Table Of Contents
Micro-Enterprise Definition
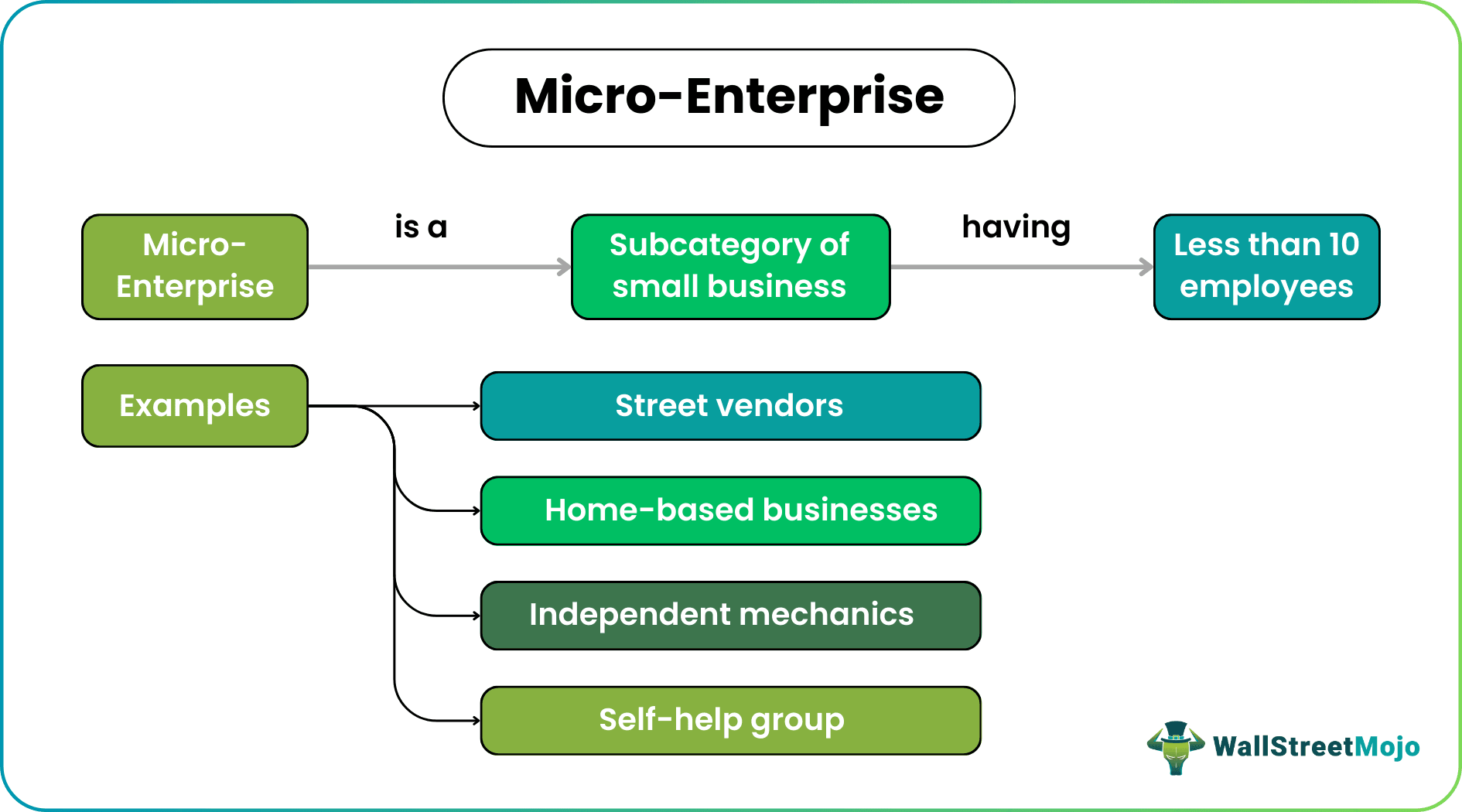
"Micro-Enterprise" refers to a "small business" subcategory with less than ten employees. Micro companies include sole proprietorships, independent contractors, supplementary income generators, and multiple proprietorships from a single physical location. These self-owned businesses aim to generate income and employment opportunities for individuals, particularly in developing countries.
Even though these companies often have a stronger relationship with their clientele and require less operating capital, they might run into greater difficulty regarding financing and marketing. A classic example of a micro-enterprise is any neighborhood grocery shop offering food items, fast-moving consumer goods, dairy products, and fruits and vegetables.
Key Takeaways
- Micro-Enterprise refers to a "small business" subcategory with less than ten employees.
- Microenterprises are small companies that are frequently financed by microcredit. Microcredit is a form of credit made available to persons who do not have any form of collateral, a credit history, or a history of work.
- Micro companies include sole proprietorships, independent contractors, supplementary income generators, and multiple proprietorships from a single physical location.
- These types of firms may have more difficulty when it comes to financing and marketing.
How Does Micro-Enterprise Work?
