Table Of Contents
Excel VBA ENVIRON(Environment)
The VBA Environ function (means ENVIRONMENT) can be categorized as an "Information Function" as this function returns the values for an operating system environment variable. Environment (operating system) variables contain information about profiles of all users, user names, user profiles, a home folder for the user, etc. This function returns a string value.
Syntax

This function has only one argument, which is 'Expression.' We can specify the numeric position (integer value) representing the numeric position of the environment variable in the environment variable table or variable name itself.
If we specify the numeric position, the function returns the environment variable and its value, with an equal sign in between.

If we specify the variable name, the function returns the only value.

Output:

How to use Environ Function in VBA?
Example #1
Open Command Prompt using Environ Function in VBA.
To do the same, the steps would be:
Insert the command button using the 'Insert' command available in the 'Form Controls' group in the 'Developer' tab or use the shortcut excel key (Alt+F11).

If the ‘Developer’ tab is not visible, use the following steps to make the tab visible.
Click on ‘File’ and choose ‘Options’ from the list.

Choose 'Customize Ribbon' from the left menu, check the box for the 'Developer' tab, and click on 'OK.'

Now, the 'Developer' tab is visible.
While inserting the command button, if we keep pressing the ALT key, then the edges of the command button will be along the cell's border. Change the properties of the inserted command button using the contextual menu, which we get by right-clicking on the 'Command button.'

Properties Window

To write the VBA code for the command button, we must select the command button and choose 'View Code' from the contextual menu.

Write the code as follows:

We have called the 'Shell' function to type a command to run a program (in our case, a command prompt).
We have used ‘ComSpec,’ which stands for ‘Command Specifier.’
Now, exit the VBE and click on the "Command" button. We have displayed a command prompt.

Example #2
Suppose we want to extract file names and details for the selected folder.
Steps to do the same are:
First, fill cells B2:H9 with light orange color.

Create the label using the 'Insert' command in the 'Form Controls' group in the 'Developer.'

Please create labels below and edit the properties like Caption, BackColor, BackStyle, BorderStyle, and Shadow.

Create the ComboBox using the ComboBox command (one of the ActiveX Controls) available in the Insert command in the Form Controls group in Developer.

After creating the Combo Box in excel, we can change the properties.

We will add code for the list to be displayed in the combo box using the View Code command in the contextual menu.

It is a code for “Select the Folder” ComboBox.

It is a code for “SortBy” ComboBox.

It is a code for “Select the Order” ComboBox.

We will create a list box containing all file types to select them to get only those files in the result. To do the same, please choose "List Box (ActiveX Control)" from the "Insert" command in the "Controls" group in the "Developer" tab.
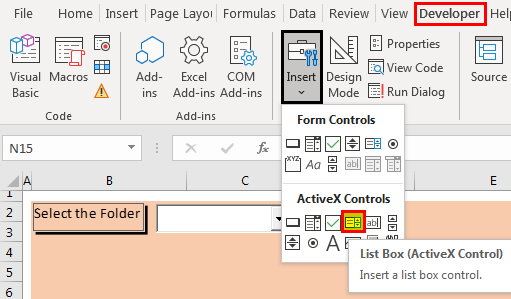
Drag the list box, as shown below.

Change the properties of the list box as follows.

