Table Of Contents
Risk Exposure Meaning
Risk exposure in any business or investment is the measurement of potential future loss due to a specific event or business activity and is calculated as the probability of the event multiplied by the expected loss due to the risk impact. A risk exposure calculator is used to differentiate the losses that are acceptable or unacceptable for a business.
The calculation of probability related to a particular event resulting in loss to the firm is an integral part of risk analysis. Therefore, understanding, estimating, and taking necessary precautions to avoid or minimize that risk is an essential decision for management. The two major types of risks are pure risk and speculative risk which shall be discussed further in the article.
Key Takeaways
- Risk exposure refers to the extent to which an organization or individual is vulnerable to the potential negative impacts of risks. It represents the level of risk they are exposed to based on their activities, assets, and operations.
- Risk exposure can be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the risks, the organization's industry, geographical location, financial position, operational complexity, and external factors such as economic conditions or regulatory changes.
- Evaluating and understanding risk exposure is essential for effective risk management. It helps identify areas of high vulnerability, prioritize risk mitigation efforts, allocate resources, and make informed decisions to minimize potential losses.
Risk Exposure Explained
Risk Exposure is essential to factor in any business, whether big or small since it gives us an estimate of the risk involved while undertaking certain activities, changes in policy, or changes in operations. The difference in the exchange rate is an integral part of today’s business world since import and export; outsourcing of services is a large part of the business of many multinational organizations. Many companies operating in the domestic market still needs some help through imports and receive the benefits of exports. Right pricing, policy, and operating strategy will help a business to manage overall risk exposure.
Risk exposure management arises from factors such as market volatility, economic downturns, regulatory changes, technological disruptions, and more. It can be quantified by assessing the potential impact of negative events on the value, performance, or goals of the entity or investment.
Managing this factor of business is crucial for mitigating potential losses and ensuring business continuity. Strategies to manage risk exposure include diversification, hedging, insurance, contingency planning, and adopting risk management frameworks.
Different industries and contexts have varying levels of exposure. Financial institutions are exposed to credit and market risks while manufacturing companies face operational and supply chain risks. Investors need to consider risk exposure when making investment decisions, aiming to achieve a balance between potential returns and the associated risks.
Effectively addressing risk exposure requires understanding the specific risks relevant to an entity or investment, analyzing their potential impact, and implementing proactive measures to minimize vulnerabilities and enhance resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Formula
Although specific risk involved in business cannot be predicted and controlled, the risk exposure calculator which is predictable and can be managed are calculated with the following formula:
Risk Exposure formula = Probability of Event * Loss Due to Risk (Impact)
How To Calculate?
Risk exposure management involves assessing the potential impact of various risks on a specific entity, investment, project, or portfolio. While the exact approach may vary depending on the context, here's a general process to calculate risk exposure:
- Identify Risks: Start by identifying and listing all the potential risks that could affect the entity or investment. These could include financial risks, operational risks, market risks, legal risks, and more.
- Assess Probability: Estimate the likelihood of each identified risk occurring. This could be expressed as a percentage or a qualitative assessment (low, medium, high).
- Quantify Impact: Determine the potential financial or non-financial impact of each risk if it were to occur. This could involve estimating monetary losses, delays, reputational damage, or other negative consequences.
- Calculate Expected Loss: Multiply the probability of each risk by its corresponding impact. This gives you the expected loss for each risk event.
- Aggregate Expected Losses: Sum up the expected losses from all identified risks. This provides an overall estimate of the potential impact of multiple risks.
- Consider Correlations: If some risks are interrelated, consider their correlations. Some risks might amplify or mitigate each other's impact when they occur simultaneously.
- Adjust for Mitigation Measures: If the entity or investment has implemented risk mitigation measures (such as hedging, diversification, or insurance), adjust the expected losses accordingly.
- Report and Analyze: Present the aggregated expected losses as the risk exposure. Analyze the results to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood.
Example
Now that we know the basics, formula, and how to use a risk exposure calculator, let us apply the knowledge to practical application through the examples below.
Example #1
There are three investment options available for an investor, which he needs to decide. An investor wants to invest $500,000 in the market for one year.

An investor has to make a decision in which investment option he prefers to invest. Although investment option C looks attractive with higher returns, the risk involved is also higher, 12%.
If an investor decides to divide investment into all three options, risk exposure would be adjusted, and he will benefit from all three assets.

