Table of Contents
What Is Order Cancellation?
Order cancellation is a process that involves revoking a previously placed order for goods or services. A cancellation letter is sent to revoke orders. It is a formal document sent to a supplier or vendor to request the termination of an order before it is fulfilled or delivered.
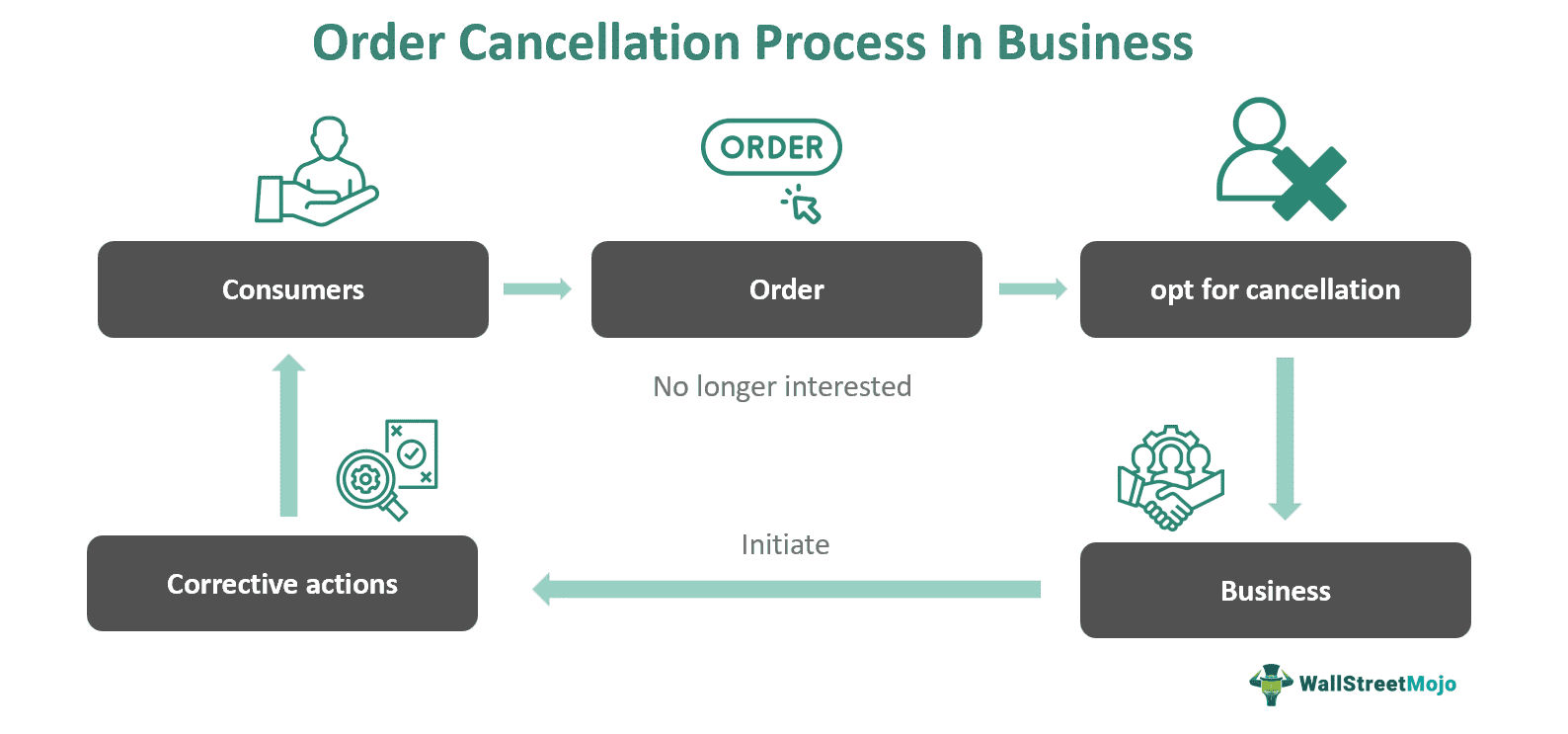
Customers may opt to cancel their orders when they no longer require the product or service they initially requested. This enables them to correct errors, alter choices, or resolve concerns before the order is dispatched. Similarly, businesses may employ order cancellation due to inventory discrepancies, pricing inaccuracies, or at the request of customers.
Key Takeaways
- Order cancellation is a process that initiates the revocation of goods and services owing to various reasons.
- It acts as a tool to align the interests of both consumers and businesses within the ever-changing marketplace.
- It empowers consumers with autonomy while enabling businesses to maintain customer-centric values, enhance operational efficiency, and nurture enduring relationships with their clientele.
- Causes of this cancellation include purchasing incorrect items, shipping wrong items, and late deliveries, defects due to shipment accidents, stock shortages, and pricing inaccuracies.
- Businesses should provide accurate product information, understand customer needs, and simplify returns, among other things, to prevent cancellations.
Order Cancellation Explained
Order cancellation refers to the action of initiating a revocation or termination of a previously initiated purchase order for goods and services prior to its fulfillment or delivery. This process grants consumers the ability to retract their buying decisions, often due to evolving preferences, mistakes, or unforeseen circumstances. Conversely, for businesses, order cancellation encompasses reversing the transaction, reimbursing the payment, and reallocating resources initially designated for fulfilling the order.
For consumers, cancellation of orders holds significant importance as it affords them flexibility and control over their purchasing choices. It permits them to rectify errors, adjust selections, or address concerns arising from post-order placement. Additionally, it relieves the financial burden associated with unwanted purchases and cultivates trust and confidence in the seller by showcasing a dedication to customer satisfaction. Moreover, clear cancellation policies reassure consumers, fostering confidence in their shopping experience and ensuring recourse if needs change or issues arise.