Please use the following code to add the file types to the list box.
Write the code in “This workbook.”
Code:
Private Sub Workbook_Open() Dim ArrFileType(25) As Variant ArrFileType(0) = "Microsoft Excel 97-2003 Worksheet(.xls)" ArrFileType(1) = "Microsoft Office Excel Worksheet(.xlsx)" ArrFileType(2) = "Microsoft Excel Macro-Enabled Worksheet(.xlsm)" ArrFileType(3) = "Word Document 97-2003(.doc)" ArrFileType(4) = "Word Document 2007-2010(.docx)" ArrFileType(5) = "Text Document(.txt)" ArrFileType(6) = "Adobe Acrobat Document(.pdf)" ArrFileType(7) = "Compressed (zipped) Folder(.Zip)" ArrFileType(8) = "WinRAR archive(.rar)" ArrFileType(9) = "Configuration settings(.ini)" ArrFileType(10) = "GIF File(.gif)" ArrFileType(11) = "PNG File(.png)" ArrFileType(12) = "JPG File(.jpg)" ArrFileType(13) = "MP3 Format Sound(.mp3)" ArrFileType(14) = "M3U File(.m3u)" ArrFileType(15) = "Rich Text Format(.rtf)" ArrFileType(16) = "MP4 Video(.mp4)" ArrFileType(17) = "Video Clip(.avi)" ArrFileType(18) = "Windows Media Player(.mkv)" ArrFileType(19) = "SRT File(.srt)" ArrFileType(20) = "PHP File(.php)" ArrFileType(21) = "Firefox HTML Document(.htm, .html)" ArrFileType(22) = "Cascading Style Sheet Document(.css)" ArrFileType(23) = "JScript Script File(.js)" ArrFileType(24) = "XML Document(.xml)" ArrFileType(25) = "Windows Batch File(.bat)" Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List = ArrFileType End Sub
Insert the checkboxes using the same “Insert” command in the “Controls” group in the “Developer” tab and change the properties for inserted ‘Checkboxes’ using the ‘Properties’ power available in the same group after selecting the objects.


Insert command buttons using the ‘Insert’ command available in the same group and change the properties like a caption and other stuff.
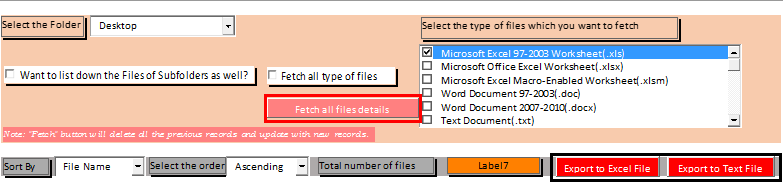
We have formed the entire structure. Now we need to write the code.
Activate the ‘Design Mode,’ and right-click on the “Fetch all files details” button to choose the “View Code” from the contextual menu to add the code for the switch.
We will declare some variables first in the module.

Below is the code added to a “Fetch all files details” button.
Code:
Private Sub FetchFilesBtnCommandButton_Click() iRow = 14 fPath = Environ("HOMEPATH") & "" & SelectTheFolderComboBox.Value If fPath <> "" Then Set FSO = New Scripting.FileSystemObject If FSO.FolderExists(fPath) <> False Then Set SourceFolder = FSO.GetFolder(fPath) If Sheet2.IncludingSubFoldersCheckBox.Value = True Then IsSubFolder = True Else IsSubFolder = False If SourceFolder.Files.Count = 0 Then MsgBox "No files exists in this Folder" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "Check your folder path and Try Again !!", vbInformation Exit Sub End If End If Call ClearResult If FetchAllTypesOfFilesCheckBox.Value = True Then Call ListFilesInFolder(SourceFolder, IsSubFolder) Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "D14", "E14") Else Call ListFilesInFolderXtn(SourceFolder, IsSubFolder) Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "D14", "E14") End If FilesCountLabel.Caption = iRow - 14 Else MsgBox "Selected Path Does Not Exist !!" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "Select Correct One and Try Again !!", vbInformation End If Else MsgBox "Folder Path Can not be Empty !!" & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & "", vbInformation End If End Sub
Define the 'ClearResult' function in the module. To insert the module, select 'ThisWorkbook,' ' Insert,' and then 'Module.'

