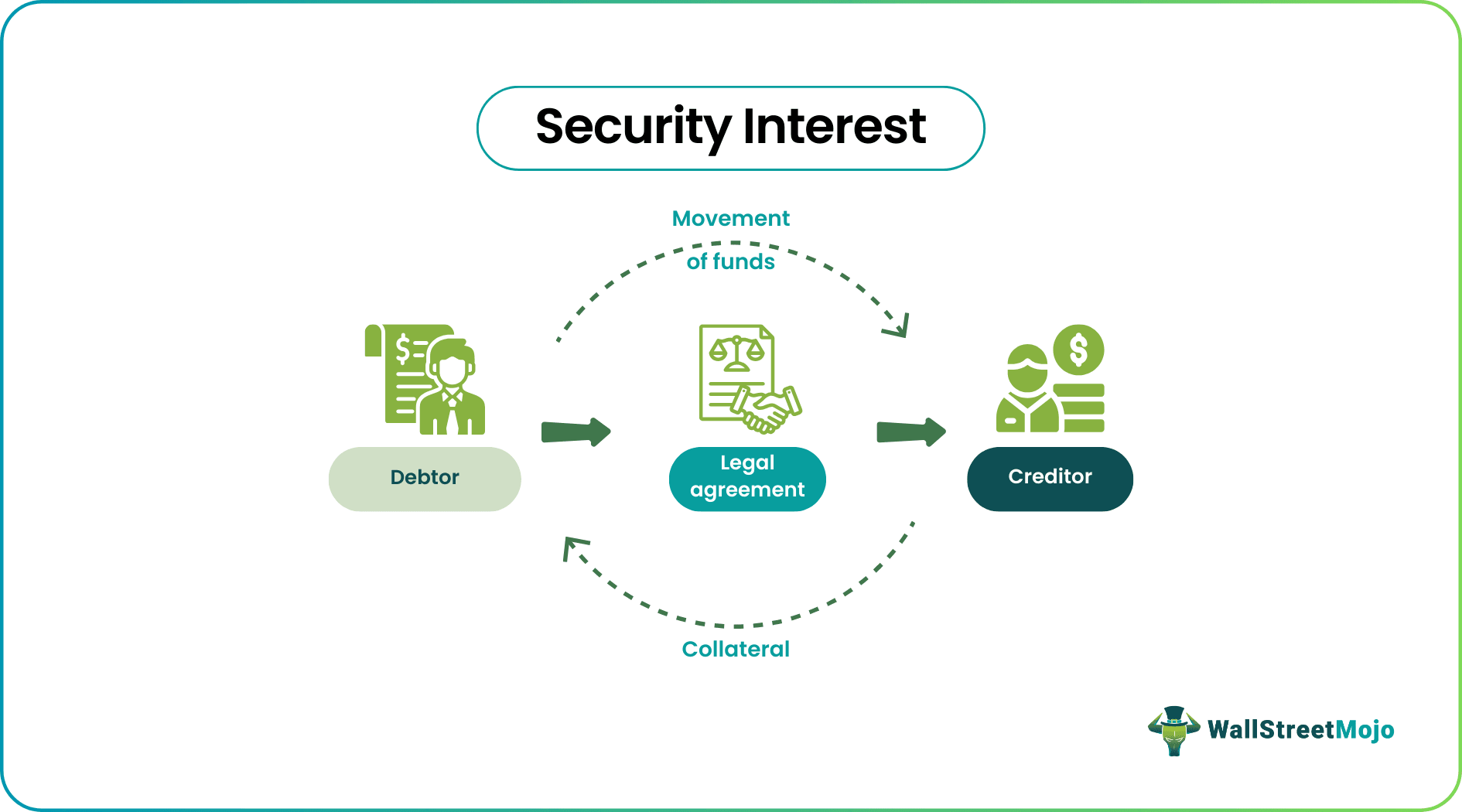
It plays a crucial role in lending and borrowing. It allows lenders to reduce risk and protect their financial interests. At the same time, borrowers can obtain more favorable loan terms by offering collateral, as this reduces the lender's risk and increases the likelihood of loan approval.
Key Takeaways
- A security interest is a legal claim that a creditor has on a debtor's asset used as collateral for a loan.
- A notice of security interest is a document filed with a government agency to publicly establish the creditor's claim to the asset.
- It protects the creditor in case of bankruptcy or other legal proceedings.
- Other creditors may claim the asset, but the creditor with the security interest typically has priority over those claims.
Security Interest Explained
Security interests are a critical aspect of lending and borrowing, reducing lending risk and protecting financial interests. Borrowers can often obtain more favorable loan terms by offering collateral. It reduces the lender's risk and increases the likelihood of loan approval.