From a business standpoint, proficient order cancellation management is equally crucial. It enables companies to uphold their reputation and goodwill by accommodating customer requests and swiftly resolving concerns. Businesses can elevate the customer journey, bolster loyalty, and stimulate positive word-of-mouth referrals by offering streamlined cancellation processes. Additionally, efficient order cancellation procedures contribute to operational streamlining by mitigating the impact of order discrepancies or fluctuations in demand. They also facilitate effective inventory management, ensuring optimal stock levels and minimizing the risks associated with overstocking or shortages.
Causes
Given below are some of the possible causes that push customers to cancel their orders:
- Purchase Of Incorrect Item Or Alteration Of Decision: It's common for customers to purchase the wrong item or change their minds upon receiving it. This is natural and often out of control of the businesses. While offering accurate product information can mitigate returns, it won't eliminate them. Nevertheless, providing detailed product descriptions empowers customers to make informed decisions, potentially reducing the frequency of returns and increasing overall satisfaction.
- Shipment Of Wrong Items: Occasionally, merchants inadvertently ship the wrong item, which can happen during the processing and shipping stages. Upon receiving their order, customers may need help finding an incorrect item. If customers reach out to return the item, the seller cannot impose charges. According to the Federal Trade Commission's mandate, it's unlawful to bill customers for unordered items. While some may return the product, there may be associated shipping and handling costs.
- Late Delivery: Customers may view a purchase as arriving late for various reasons, like missing an event or impatience due to prolonged delivery times. This delay often leads to items needing to be revised or customers altering their decisions. To tackle this, merchants should offer transparent, up-to-date shipping updates with tracking numbers and prioritize swift order processing to guarantee timely dispatch, thereby minimizing the chances of discontent or canceled orders.
- Defects Arising Due To Shipment Accidents: Shipping accidents can occur, resulting in items arriving damaged despite careful packaging. If consistent reports of damaged goods are received, the business needs to review packing procedures to improve product protection. For defective items, they shall conduct inventory inspections and promptly remove any that meet the criteria. If a significant portion of products are returned due to defects, warehousing practices should be examined, as environmental factors like temperature and moisture can harm various merchandise types.
- Stock or Inventory Challenges: Businesses might need to cancel orders when they face difficulties fulfilling them due to stock shortages, discontinued items, or other inventory-related issues.
- Pricing or Listing Inaccuracies: In cases where businesses inadvertently list incorrect prices, quantities, or other details, they may cancel affected orders to address the inaccuracies.
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
A hypothetical example is Danny, an individual opting to cancel an order on Amazon for electronic goods. Suppose Danny, an online shopper, accidentally ordered an electronic product from Amazon but realized he had overlooked an essential feature for his specific needs. To rectify the situation, he logged into his Amazon account, navigated to "Your Orders," and clicked on the "Cancel Items" button. Danny carefully selected the items to be canceled, provided a brief reason for the cancellation, and highlighted the mismatch of features and his specific requirements. After confirming his cancellation request, he received an email notification acknowledging his request and informing him that he would be refunded.
Danny's decision to cancel his order with Amazon was driven by his desire to obtain the electronic goods that met his needs, avoid the inconvenience of receiving and potentially returning products that did not serve his intended purpose, and ensure a well-informed purchase decision. By canceling the order, Danny demonstrated a responsible approach to online shopping, actively engaging with Amazon's order cancellation process, sending a cancellation email when asked, and allowing the marketplace to process his request and refund him promptly. However, there is little to no need to send a cancellation letter for the cancellation of a money order. This not only ensured customer satisfaction but also allowed Danny to explore alternative options and make a more suitable purchase decision that aligned with his specific requirements.
Example #2
A real-life example of a study on cancellations of orders on online retailing shows that high levels of order cancellations are a common occurrence in e-commerce, as evidenced by data showing that approximately 35% of consumers opt to cancel their orders. A survey conducted among 1,000 US-based consumers further supports this trend, with 92% reporting experiences of order cancellations. Various factors drive these cancellations:
- Consumers may decide to cancel orders due to evolving preferences, financial limitations, or the discovery of more appealing deals elsewhere.
- Issues related to product availability, discrepancies in pricing, or delays in delivery can serve as catalysts for cancellations.
- Dissatisfaction with product descriptions or perceived quality upon receipt often prompts customers to cancel.
Similarly, the complexity of the checkout process also deters them.
How To Avoid?
Some of the ways businesses can avoid order cancellations are:
- Ensure that product details, pricing, and stock availability are accurately displayed on websites or other sales channels.
- Understand customer needs by identifying reasons behind cancellations and offering solutions to retain customers, such as discounts or product enhancements based on feedback.
- Simplify returns by ensuring cancellation and return processes are seamless, enhancing customer confidence, and promoting repeat purchases.
- Maintain updated inventory records to minimize the chances of overselling or encountering stock shortages.
- Efficiently process and fulfill orders to reduce the likelihood of delays or errors that may lead to cancellations.
- Keep customers informed about their orders, including any possible delays or issues that may arise.
- Double-check orders for accuracy before processing them, reducing the chances of errors or discrepancies.
- Providing comprehensive product information helps manage expectations, reduce complaints, and build customer trust.
- Clearly communicate their cancellation policy to customers, outlining any applicable fees, deadlines, or procedures.
- Show empathy by approaching cancellations with empathy and respecting customers' decisions while upholding a positive brand image.
- Shall accept order cancellation letters, emails, or even money, etc.
- Address issues by collaborating with customers to find mutually beneficial solutions, ensuring their needs are met, and fostering loyalty.
- Address customer inquiries promptly, resolve issues effectively, and offer alternatives or solutions when cancellations are requested.