The risk column in the table represents the probability of loss on investment.
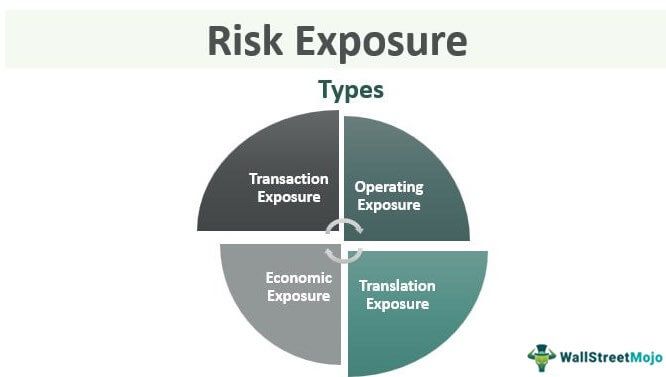
Types
Businesses of different nature face exposures in different magnitude and natures. Let us understand the risk exposure management through the discussion below which also has an example for each type.
#1 - Transaction Exposure
Transaction Exposure occurs due to changes in the exchange rate of foreign currency. Such exposure is faced by a business operating internationally or dependent on components, which need to be imported from other countries, resulting in a transaction in foreign exchange. Buying and selling, lending, and borrowing, which involves foreign currency, have to face transaction exposure.
The following risk involved in Transaction exposure:
- Exchange Rate: It occurs in case of the difference between the date of the transaction contract made and the transaction executed, for, E.g., Credit Purchase, Forward Contracts, etc.
- Credit Risk: Default risk in case the buyer or borrower is unable to pay.
- Liquidity Risk: In the case of contracts involving future date payments denominated in foreign currency, which might affect the credibility of the buyer or borrower.
Transaction Exposure is mostly managed using various derivatives contracts to hedge, so risk arising from these transactions will not affect income or expense.
Example
Indian Mobile manufacturers operating in India need to import certain internal parts of mobile from China and the United States. Price total imports of components required for manufacturing a single mobile phone costing ¥500 and $50. The company manufactures 100,000 mobiles every month.
Current Exchange Rate

Current Manufacturing Cost of A Single Unit

Current Exchange Rate

Change in Manufacturing Cost per Unit

Total Manufacturing Cost


Manufacturing Cost per month increased by ₹ 5,00,00,000 due to a change in the exchange rate.
#2 - Operating Exposure
Measurement of business operating cash flow is affected due to a change in the exchange rate, which results in a growth in profit. Competitive effect and conversion effect will take place in the case of multinationals compared to local businesses operating in their domestic country. Such risk is managed by adopting a proper pricing strategy and reducing costs through local operations, outsourcing, etc.
Example
US Refrigerator Manufacturer operating in the Indian market faces loss due to appreciation in the dollar resulting in less cash flow.

#3 - Translation Exposure
Translation Exposure arises due to changes in assets or liabilities of the balance sheet having a subsidiary in a foreign country while reporting its consolidated financial statements. It measures changes in the value of assets and liabilities of the company due to exchange rate fluctuation. Translation exposure does not affect the company’s operating cash flow or profit from overseas, but such risk only arises while reporting consolidated financial statements.
Translation Exposure is managed by the use of derivative strategies in foreign exchange to avoid ambiguity in the mind of investors of the company. The company accepts specific ways while maintaining reporting financial statements.
Various Methods
- Current/non-current method
- Monetary/Non-monetary method
- Temporal
- Current rate
Example
US company has a subsidiary in Europe use various methods while reporting the following is one method to calculate translation exposure. Following is a Monetary/Non-monetary way.

#4 - Economic Exposure
Change in value of business due to a change in the exchange rate. The cost of the business is calculated by discounting future cash flows discounted at a specific rate. Economic exposure is a mixture of relevant items in firms’ operations related to transaction exposure and translation exposure. The company’s operating exposure and transaction exposure makes economic exposure to a business. Economic vulnerability always exists in business due to its continuous nature. Present value calculations applied in all future cash flows of business as per expected and real change in the exchange rate affect the value of the business.
Example
US company operating through a subsidiary company in Europe faces loss due to a change in the exchange rate in a year.

Income changed because of exchange rate fluctuation, which will change income from operations and the value of a business.