Security interest collateral is the property or asset the borrower offers to secure the loan. The lender takes a security interest collateral to recover the money lent in case of a default. An appraisal often determines the value of the collateral. Therefore, lenders will usually only lend a percentage of the appraised value.
A purchase of money security interest is when a lender funds a borrower's purchase of specific assets. Assets purchased with the lender's funds serve as collateral for the loan, and the lender takes an interest in them. Lenders prefer to purchase money security interests for higher priority claims in case of default.
A security interest agreement is a legal document consisting terms and conditions of the loan granted by the borrower. It typically identifies the collateral used to secure the loan, the loan duration, repayment terms, and applicable interest rates. Lenders and borrowers need to understand the terms of the agreement to get protected in the event of a default. The agreement may also include provisions for default remedies, such as foreclosure or repossession.
Types
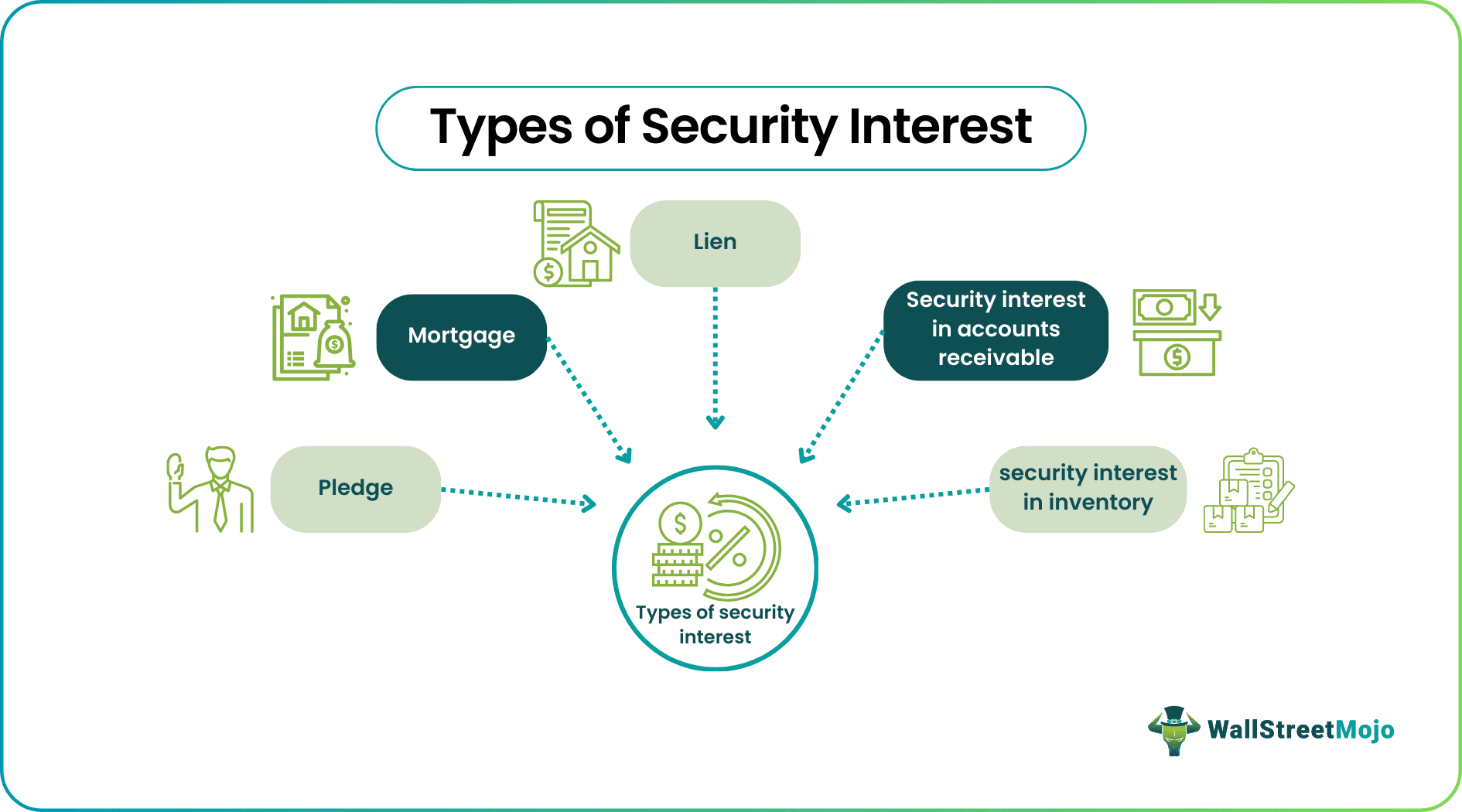
Various types of security interest agreements allow lenders to take over a borrower's property or assets to secure a loan, including:
- Mortgage: It takes over a borrower's real estate property to secure a loan.