Write the following code in the module.
Code for ClearResult

There are more subroutines like 'ListFilesInFolder,' 'ListFilesInFolderXtn,' 'ResultSorting,' and we will define all these subroutines in the module.
'ListFilesInFolder'
Code:
Public Sub ListFilesInFolder(SourceFolder As Scripting.Folder, IncludeSubfolders As Boolean)
For Each FileItem In SourceFolder.Files
' display file properties
Cells(iRow, 2).Formula = iRow - 13
Cells(iRow, 3).Formula = FileItem.Name
Cells(iRow, 4).Formula = FileItem.Path
Cells(iRow, 5).Formula = Int(FileItem.Size / 1024)
Cells(iRow, 6).Formula = FileItem.Type
Cells(iRow, 7).Formula = FileItem.DateLastModified
Cells(iRow, 8).Select
Selection.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection, Address:= _ FileItem.Path, TextToDisplay:="Click Here to Open"
'Cells(iRow, 8).Formula = "=HYPERLINK(""" & FileItem.Path & """,""" & "Click Here to Open" & """)"
iRow = iRow + 1 ' next row number
Next FileItem
If IncludeSubfolders Then
For Each SubFolder In SourceFolder.SubFolders
ListFilesInFolder SubFolder, True
Next SubFolder
End If
Set FileItem = Nothing
Set SourceFolder = Nothing
Set FSO = Nothing
End Sub
'ListFilesInFolderXtn'
Public Sub ListFilesInFolderXtn(SourceFolder As Scripting.Folder, IncludeSubfolders As Boolean) On Error Resume Next Dim FileArray As Variant FileArray = Get_File_Type_Array For Each FileItem In SourceFolder.Files Call ReturnFileType(FileItem.Type, FileArray) If IsFileTypeExists = True Then Cells(iRow, 2).Formula = iRow - 13 Cells(iRow, 3).Formula = FileItem.Name Cells(iRow, 4).Formula = FileItem.Path Cells(iRow, 5).Formula = Int(FileItem.Size / 1024) Cells(iRow, 6).Formula = FileItem.Type Cells(iRow, 7).Formula = FileItem.DateLastModified Cells(iRow, 8).Select Selection.Hyperlinks.Add Anchor:=Selection, Address:= _ FileItem.Path, TextToDisplay:="Click Here to Open" 'Cells(iRow, 8).Formula = "=HYPERLINK(""" & FileItem.Path & """,""" & "Click Here to Open" & """)" iRow = iRow + 1 ' next row number End If Next FileItem If IncludeSubfolders Then For Each SubFolder In SourceFolder.SubFolders ListFilesInFolderXtn SubFolder, True Next SubFolder End If Set FileItem = Nothing Set SourceFolder = Nothing Set FSO = Nothing End Sub
'ResultSorting'
Sub ResultSorting(xlSortOrder As String, sKey1 As String, sKey2 As String, sKey3 As String) Range("C13").Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select Selection.Sort Key1:=Range(sKey1), Order1:=xlSortOrder, Key2:=Range(sKey2 _ ), Order2:=xlAscending, Key3:=Range(sKey3), Order3:=xlSortOrder, Header _ :=xlGuess, OrderCustom:=1, MatchCase:=False, Orientation:=xlTopToBottom _ , DataOption1:=xlSortNormal, DataOption2:=xlSortNormal, DataOption3:= _ xlSortNormal Range("B14").Select End Sub
In the ‘ListFilesInFolderXtn’ subroutine, we have called a function named ‘ReturnFileType’ and ‘GetFileTypeArray’. We need to define the functions in the same module.
'ReturnFileType'
Code:
Public Function ReturnFileType(fileType As String, FileArray As Variant) As Boolean Dim i As Integer IsFileTypeExists = False For i = 1 To UBound(FileArray) + 1 If FileArray(i - 1) = fileType Then IsFileTypeExists = True Exit For Else IsFileTypeExists = False End If Next End Function
'GetFileTypeArray'
Code:
Public Function Get_File_Type_Array() As Variant Dim i, j, TotalSelected As Integer Dim arrList() As String TotalSelected = 0 For i = 0 To Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.ListCount - 1 If Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.Selected(i) = True Then TotalSelected = TotalSelected + 1 End If Next ReDim arrList(0 To TotalSelected - 1) As String j = 0 i = 0 For i = 0 To Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.ListCount - 1 If Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.Selected(i) = True Then arrList(j) = Left(Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List(i), InStr(1, Sheet2.FileTypesListBox.List(i), "(") - 1) j = j + 1 End If Next Get_File_Type_Array = arrList End Function
We have a command button captioned ‘Export to Excel File,’ we need to write the code for this button as follows:


