Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Operators
In VBA, operators check whether one number is greater than another, less than another, equal to another, and not equal. The method is similar to the operators we use in Excel, such as A>B using a comparison operator.
It does not matter how good or proficient we are at our work. However, everything will be messy if we do not do the basics correctly. Firstly if we do not learn the basics right, then we cannot progress to the next level, be it any profession. We are pressing so much on basics because, in today's article, we will show you one of the basic concepts, "VBA Operators."
Operators are the heart of any calculation. They are the signs we use to compare one thing with another. We are sure you must have used this logic in your daily workplace.
List of Mathematical Operators
Below is the mathematical operator’s list we use regularly.

Above are the mathematical operators and those are common to everybody. We have comparison operators as well. Below is the list of those.
List of Comparison Operators for VBA
- Equal Sign (=)
- Greater Than Sign (>)
- Greater Than or Equal to Sign (>=)
- Less than Sign (<)
- Not Equal to Sign (<>)
Let's discuss these operators in detail.
Equal Sign (=)
One may use this sign to compare whether one thing is equal to another. The result of this operator sign is either TRUE or FALSE. If one thing equals another, we will get TRUE or else FALSE.
Below is the VBA Code to understand the use of the Equal(=) operator.
Code:
Sub Equal_Operator()
Dim Val1 As String
Dim Val2 As String
Val1 = 25
Val2 = 25
If Val1 = Val2 Then
MsgBox "Both are same and result is TRUE"
Else
MsgBox "Both are not same and result is FALSE"
End If
End Sub
It will return the result as TRUE because variable values "Val1" and "Val2" are the same.

Greater Than Sign (>)
This sign checks whether one number is greater than the other number. It is also a logical VBA operator where the result is either TRUE or FALSE.
Below is the VBA Code to understand the use of the Greater Than (>) operator.
Code:
Sub Greater_Operator()
Dim Val1 As String
Dim Val2 As String
Val1 = 25
Val2 = 20
If Val1 > Val2 Then
MsgBox "Val1 is greater than the val2 and result is TRUE"
Else
MsgBox "Val1 is not greater than the val2 and result is FALSE"
End If
End Sub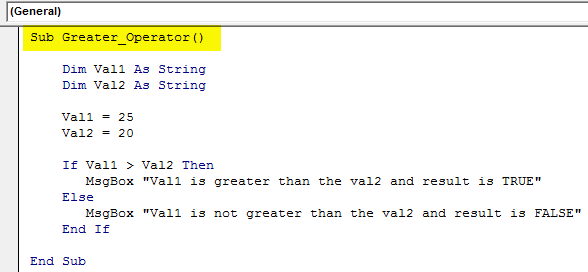
And the result will be:

Greater Than or Equal to Sign (>=)
This sign works the same as the above operator is greater than but checks whether the number is equal or not.
Below is the VBA Code to understand the use of the Greater Than or Equal to(>=) operator.
Code:
Sub Greater_Than_Equal_Operator()
Dim Val1 As String
Dim Val2 As String
Val1 = 25
Val2 = 20
If Val1 >= Val2 Then
MsgBox "Val1 is greater than the val2 and result is TRUE"
Else
MsgBox "Val1 is not greater than the val2 and result is FALSE"
End If
End Sub
Now, we will change the Val2 amount to 25 and run the code.
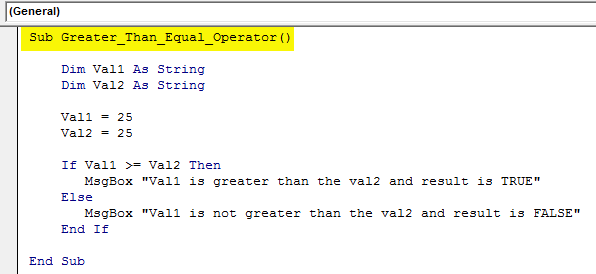
Both the results return TRUE because we have applied >= sign.

Less than Sign (<)
This sign checks whether one number is less than the other number. It is also a logical operator in VBA, where the result is either TRUE or FALSE.
Below is the VBA Code to understand the use of the Less Than (<) operator.
Code:
Sub Less_Operator()
Dim Val1 As String
Dim Val2 As String
Val1 = 25
Val2 = 20
If Val1 < Val2 Then
MsgBox "Val1 is less than the val2 and result is TRUE"
Else
MsgBox "Val1 is not less than the val2 and result is FALSE"
End If
End Sub
It returns FALSE because 25 is not less than 20.

Not Equal to Sign (<>)
It is not equal to sign if the inverse operator returns inverse results. If one thing is equal to another, it returns FALSE or TRUE.
Below is the code to understand the use of the VBA Not Equal (<>) operator.
Code:
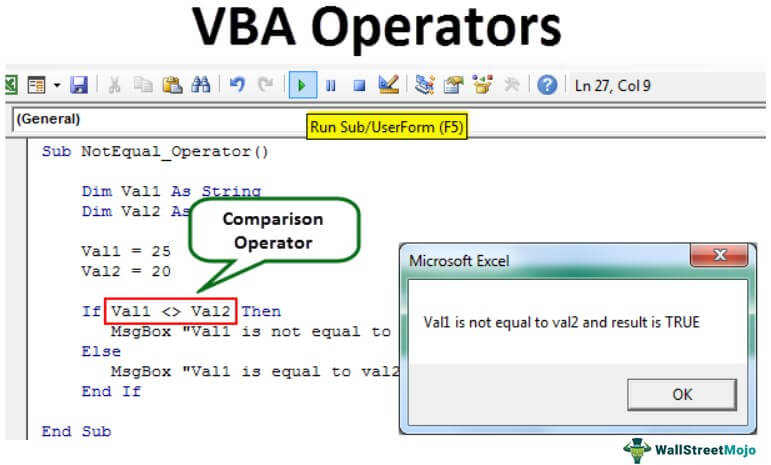
Sub NotEqual_Operator()
Dim Val1 As String
Dim Val2 As String
Val1 = 25
Val2 = 20
If Val1 <> Val2 Then
MsgBox "Val1 is not equal to val2 and result is TRUE"
Else
MsgBox "Val1 is equal to val2 and result is FALSE"
End If
End Sub
You will get the following output.