- Lien: It took over a borrower's personal property, such as a car or boat, to secure a loan.
- Pledge: It takes over a borrower's personal property, such as stocks or bonds, to secure a loan.
- A security interest in accounts receivable: It takes over a borrower's accounts receivable to secure a loan.
- A security interest in inventory: It takes over a borrower's inventory to secure a loan.
- Purchase Money Security Interest (PMSI): A specific type of agreement occurs when a lender provides funds for a borrower to purchase specific assets, such as equipment or inventory.
Examples
Let's see some examples to understand it more:
Example #1
Suppose a business owner obtains a loan from a bank to purchase equipment for their business. The bank requires the business owner to provide collateral in the form of the equipment itself, which serves as the security for the loan. In addition, the business owner agrees to execute an agreement that outlines interest rates, repayment schedules, loan terms, and the consequences of default.
If the borrower fails in repayment, the bank can take possession of the equipment to recover the money lent. The bank's interest in the equipment gives them a priority claim over other creditors who claim the business's assets.
Example #2
In the case of JPMorgan Chase & Co. vs. American Realty Capital Properties Inc. (ARCP), JPMorgan Chase had provided ARCP with a $1.5 billion credit line secured by a security interest in ARCP's real estate assets.
However, it turned out that ARCP had overstated its financial performance, and JPMorgan Chase demanded that ARCP repurchase $500 million in shares from its investors to compensate for the misrepresentation. When ARCP refused to comply with the demand, JPMorgan Chase seized control of 224 of ARCP's properties, citing it as justification.
The dispute between JPMorgan Chase and ARCP ended in court, with JPMorgan Chase arguing that it had the right to seize the properties under the security interest agreement. However, the court ultimately ruled in favor of JPMorgan Chase, and the properties were sold to pay ARCP's debts.
It allowed JPMorgan Chase to recover some of the money it had lent to ARCP, and the court's ruling upheld the validity of the agreement on properties.
Security Interest vs Lien
Security interest and lien are two legal interests creditors can have over a borrower's property or assets to secure debt payment. Here are some key differences between them:
- Scope: It can be taken over real and personal property, while liens typically take over real property.
- Creation: A security interest is created through an agreement between the lender and borrower. At the same time, a lien can be created through a court order or a statute.
- Priority: An adequately perfected interest can have a higher priority than a lien, giving the creditor a better chance of recovering the debt in default.
- Enforcement: In the event of default, a creditor with the agreement can seize and sell the collateral to recover the debt. At the same time, a lien holder may need to process a legal action to foreclose on the property.
- Transferability: It can be transferred or sold to other parties, while liens generally cannot be transferred or sold.
While both serve the same purpose of securing debt payment, they differ in scope, creation, priority, enforcement, and transferability.
Perfected vs Unperfected Security Interest
Based on priority over collateral, it is divided into perfected and unperfected. Here is a table outlining the differences between them:
| Basis | Perfected Security Interest | Unperfected Security Interest |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A security that has been properly recorded or filed, giving the creditor the highest priority over other creditors in the event of default. | A Security that has not been properly recorded or filed, giving the creditor a lower priority in the event of default. |
| Priority | It generally has priority over all other creditors in the event of default. | It may be subordinate to other creditors. |
| Creation | It is created by taking the necessary steps to properly record or file the security interest, such as filing a financing statement. | It may be created by simply entering into a security agreement with the debtor without taking the necessary steps to record properly. |
| Enforcement | A creditor has the right to seize and sell the collateral to recover the debt in the event of default. | A creditor may need to go through a legal process to enforce the agreement and may have difficulty recovering the debt. |
| Transferability | It interest can be transferred or sold to another party, and the priority of the interest will be maintained. | It may lose its priority if transferred or sold, as the transferee or buyer must also properly record or file the charge. |
A perfected security interest provides excellent protection for a creditor in the event of default, giving the creditor the highest priority over other creditors. Creditors must take the necessary steps to properly record or file their interest to ensure it is perfected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
To perfect it, a creditor must take the necessary steps to record or file it correctly, such as filing a financing statement or obtaining possession of the collateral. It ensures that the creditor has the highest priority over other creditors in the case of default.
A security filing is a legal document filed with a government agency, such as the Secretary of State, to record a creditor's interest in a debtor's property or assets. It is a critical step in perfecting a security interest and protecting the creditor's rights in the event of default.
It attaches when the debtor has rights in the collateral and there is an agreement between the creditor and debtor granting the security interest.
It is a legal document filed to publicly identify a creditor's claim to a debtor's asset used as collateral for a loan, protecting it in legal proceedings.
