Table Of Contents
What Is Job Order Costing?
Job order costing is a system of assigning the cost of production to a specific manufacturing job and is mainly used by organizations providing customer-specific jobs. Also, this system is used when each output is different from the others. It means others cannot use the same product.
The professional services like doctors, lawyers, and chartered accountants are client-specific. Therefore, the job order costing method calculates the cost of these services. Business gets clarity regarding various costs of products and services since they are customized and requires cost tracking for each project or order.
Key Takeaways
- Job order costing is a method of allocating the cost of production to a particular manufacturing job.
- It is used by organizations that enable customer-specific jobs. Moreover, this system is used if each output differs from the others.
- Direct material, direct labor, and overhead are the costs involved in job order costing.
- It is costly since it needs expertise and skill to identify, analyze, and control costs. Nevertheless, it is essential to recognize all the expenses incurred in completing an assignment.
Job Order Costing Explained
Job order costing is the process of tracking and allocating the cost of manufacturing or producing products and services that are unique in nature. It is suitable for sectors or businesses that produce output which are different from each other. Job order costing system helps the business associate those costs to that specific projects and act as a guide while setting prices, controlling the expenditure and evaluating the profitability of each investment.
The jobs vary based on specification, uses, requirements, etc and the process involves tracking cost of overheads, raw materials and labor separately. There will be a job cost sheet mention details like job name, number, description, breakdown of all costs, etc. Each cost driver is matched with the associated consumption and allocated for each item.
Job order costing is valid only for organizations based on customer requirements and where one job is different from another so that they can calculate the cost. It is costly because it requires skills and knowledge to identify, analyze, and control costs. Still, it is vital to identify all the expenses incurred in completing an assignment. Otherwise, the company can lose it because they cannot assign one job cost to another job.
It is to be noted that this process of job order costing system is very useful because is provides an accurate and detailed cost structure that are customised for each good or service. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction, printing and advertising and various services like doctors, lawyers, etc.
Types Of Costs
A job order costing typically involves three types of costs:
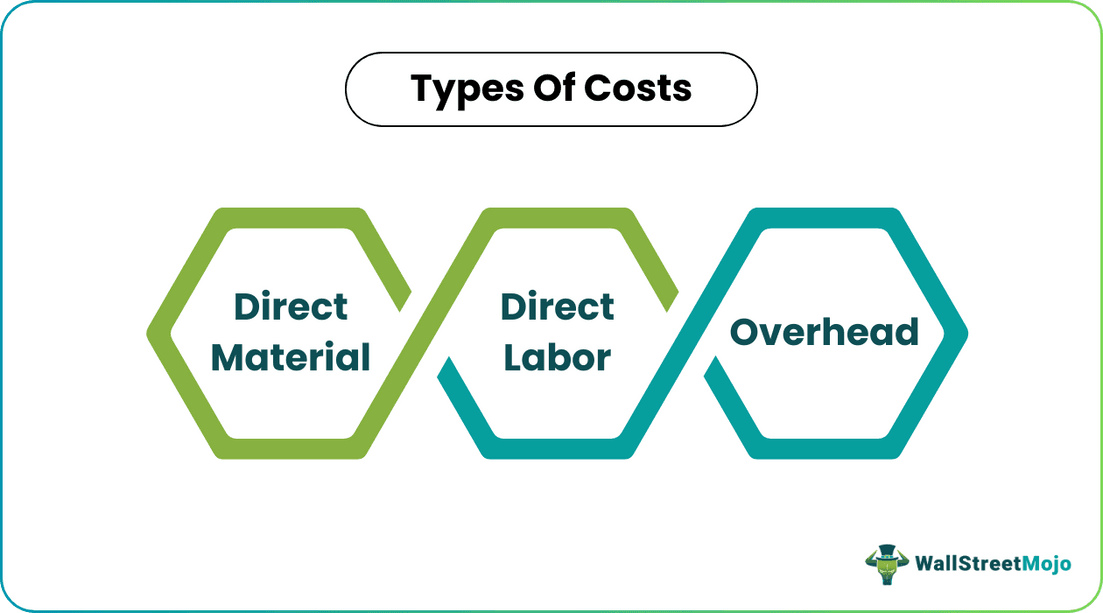
- Direct Material – Direct materials are the major contributors to job order costing. These costs are entirely dependent on the quality and quantity of finished goods. Raw materials directly consumed for completion of specific jobs or manufacturing of finished goods come under direct material.