In the module, define the subroutine named ‘Export_to_excel.’
Code:
Sub Export_to_excel() On Error GoTo err Dim xlApp As New Excel.Application Dim xlWB As New Workbook Set xlWB = xlApp.Workbooks.Add 'xlWB.Add xlApp.Visible = False ThisWorkbook.Activate Range("B13").Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Select Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlToRight)).Select Selection.Copy xlApp.Visible = True xlWB.Activate xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Select xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").PasteSpecial Paste:=xlPasteValues xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.Select xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Cells.EntireColumn.AutoFit xlWB.Sheets("Sheet1").Range("B2").Select Exit Sub err: MsgBox ("Error Occured while exporting. Try again") End Sub
We have one more command button captioned as ‘Export to Text File.’ We will write the code for the command button as follows:


In this code, we can see that we have a user form, which we need to design using the following steps:
Right Click on the ‘Sheet2 (Example2)’ sheet and choose ‘Insert’ and then ‘UserForm’ from the menu.

Design the UserForm using tools from the toolbox.

We have used ‘Labels,’ ‘Combo Box,’ ‘Text Box,’ and ‘Command buttons’ for the Userform and have changed the caption and name for all the components.
For the first command button (OK), we have to write the code as follows:
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim iSeperator As String
If ComboBox1.Value = "Other" Then
iSeperator = TextBox1.Value
Else
iSeperator = ComboBox1.Value
End If
If iSeperator = "" Then
If MsgBox("Hello You have not selected any delimeter." & vbNewLine & vbNewLine & _ " It will be very difficult to read the Text file, without specific delimiter", vbYesNo) = vbYes Then
Call textfile(iSeperator)
Else
Exit Sub
End If
Else
Select Case ComboBox1.ListIndex
Case 0: iSeperator = ","
Case 1: iSeperator = "|"
Case 2: iSeperator = "vbTab"
Case 3: iSeperator = ";"
End Select
Call textfile(iSeperator)
Unload Me
End If
End Sub
We have called the ‘textfile’ function in the subroutine for the command button, so we need to define the ‘textfile’ function in the module.
Code:
Sub textfile(iSeperator As String) Dim iRow, iCol Dim iLine, f ThisWorkbook.Activate Range("B13").Select TotalRowNumber = Range(Selection, Selection.End(xlDown)).Count - 12 If iSeperator <> "vbTab" Then Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Output As #1 Print #1, "" Close #1 Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Append As #1 For iRow = 13 To TotalRowNumber iLine = "" For iCol = 2 To 7 iLine = iLine & iSeperator & Cells(iRow, iCol).Value Next Print #1, iLine Next Close #1 Else Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Output As #1 Print #1, "" Close #1 Open ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" For Append As #1 For iRow = 13 To TotalRowNumber iLine = "" For iCol = 2 To 7 iLine = iLine & vbTab & Cells(iRow, iCol).Value Next Print #1, iLine Next Close #1 End If f = Shell("C:WINDOWSnotepad.exe " & ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt", vbMaximizedFocus) MsgBox "Your File is saved in " & ThisWorkbook.Path & "File1.txt" End Sub
We must write the following code for command button 2 (Cancel). Double click on the cancel button to write the code.

For the Combo Box for selecting a specifier, write the following code.

For the UserForm, write the following code.

Write the following code for the 'Fetch all type of files' checkbox.


For the ‘ListBox’ for file types, write the following code.


For the ‘SelectTheOrder’ combo box, write the following code.

Code:
Private Sub SelectTheOrderComboBox_Change() Select Case (SelectTheOrderComboBox.Value) Case "Ascending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case "Descending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case Default Exit Sub End Select End Sub
We will write the following code for the 'Sort By' combo box.

Code:
Private Sub SortByComboBox_Change() Select Case (SelectTheOrderComboBox.Value) Case "Ascending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlAscending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case "Descending" If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Name" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "C14", "E14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Type" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "F14", "E14", "C14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "File Size" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "E14", "C14", "G14") End If If SortByComboBox.Value = "Last Modified" Then Call ResultSorting(xlDescending, "G14", "C14", "E14") End If Case Default Exit Sub End Select End Sub
Now, we have written the entire code. Now we can select the desired folder and file type and find the list of files, which we can sort by 'File Name,' 'File Type,' 'File Size,' or 'Last-Modified' and export the list to Excel or text file.

Things to Remember
If the value we specify for the ‘investing’ argument is not in the environment string table, the ENVIRON function returns the zero-length string.

