Table of Contents
What Is Regulation FD?
Regulation Fair Disclosure (Reg FD) refers to a law set up by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in October 2000 to stop any selective disclosure of non-public material information by publicly listed companies. It aims at providing equal access to information to all leading to market transparency and integrity.
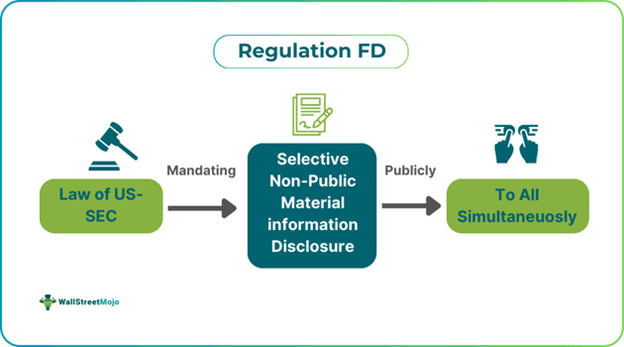
It demands that companies publish any information provided to analysts immediately and simultaneously. It applies particularly to communication about securities professionals and tries to create a level playing field for all. It also helps reduce the risk pertaining to insider trading and restore confidence concerning corporate disclosures.
Key Takeaways
- The SEC established Regulation Fair Disclosure (Reg FD) in October 2000 to mandate simultaneous public disclosure of non-public significant information.
- It tries to provide everyone equal access to information, resulting in integrity and openness in the market.
- It was introduced in 2000 to prevent selective disclosures, offering equal access to material information to all investors, evolving with technology since 2013.
- It mandates fair disclosure of non-material data, ensuring equal access, transparency, and prompt disclosure of unintentional data releases to investors and analysts.
Regulation Fair Disclosure (Reg FD) Explained
Regulation fair disclosure (Reg FD) represents a rule formulated by the SEC to prohibit listed companies from disclosing material selectively non-public data to specific persons like institutions or analysts. It has been made mandatory for all companies listed on the exchange to disclose non-public data available to the public simultaneously. Moreover, if the Regulation FD disclosure has been intentional, then it must be shared with the public simultaneously. However, if the disclosure was done unintentionally, then the companies have to disclose the information simultaneously in the public domain through SEC filings, social media websites, or press releases.
The Regulation FD SEC encourages transparency and avoids insider trading, reducing insider advantages. It also minimizes analyst favoritism, thereby promoting equitable access to disclosed data for all stakeholders and the public simultaneously. It has been used in financial disclosures, corporate communications, and earnings calls, making it mandatory for all public releases to be equally available to the public.
Since the regulation of FD policy has focused on transparency in dealing with the companies and open disclosures of non-material data, it has increased market fairness, investor confidence, and trust in the financial market. It has led to a level playing field for all investors. Companies have begun adopting policies to comply with it and avoid penalties.
any traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
History
Its history is discussed below:
- On 27 Feb 1998, the SEC chairman stressed the need to have a mechanism to deal with insider trading and ensure transparent investors reach data.
- Although proposed on 20 December 1999, the SEC adopted Regulation Fair Disclosure on 15 August 2000 to provide fair and just public access to information regarding non-public material.
- Arthur Levitt, the then SEC chairman, supported it as he felt it was vital to prohibit selective disclosures by companies to market professionals.
- A 3-1 vote passed the rule on 15 Aug 2000 despite the worry that it could overload investors with disclosures or stop company communication.
- Since then, it has mandated public companies to avoid selective disclosures to special investors and broadcast the material information publicly by providing an interpretive framework on 1 Aug 2008.
- Over time, it has shaped the communications of public companies, adapting to technological changes.
- Companies can now use SEC filings, press releases, and properly notified webcasts for disclosures, which the SEC supplemented with websites and social media on 2 Apr 2013.
Compliance Requirements
It has the following compliance requirements:
- All companies must avoid selective sharing of non-material data, which must be disclosed to all simultaneously.
- All disclosures must be made public through means like open conference calls, SEC filings, and press releases to ensure fair access by all.
- Intentional disclosures are a read mark to all companies unless released to the public simultaneously immediately.
- All communications of companies regarding non-material information must be transparent with investors and analysts to level the information field.
- Any unintentional release of data to the selective party must be publicly disclosed promptly.
Real-World Examples Of Reg FD Violations
Let us use some real-world examples to understand its significance and meaning.
Example #1
An online article published on 12 Mar 2021 discusses the SEC‘s legal case against AT&T and its three executives regarding the alleged violation of Regulation Fair Disclosure. As per SEC, AT&T has selectively shared vital data concerning an estimated $1 billion revenue shortfall pertaining to smartphone sales, affecting its earning estimation. Moreover, it was also disclosed that the CFO of AT&T instructed investor relations employees to handle market anticipation by urging analysts to make lower projections.
However, AT&T called out against the allegation and disputed the charges, terming them as against the testimony and policies of the SEC. Such a case has become the only second one in the last five years related to violation of regulation fair disclosure. The litigation highlighted the need for adopting rigorous regulation and fair disclosure adherence practices. It also emphasized the importance of Regulation FD training to prevent risks associated with selective exposure in analyst communication.
Example #2
An online article published on 27 Sept 2024 discusses the charges of the SEC related to violation of regulation fair disclosure against DraftKings. It happened because DraftKings was alleged to disclose material non-public data using social media. SEC came to know about the social media marketing story 24 hours after DraftKings' CEO regarding strong growth even before public earnings were made public, violating disclosure laws.
As a result, DraftKings accepted a $200000 penalty and increased staff training on compliance with fair disclosure regulations. The SEC stressed that all listed firms must provide equal access to material information and must report all inadvertently shared data promptly to the SEC. Hence, the case reminded us of the importance of fair disclosure practices being used by listed companies, especially on social media.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