Micro-enterprises can enhance the quality of life for the people who run them and provide value to the surrounding community's economy. They have the potential to increase one's purchasing power, one's earnings, and the number of employment available.
Micro-Enterprises are given access to smaller amounts of capital through microcredit, part of the microfinance movement. Because of this, people with intermediate, poor, or no income can create enterprises, allowing them to make cash and contribute to their communities.
Some financial institutions make microloans available to persons in need; however, most of these loans are made by charitable groups focusing on micro-enterprises. Repayment with interest is necessary, just as it is with standard loans.
Micro-Enterprises and microfinance were created in Bangladesh in the late 1970s to offer economically and financially disadvantaged individuals a means to support themselves and their families. Micro-Enterprises are small businesses that employ fewer than ten people. For example, Grameen Bank was founded in 1976 by Muhammad Yunus to provide microloans to those living in poverty, the majority of whom were women.
Objectives
- Independent of the traditional business sector, the objective of micro companies is to generate large-scale economic employment. And they can accomplish this objective with very little financial resources and commitment.
- An additional goal is to broaden the scope of industry and commerce in economically underdeveloped regions. This contributes to the continued growth of the economy as a whole.
- The underdeveloped regions are supposed to be included in the overall strategy for national development. Therefore, their goal is to encourage the growth of the region.
- Micro Businesses also aim to increase the amount of our country's abundant natural resources that may be put to productive use.
- In addition, it enhances the quality of life for all people of the nation, irrespective of the region in which they make their home or earn their livelihood.
Characteristics
The following are the features of a microenterprise.
- In most cases, a single person runs a tiny or micro firm. However, even in the smallest divisions managed by a partnership business or corporation, most day-to-day operations are often carried out by just one of the organization's partners or directors.
- The gestation period, or the time before an investor gets a return on investment, is shorter.
- The scope of micro ventures is often confined so that they may respond to the demands of their immediate environment and the surrounding region.
- Micro units use local resources; hence, they may be situated anywhere, subject to the accessibility of such resources as raw materials, labor, etc.
- Micro businesses require a significantly lower investment in time and money spent on labor than bigger units.
- Micro businesses are decentralized and distributed throughout rural regions using local resources. Therefore, micro-business growth in rural regions promotes a more diversified regional development.
- The ability of small-scale entities to be more adaptable to change, highly reactive, and sensitive to societal and economic situations.
Examples
Let us have a look at the examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
According to a recent story in Forbes, the United States is amid a "microbusiness Renaissance." Small business owners not located on the main street are also moving their operations online to provide new goods and services to customers whose preferences and habits have shifted due to the epidemic. All microbusinesses are rethinking the conventional ways of conducting trade and forging their paths to commercial success according to their standards.
An additional quotation from the article states that individuals want to be their boss, discover new hobbies, and reevaluate their priorities. Moreover, there has been a rise in the number of micro-businesses owned and operated by women.
Example #2
The article "The Economic Impact of Microbusiness in the United States," which was found on networks, discusses the topic. Microbusinesses account for 92% of all businesses in the United States. Microbusinesses are well-positioned to benefit from the changes occurring in our labor market and the wider economy as the economy in the United States continues to transform.
Although micro businesses are often very small operations, taken as a whole, they play a significant role in the economy. Because there are fewer obstacles to overcome, beginning a micro business can be an essential step in today's economy and is also becoming an increasingly realistic alternative.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Some important advantages of tiny businesses are as follows.
- One of the primary benefits of owning a small business is the personal gratification from putting ideas into practice. In addition, to turn a company into a successful enterprise, one is at liberty to make the most of the resources at their disposal and put the very finest employees to work effectively.
- The greatest latitude for making decisions is seen in micro-enterprises. A signified entrepreneur may do everything it takes to bring excellence to the firm.
- They can collaborate with anybody they like and place individuals in the appropriate roles inside the organization.
- Whether the micro firm entrepreneur makes a profit, no one will suspend them or penalize them for making mistakes. With errors, kids get to learn more.
- A small firm can start with a little initial investment.
The following are some of the drawbacks of running a micro business:
- Micro Businesses typically do not have access to resources. They are typically founded with only four or five people and little cash.
- There is no set time to schedule one's own business. However, in the beginning, one might have to work long hours because the primary focus will be building the firm.
- The number of people involved in small firms, partners, or workers is often restricted. This is because they may have to tackle tasks they are not particularly skilled at regularly.
Micro-Enterprise vs Small Enterprise
- Investments of less than one crore rupees are required for micro businesses. In contrast, investments of fewer than ten crore rupees are required for small businesses.
- Turnover of less than ₹5 crores is considered to be that of a micro business, while less than ₹50 crores are considered to be that of a small enterprise.
- A firm is deemed in the "small business" category if it has less than 1,500 workers. But, on the other hand, a micro business is far less substantial than that. In most cases, micro-businesses consist of a workforce of fewer than ten individuals.
- Small businesses have a negligible amount of brand equity compared to micro firms, while micro-enterprises, unless they expand, have none.