- Direct Labor – In job order costing process, the cost of labor used in a specific job is identified and added to the cost of production. Direct labor cost is calculated based on workforce and hours worked. If the particular job provides service, direct labor costs comprise almost 80%–90% of the total cost.
- Overhead – Overhead costs incurred in manufacturing a product or providing service other than the direct labor and direct material like rent, electricity, depreciation, legal fees, and any other. Some overhead costs are variable, and some are fixed.
Features
Let us look at some important features of the system:
- In job order, each job has its characteristics. They are unique with their own specification and scope and thus, has to be treated separately.
- In this type of cost, each job is done against customer orders only, not as a regular production. Therefore they are customized and have their own requirements of raw material, labor, overhead etc.
- In this costing method, each job is treated as a cost center.
- A job cost sheet has to be maintained in job order costing process to keep track of the costs allocated for each job. This is a document that will contain all details of the particular job like name, code, description, requirements, etc.
- The cost are allocated based on matching of each cost drivers with the specific requirements or resource consumed. For instance, labor cost is allocated based on labor hours or machine hours are used for allocating overhead cost.
- This process helps in profitability assessment and decision making.
How To Calculate?
There are various steps involved in the job order costing method, which are as follows:
- Job identification – The first step is to identify the order, project or job for which costing will be done.
- Assign a number – Each job will be assigned with a unique number that will help in identifying the job and distinguishing it from others.
- Record direct cost – Then the cost related to material, labor and overhead has to be recorded and summed up to get the total cost related to that job.
- Record indirect cost – Then the indirect costs, lik rent, supervision cost, utility etc has to be identified and allocated. They are indirect because they cannot be specified against a particular job.
- Select a cost allocation method – Then select a proper allocation method to allocate the indirect cost.
- Calculate total – Here, the total is calculated for all direct and indirect cost allocated for the job.
- Cost per unit – Next, it is necessary to find the total number of units for the job and divide the total cost by the number of units to get cost per unit.
- Analysis – Finally , all the data related to allocation and calculation will be clearly recorded in the job cost sheet. This accounting will help for future references and identify costs and assess profitability.
The above steps are essential for decision making related to cost control, price targets, revenue and sales, or investment on changes in product features and services.
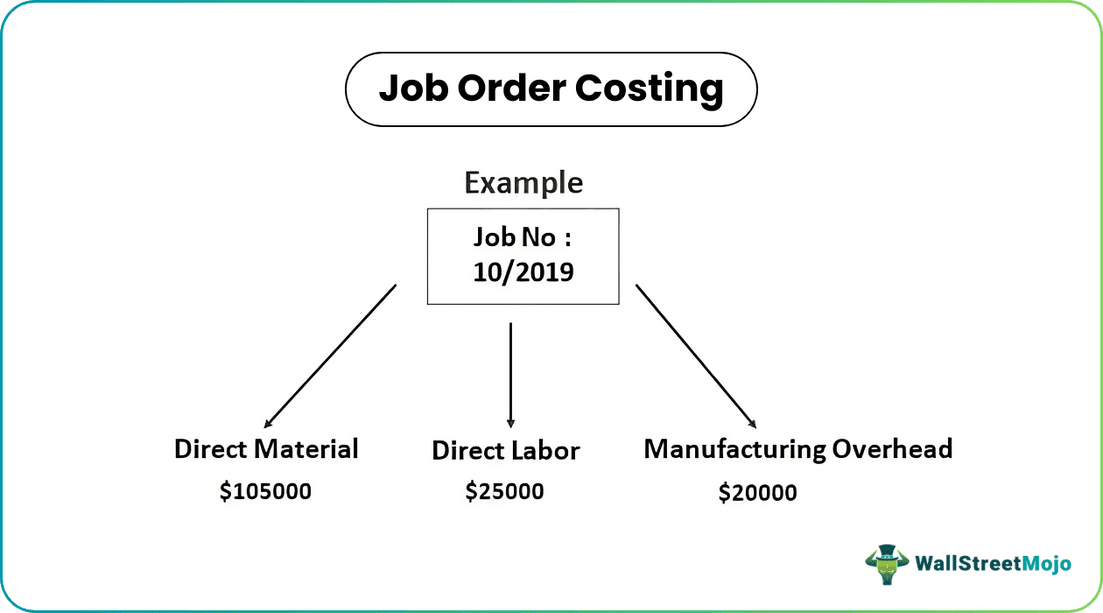
Example
Let’s take the example of a job order costing system.
Notebook Inc is a printing & stationery company that has received an order of 5000 copies of invoices from one of its customers. According to the specification provided by the customer as of August 1, 2019, notebook Inc has to deliver on or before August 20, 2019. As per the company, they can finish the work within ten days. Therefore, they started on August 5, 2019, and assigned this work as a job no. 10/2019. The below cost has been incurred by the company while completing this job:
- Direct Materials: In producing one copy of the invoice, two units of raw material are required. Therefore, for the production of 5000 documents, 10000 units of natural material will be consumed, which the company has procured at different dates as per requirement. Initially, the cost of raw materials was $10 per unit. However, from August 13, 2019, it has increased by $1 because of a shortage of raw materials in the market. As a result, the total cost of raw material consumed is $ 10,500.
- Direct Labor: In producing one copy of the invoice, one workforce hour is required, and the cost of one workforce hour is $5. To complete this job, 5000 workforce hours have been consumed, which the company has taken on different days according to the availability of raw materials. The total cost of direct labor is $ 25,000.
- Manufacturing Overhead: The cost incurred by the company is $20,000, which includes depreciation of plant and machinery, factory and office rent, and other overheads consumed in the production of these 5000 copies of invoices.

Advantages
Here are some advantages of the concept.
- It helps management analyze the material, labor & overhead cost incurred in production or completion of the job.
- It helps in the identification of the efficiency of machines and the workforce.
- The job order costing method helps in cost control and better utilization of resources.
- With the help of the job order costing method, management can ascertain which job is profitable and which is not.
- It helps compare a similar job that will be done in the future and become the basis of future employment.
- It also helps identify the scrap and defects that arise in the production or completion of the job and take steps to minimize this.
Disadvantages
Some disadvantages of the procedure of job order costing are given below:
- It is time-consuming and costly as it involves daily and specific job-wise recording of material, labor, and overhead.
- A cost comparison is problematic because, in this method, the cost sheet is prepared for each job separately according to the specification.
- If two or more jobs are going simultaneously, there is a risk of posting the cost of one position in another job.
- In job order costing, overhead costs are based on estimates. It is also challenging to know if the overhead cost is directly linked with the specific job because most overhead facilities are used for more than one job. Therefore, there is a chance of excess/shortage of cost allocation.
- It mainly depends on the expertise of the production manager. Therefore, someone allocating costs to a specific job must know of it. A small mistake can change the product's price.
Job Order Costing Vs Process Costing
Given are two widely used methods in the field of cost accounting and allocation of costs to products and services. There are some differences between them, which are as follows.
- The procedure of job order costing is mainly used for industries where the products are unique in nature and customized to meet the client requirements. But the latter is used in industries where the same kind of products are manufactured repeatedly or continuously.
- For the former, the cost of each type of job is aloocated related to raw material overhead or labor cost, whereas for the latter, the total cost incurred in the production is allocated equally to every unit.
- The main objective of the former is to find the cost of each unit since each unit is different, whereas the objective of the latter is find the per unit cost in an uniform manner so as to allocate them for each unit.
A business will determine which method of costing it will use, based on the nature and type of business, products and services manufactured and the details required for each allocation.


